Possible short answer questions for Zoology Exam #2
advertisement

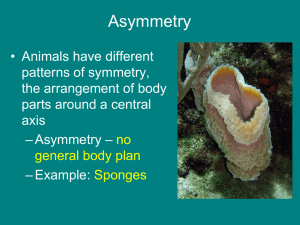
Possible short answer questions for Zoology Exam #2. Selected items from Chapter 7. A) Describe the three major ‘Animal-like’ groups. Describe ways in which we can characterize the various animals- i.e. single cell, multi cell, diplo, triplo, developmental etc. B) Describe the developmental characteristics of Protostomes and Deuterostomes. Chapter 8 C) Describe the characteristics of the Kingdom Protozoa. Is it animal or plant? Why? D) Describe the symbiotic lifestyle of the Zooflagellated Protozoa Phylum Apicomplexa: Plasmodium that causes Malaria. Chapter 9 E) Describe the evolutionary perspective of the multicellular animal. Be sure to include theories and ancestral origins. F) Describe the characteristics of the Phylum Porifera. Include the cell types found in the body wall and their general function. Also include the various skeleton structures found in sponges. G) Describe the general characteristics of the Phylum Cnidaria and its “alteration of generations”- Describe the reproductive process of Cnidarians. Selected items from Chapter 10 H) Describe the evolutionary relationship between the tribloblast acoelomate body plan, radial diploblastic body plan- Cnidirian and tripoblastic coelemate body plan. I) Describe the important evolutionary characteristics of the Triploblastic Acoelomate body plan. 1 Key Terms Selected items from Chapter 7 Bilateral symmetry, coelom, radial symmetry, kingdom, cladogram, domain, phylogenetic tree, clade, oral, aboral, caudal, cephalic, dorsal, ventral, posterior, anterior, transverse plane, frontal plane, median plane, superior, inferior, ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm, pseudocoelom, peritoneum, diploblastic, triploblastic Chapter 8 Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species, Polyphyletic, autotrophic, heterotrophic, asexual reproduction, flagellated, phytoflagellated protozoa, symbiosis, parasitism, commensalisms, mutualism, host, definite host, intermediate host, dinoflagellate, Fission, host, pellicle, protozoan, euglena, stigma, pyrenoid, mastigophora, zooflagellated protozoa, Life cycle of Trypanosoma brucei causes African sleeping sickness- Tsetse flies, Phytomastigophora, Zoomastigophora, trypanosoma, trichonympha, volvox, sarcodina, amoebas, pseudopodia, difflugia, test (shell), coccidea, apicomplexa, sporozoan, plasmodium life cycle, sporozoites, gametocytes, ciliophora, conjugation, paramecium Chapter 9 Polyphyletic, Monophyletic, colonial hypothesis, synctial hypothesis, Physalia physalis- Portuguese Man-of-War, Phylum Porifera- Sponges, pinacocytes, mesenchyme- ameobocytes, choanocytes- collar cells, central cavity, spicules, sponging, ascon, sycon, leucon, ostia, spongocoel, osculum, monoecious, larva, mesohyl, vacuoles, Phylum Cnidaria, radial symmetry, sensory receptors, diploblastic, mesoglea, gastrodermis, gastrovascular cavity, cnodocytes, ectoderm, endoderm, epidermis, nematocyst, operculum, cnidocil- modified cilium, , medusa, polyp, alteration-of-generations, asexual, sessile, dioecious, gemmules, budding, colony, planula, hydrozoan, hydras, Gonionemus, Class Scyphozoa, Aurelia, Class Anthozoa- anemone and corals, mesenteries, gonads, pharynx, oral end, aboral end, tentacles, bioluminescence Selected items from Chapter 10 Acoelomate, bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, diploblastic, coelomate, cephalization, germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm, organ-system level of organization, flattened dorsoventrally, gastrovascular cavity, monoecious, parenchyma, excretory system, muscle system, digestive system, reproductive system, ciruculatory system, respiratory system, Phylum Platyhelminthes, Class Turbllaria- flat worms, protonephridia, osmoregulatory structures, nephros- kidney, flame cells, nephridiopore, nervous system- ganglion, Ocelli, asexual, sexual, Class Tremotodaparasitic flukes, tegument, Chinese liver fluke, Class Cestoda- tapeworms, endoparasites, scolex, proglottids, strobila, gravid proglotid, immature proglotid, neck and head of tapeworm, holdfast, Class Mongenea- parasitic flukes, ectoparasite, predator, scavenger, host, definite host, intermediate host, Phylum Nemertea, unsegmented body, closed circulatory, ciliated epidermis, cerebral gangion 2