Heart Notes Handout
advertisement

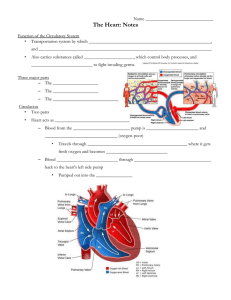
Name ______________________________ The Heart: Notes Function of the Circulatory System • Transportation system by which ______________________________________________________, and ____________________________________________________________________________. • Also carries substances called ______________________, which control body processes, and ___________________________ to fight invading germs. Three major parts – The ____________________ – The ____________________ – The _____________________________ Circulation • Two parts • Heart acts as _________________________________ – Blood from the _________________________ pump is _______________________ and ________________________________ (oxygen-poor) • Travels through ____________________________________________ where it gets fresh oxygen and becomes ___________________________ – Blood ___________________________ through __________________________________ back to the heart's left side pump • Pumped out into the ________________ Three Kinds of Circulation: • Pulmonary circulation – Movement of blood __________________________________________________________ • Coronary circulation – Movement of blood __________________________________________________________ • Systemic circulation – _________________________________________________________________ , except for the heart and lungs The Heart’s Role in Blood Circulation • Systemic circulation – Blood flows from the ______________ of the heart through the ___________ tissues and back to the ________________ of the heart • Pulmonary circulation – Blood flows from the __________________ of the heart to the _______________ and back to the ______________________ of the heart Cardiac Circulation • Blood in the heart chambers does not nourish the myocardium • The heart has its own nourishing circulatory system consisting of – ______________________________—branch from the aorta to supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood – ______________________________—drain the myocardium of blood – ______________________________—a large vein on the posterior of the heart, receives blood from cardiac veins • Blood empties into the right atrium via the coronary sinus The Heart • Location • Thorax between the lungs in the inferior _____________________ • Orientation • Pointed apex directed toward left hip • Base points toward right shoulder • About the ____________________________ Coverings • _____________________________—a double-walled sac – Fibrous pericardium is loose and superficial – Serous membrane is deep to the fibrous pericardium and composed of two layers • _____________________________ – Next to heart; also known as the epicardium • _____________________________ – Outside layer that lines the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium – Serous fluid fills the space between the layers of pericardium Wall • Three layers – ________________________ • Outside layer • This layer is the visceral pericardium • Connective tissue layer – ________________________ • Middle layer • Mostly cardiac muscle – ________________________ • Inner layer • Endothelium Chambers • Right and left side act as separate pumps • Four chambers – ______________ • Receiving (_______) chambers – Right atrium – Left atrium – _________________ • Discharging (_________) chambers – Right ventricle – Left ventricle Septum • _____________________ septum – Separates the two ventricles • _____________________ septum – Separates the two atria Valves • Allow blood to flow in only one direction to prevent backflow • _____________ valves – Atrioventricular (AV) valves—between atria and ventricles • _______________ (mitral) valve (_______ side of heart) • _______________ valve (__________ side of heart) – Semilunar valves—between ventricle and artery • ___________________ semilunar valve • ___________________ semilunar valve • AV valves – Anchored in place by ____________________________ (“heart strings”) – __________________________________________ and closed during ventricular contraction • Semilunar valves – __________________________________________ but open during ventricular contraction • Notice these valves operate opposite of one another to force a one-way path of blood through the heart Heart Sounds • Heart sounds are _____________________________ as they open and close • Valves _______________________________ from one chamber to another • Prevent ____________________ Associated Great Vessels • Arteries – _______________ • Leaves left ventricle – _____________________________ • Leave right ventricle • Veins – ____________________________________ • Enter right atrium – _______________________________ (four) • Enter left atrium Blood Flow Through the Heart • ______________________________________________________ dump blood into the right atrium • From _______________________, through the _______________________, blood travels to the right ventricle • From the ________________________, blood leaves the heart as it passes through the ___________ _________________________________ into the pulmonary trunk • _________________________ splits into right and left ____________________________________ that carry blood to the lungs • Oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is dropped off by blood in the __________________ • Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart through the four ________________________________ • Blood enters the ______________________ and travels through the __________________________ into the left ventricle • From the _______________________, blood leaves the heart via the _________________________ valve and ___________________ How does the heart work? Heart Beats (Lub Dub) • _______________________________________ – Group of cells on the ______________________________________ near the entrance of the superior vena cava – “___________________” of the heart • _______________________________________ – Electrically ________________________________________________ – Signals go from the ____________________ through the ____________________________ allowing the ventricles to contract Heart Attack • Also called a __________________________ • Caused by _______________________________________________ feeding the heart with oxygenrich blood “Having a coronary” Symptoms of a heart attack • Chest pain, tightness, discomfort (pressure, squeezing, fullness, pain, heartburn/indigestion feeling) • Shortness of breath (when resting) • Upper body discomfort (pain/discomfort in one/both arms, back, shoulders, neck, jaw, above belly button) • Breaking out in a cold sweat • Feeling unusually tired for no reason, sometimes for days (especially if you are a woman) • Nausea (feeling sick to the stomach) and vomiting • Light-headedness or sudden dizziness • Any sudden, new symptom or a change in the pattern of symptoms you already have (for example, if your symptoms become stronger or last longer than usual) What to do • Call 911 immediately • Chew and swallow a regular-sized ______________________ • Get to the hospital (ambulance or have someone else drive you) Treatment for a Heart Attack • ___________________________________ Examination of the coronary arteries to check for blockages (feed a catheter up to the heart through the femoral artery and inject dye) • ___________________________________ Performed in conjunction with a cardiac cath Balloon is inserted through a catheter and inflated to press plaque against the vessel walls • ___________________________________ Performed if necessary during an angioplasty Put around a balloon and fed into the coronary artery, balloon is inflated and stent is pushed into the vessel walls to hold the artery open permanently • ___________________________________ Piece of a vein from the leg is harvested and sewn onto the blocked blood vessel on either side of the blockage to restore blood flow