Chapter 7 Notes - Herscher CUSD #2
advertisement

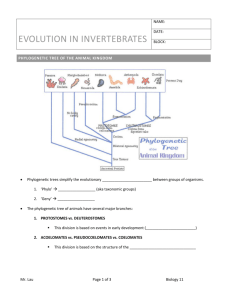
Classification, Phylogeny, & Organization Chapter 7 Notes Classification Review • Taxonomic Hierarchy • Nomenclature Review • What are the three Domains? • What are the six Kingdoms? Domains & Kingdoms Bacteria Archea Eukarya Bacteria Archea Plantae Fungi Protista Animalia Eukaryotes Plantae Fungi Protista Animalia Multicellular Multicellular Unicellular Multicellular Cell wall Cell wall Some have cell wall No cell wall Autotrophic Heterotrophic Auto/Heterotrophic Heterotrophic Non motile Non motile Motile Motile Patterns of Organization • Symmetry – parts of an organism are equally arranged around a point or axis – Bilateral symmetry: • A single plane divides the organism into right and left mirror images – Ex: humans, dogs, fish, kangaroo , vertebrates – Radial symmetry: • Any plane passing through the central axis divides the organism into a mirror image – Ex: Sea Urchins, Jelly Fish, sea anemones, Echinoderms – Sea Star = “Penta-radial” • Asymmetry – absence of symmetry – Ex: sponges Cephalization • The formation of a distinct head • Only occurs in animals Terms of Direction • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Aboral – End opposite of mouth Oral – Mouth end Anterior – front Posterior – behind Dorsal – backside Ventral – belly side Cephalic – towards head Caudle – towards tail Superior – above Inferior – below Medial – along the symmetry plane Lateral – away from the symmetry plane Distal – away from point of attachment Proximal – toward point of attachment Other Patterns of Organization • Unicellular Level of Organization – Protists – Must provide for the functions of • • • • • • Locomotion Food acquisition Digestion Water and ion regulation Sensory perception Reproduction • Diploblastic Level of Organization • Triploblastic Level of Organization Diploblastic Organization • Simplest tissue-level organization • Tissues derived from two embryological layers – Ectoderm – gives rise to epidermis; outer layer • Epithelial cells - the epidermis or skin • Brain • nervous system – Endoderm – gives rise to gastrodermis, tissue that lines the gut cavity • lining of the stomach & intestines – Middle Layer = Mesoglea; noncellular Triploblastic Organization • Tissues derived from three embryological layers – Ectoderm – Mesoderm – gives rise to supportive tissues (bones), contractile tissues (muscles), and blood cells. – Endoderm – Most organisms with this level of organization develop organ systems. • Excretory, nervous, digestive, reproductive, circulatory systems Triploblastic Animals are further Organized based on… Presence or Absence of a Body Cavity • Acoelomate – solid mass/without cavity • Pseudocoelomate - body cavity not entirely lined by mesoderm • Coelomate – body cavity completely surrounded by mesoderm Coelom = Cavity Protostomes & Deuterostomes Protostomes • Mouth forms from an embryonic blastopore – Blastopore: an indention in the blastula – Blastula: an early stage in the development of an embryo • Sphere of cells enclosing a fluid filled cavity • Ex: Platyhelminthes, Nematodes, Molluscs, Annelids, and Arthropods Deuterostomes • Anus forms from an embryonic blastospore • Ex: Echinoderms, Hemichordates, Chordates