File
advertisement

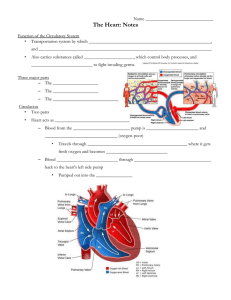
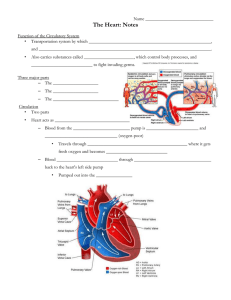
Guided Notes for Structure of the Heart 1. Heart Size – about 14 cm x 9 cm (the size of a fist). It is located in the __________________________ (space between lungs, backbone, sternum), between the 2nd rib and the 5th intercostal space. The distal end of the heart is called the _____________. 2. A _____________________ pericardium encloses the heart (like a bag) and has 2 layers: (1) _________________ pericardium (inner layer) (2) __________________ pericardium (outer, attached to diaphragm, sternum and vertebrae) 3. The ______________ cavity contains fluid for the heart to float in, reducing friction. The wall of the heart consists of three layers: 1. __________________ – outer layer, reduces friction 2. ________________ – middle layer, mostly cardiac muscle 3. __________________ – thin inner lining, within chambers of the heart 4. Your heart is a ____________________ pump. Circulation is a double circuit: _______________________ (lungs only) and ________________________ (rest of the body) The heart has ______ chambers: 1. 2 ______________ – thin upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart through the _________________________ (Right and Left Atrium) 2. 2 ___________________– thick, muscular lower chambers. Receive blood from the ________________ above them. The ventricles force (pump) blood out of the heart through arteries. (Right and left ventricle) The ______________________ separates the right and left sides of the heart. 5. The valves of the Heart allow ______-way flow of blood. There are ____ total valves. 2 _________________________ valves (AV) & 2 ________________________ valves (SV) – Left Atrioventricular valve – also called the _________________ valve or ______________ valve. Between left atrium and ventricle – Right Atrioventricular valve – also called the ___________________ valve. Between right atrium and ventricle Aortic Semilunar – or just ______________ valve. Between the left ventricle and the aorta Pulmonary Semilunar, or just __________________ valve. Between the left ventricle and the aorta 6. ___________________ Circulation – delivers blood to all body cells and carries away waste, while _____________________ Circulation – eliminates carbon dioxide and oxygenates blood (lung pathway). 7. There are three main types of blood vessels: (1) _______________ - carry deoxygenated blood away from the tissues towards the heart (2) _______________ - carry oxygenated blood from the heart and lungs to the rest of the body (3) ________________- where the exchange of water and chemicals between tissue and blood occur 8. All blood vessels have three main layers: (1) Tunica __________________ (innermost layer) - thinnest layer – provides a smooth surface to decrease _______________________ to blood flow; this is the only layer found in ____________________________ (2) Tunica _________________ (middle layer)- thickest layer in __________________; only layer involved in directly regulating blood ______________________ (3) Tunica _________________ (adventitia) (outermost layer) – thickest layer in veins; provides _____________ Name the valves. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. (not a valve)