HINDUISM
advertisement

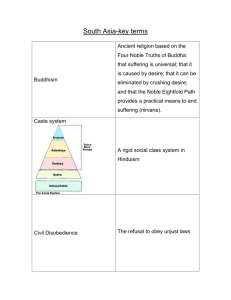
HINDUISM HINDUISM • No formal founder • No formal church • roots lie in the beliefs and practices of the ancient Aryans – crossed thru the Khyber Pass into South Asia from Caucasus Mtns – brought Hindu beliefs Khyber Pass Indus River Valley Civilizations • 2500 -1500 BCE • over 1000 miles – worlds largest early civ • Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro most important cities • • • • • • • capital cities well organized gov’ts checkered board pattern streets walled fortress supply warehouses sewer system taxed in form of food – traded w/ ancient Sumer of Mesopotamia Archaeology • Theories for decline of Indus Valley Civ’s – natural causes • too dry for farming • over-farmed land • floods? – invaders from the north • Scholars believe that the DRAVIDIANS are descendents from the ancient Aryans ARYAN Culture • migration took 100s of years • invented Chariots • brought Hinduism – developed Sanskrit • • • • INDRA: warrior god also farmers & herders cattle as wealth Rajahs: hereditary chiefs that rule the villages Aryan Migration into South Asia SACRED TEXTS of HINDUISM • VEDAS: contain eternal truths that were revealed to wise men – ca. 6000 - 1500 BCE – contain hymns, incantations, and rituals from ancient India – give a unique view of everyday life in India four thousand years ago – 4 VEDAS • UPANISHADS: helps to explain the Vedas • Written in SANSKRIT SACRED TEXTS • UPANISHADS: helps to explain the Vedas • the Epics – Mahabharata: “the great story” • longest written story – 100,000 verses • poem @ 12 yr war btwn two royal families • Bhagavad Gita: “song of God” – Ramayana: “Rama’s Way” • to avoid war, Rama places himself in exile, thus not becoming heir to the throne • written in SANSKRIT The CASTE SYSTEM • Varna means color – suggest that caste was first determined by skin color • Brahmins: – priests • Kshatriyas: – warriors, rulers • Vaisyas: – landowners, merchants, herders • Sudras: – servants, peasants • UNTOUCHABLES Harijans (Untouchables or Dalits) • Considered to by so lowly that – they do not have a caste. • Perform the despicable tasks like killing animals, tanning hides, sweeping and cleaning. • Gandhi called them the children of God • 1950 Indian Constitution abolished untouchability…but still exists Weakening of the Caste System • Greater educational opportunities • Movement of people to cities – blurs caste lines. • Constitutional changes: Cities – all people have the right to vote. • The work of Gandhi • Globalization – Growth of industry and need for jobs – Technology Gandhi 4 Principles of Hinduism • Dharma: duties & responsibilities according to one’s caste. • Karma: one’s actions in this life, will effect the next lives (vice-versa) • Samsara: Wheel of Life – birth, disease, death, rebirth • Moksha: – Hindu enlightenment – escape fm Samsara – becomes one w/ Brahman HINDU Beliefs • Brahman “single supreme force” – universal soul – formless & unlimited • ATMAN “essential self is part of the universal soul” – unity of ALL life • Reincarnation thru KARMA-SAMSARA – “wheel of life” • good deeds bring joy • bad deeds bring sadness • Maya: illusion The HINDU TRINITY • Brahma: Creator God – all other gods come from Brahma – Monist • Vishnu: Preserver God – ten avatars “incarnations” – returns to earth as avatars to bring justice/balance • Shiva: Destroyer God – “The Cosmic Dance” – equivalent to the oscillating universe theory BRAHMA • The Creator God • all other gods come from Brahma • four faces represent the four corners o/t universe • He holds – a sacrificial ladle – the four Vedas – jar of holy water from the Ganges River – necklace of prayer beads VISHNU • “The Preserver God” • greatest of the gods • maintain balance of good and bad • ten avatars “incarnations” – returns to earth as avatars to bring justice/balance • Krishna • Buddha SHIVA • The Destroyer God • “The Cosmic Dance” – the dance of Shiva symbolizes the creation and destruction of the universe – equivalent to the oscillating universe theory – pg. 241 SRI YANTRA • symbol of spiritual evolution • focal point for meditation • 9 triangles intersect to form 43 triangles • 3 concentric circles • framed by a square • This form is the geometric expression of the divine sound of creation... OM Hindu Religious Symbols • Sri Yantra – symbol of spiritual evolution – focal point for meditation – This form is the geometric expression of the divine sound of creation... OM • OM or AUM – Main symbol of Hinduism – visual and verbal expression of god – transcend one’s thoughts & merge w/ god. – “a” = beginning – “u” = progress – “m” = dissolution – “reflects the POWER responsible for creation, development and destruction of the universe OM or AUM • Main symbol of Hinduism • visual and verbal expression of god – transcend one’s thoughts & merge w/ god. • “a” = beginning • “u” = progress • “m” = dissolution – “reflects the POWER responsible for creation, development and destruction of the universe” SRI YANTRA This form is the geometric expression of the divine sound of creation... OM SIKHISM • Combination of Hinduism and Islam – reincarnation – Allah • Founder: Guru Nanak • Holy book: Guru Granth • Place of worship: Gurdwara SIKHISM symbols • Khanda – God’s universal and creative power • Five K’s – Kesh: Uncut Hair and Beard • honors the way of nature • A TURBAN covers the head of males – most visible symbol – sign of Sikh power – Kangha: Comb holding hair in place • keeping the spirit in place SIKHISM symbols con’t • Kara: Steel bracelet • worn on right wrist • symbolizes strength • unity of god Kirpan: double edged dagger or sword – duty to defend Sikhism • Kaccha: trousers worn by warriors – symbol of modesty and moral restraint Sikh Golden Temple Amritsar, Punjab Sikh Discrimination • Discriminated against by Muslims & Hindus • Tried to stay neutral during India – Pakistan partition • Current Prime Minister of India is a Sikh: – Manmohan Singh • Sikh diaspora THERAVADA BUDDHISM • “Doctrine o/t Elders” • conservative branch • The Little Wheel – less followers • Buddha is a teacher • Spread to Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand THERAVADA BUDDHISM • ideal is arhat – become an enlightened saint – wisdom • few possessions – – – – – – – begging bowl three colored robes a belt a mending needle fan to cover face razor to shave head water strainer MAHAYANA BUDDHISM • “Great Vehicle” or “Big Wheel” – majority of followers • non-monastic life • Buddha is a god • Spread to China, Tibet, Korea & Japan • ideal is compassion – can attain nirvana through assisting others • Bodhisattva: holds back on attaining nirvana to help others