What's an Animal?
advertisement

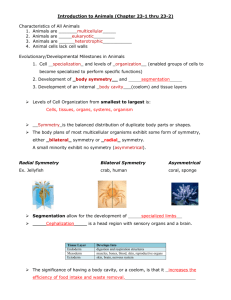
What’s an Animal? Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html 3. Notochord (some encased in a backbone) Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods VertebratesAnimals with backbones Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Numbers of species Arthropoda Mollusca Chordata Platyhelminthes Nematoda Annelida Porifera Echinodermata Other Sarcomastigophora Apicomplex Ciliophora Characteristics of ALL Animals: 1. Are ____________________ EUKARYOTES cells have nucleus & membrane bound organelles HETEROTROPHIC 2. Are ____________________ get food from consuming other organisms MULTICELLULAR 3. Are ____________________ made of many cells SPECIALIZATION 4. Show __________________ different kinds of cells do different jobs Characteristics of ALL Animals: MOVE 5. _____________ (at some point in life cycle) for food, find mates, escape danger DNA 6. Contain _____________ which carries the genetic code REPRODUCE 7. ____________________ Make offspring, Most have sexual reproduction (few asexual) NO CELL WALL allows flexibility 8. ____________________ How are animals classified? 1. Symmetry No symmetry Radial symmetry Bilateral symmetry ASYMMETRY ___________________ No symmetry Doesn’t matter how you cut it; you never get 2 identical halves. Image from: http://mbgnet.mobot.org/salt/animals/sponges.htm Radial Symmetry _______ Jelly fish image: http://www.redfishbluefish.com/BellaLuz/Jellyfish.jpg http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/animal%20dissections.htm Image from: http://biodidac.bio.uottawa.ca/ Get 2 identical halves in several directions. Bilateral ___________ Symmetry If divide animal down the middle you get 2 mirror images BUT only divides equally in ONE direction Image from: http://www.okc.cc.ok.us/biologylabs/Documents/Animals/Symmetry.htm Which way is up? DORSAL (top) ANTERIOR head end POSTERIOR tail end VENTRAL (underneath) Image from: http://www.ca4h.org/4hresource/clipart/animals/pics/dog.gif CEPHALIZATION ________________ Concentration of nervous tissue and sensory organs in anterior end of an organism (head area) 2. EMBRYOLOGY Image from: http://calspace.ucsd.edu/virtualmuseum/litu/03_3.shtml EARLY DEVELOPMENT Becomes digestive system Image from: http://io.uwinnipeg.ca/~simmons/16cm05/1116/16anim3.htm A. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? ANUS HERE POSSIBLY Images modified from: http://io.uwinnipeg.ca/~simmons/16cm05/1116/16anim3.htm ANIMALS PROTOSTOMES DEUTEROSTOMES Blastopore becomes MOUTH Blastopore becomes ANUS ALL INVERTEBRATES except ECHINODERMS ALL VERTEBRATES (Fish, amphibians, birds, reptiles, mammals) plus ECHINODERMS EMBRYOLOGY __________________ Echinoderms are the “exception to the rule”! They are INVERTEBRATES but their embryos act like DEUTEROSTOMES _________________________ Image from: http://www.bsac21.freeserve.co.uk/images/Critters/Starfish%20Bloody%20Henry.JPG