Cardiovascular System
advertisement

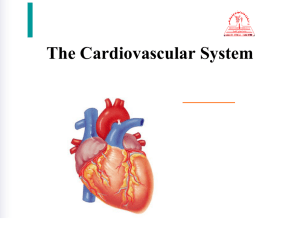
Cardiovascular System The Heart Location & Size Size of a fist; less than a pound Apex – points to left hip Base – points towards right shoulder Pericardium Visceral pericardium (epicardium) – hugs external surface of heart – part of the heart wall Parietal pericardium – anchors the heart to surrounding structures such as the diaphragm and sternum. Layers of Heart Wall Epicardium (visceral pericardium) – Outer layer Myocardium – Layer that contracts – Thick bundles of cardiac muscle Endocardium – Thin sheet of endothelium – Lines the heart chambers Chambers Atria (2) – Receiving chambers Ventricles (2) – Discharging chambers Interventricular or interatrial septum – divides the heart longitudinally http://www.starsandseas.com/SAS_Images/SAS_Physiol_Images/SAS%20cardiopics/heart_chambers.jpg Blood Vessels Superior & inferior venae cavae – Receives deoxygenated blood from veins of the body Pulmonary trunk – Receives deoxygenated blood pumped out from the right ventricle Blood Vessels Right and left pulmonary arteries – Branches off from pulmonary trunk Pulmonary veins (4) – Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs Aorta – Receives oxygenated blood pumped out from the left ventricle Valves Atrioventricular valves (AV valves) Chordae tendineae Semilunar valves Atrioventricular valves (AV valves) Located between atrium and ventricle Prevents backflow into the atria when ventricles contract Bicuspid valve – Left AV valve – Consists of two cusps or flaps Tricuspid valve – Right AV valve – Has three cusps Chordae tendineae Tiny white cords that anchor the cusps to the walls of the ventricles. Semilunar valves Each valve has three cusps – cusps forced open as ventricles contract – Blood flows back after contraction closing cusps. Pulmonary semilunar valve – Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk Aortic semilunar valve – Between left ventricle and aorta