The Heart
advertisement

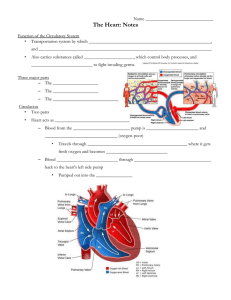
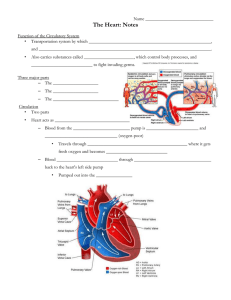
Bell ringer • Why does our heart need to have fluid surrounding it? Cardiovascular System: The Human Heart EQ • What are the different structures of the heart that allow it to pump blood throughout our bodies? • FOCUS: external layers of the heart and heart wall. The Human Heart • Located between the lungs in thoracic cavity • Pointed end called apex • Acts as a pump to propel blood through the body Layers of the heart • Outer Membrane –Pericardium • Heart Wall ( from outside to inside) –Epicardium –Myocardium –Endocardium Pericardium • Membrane that surrounds and protects the heart • Made of two layers: – Fibrous Pericardium – Serous Pericardium Fibrous Pericardium (Outer) • Outer layer of the pericardium • Tough, dense, inelastic connective tissue • Prevents stretching of the heart • Provides protection • Anchors heart in place Serous Pericardium (Inner) • Thin membrane • Forms a double layer around the heart – Parietal Layer (outer layer) – Visceral Layer (inner layer) • Same as epicardium • Pericardial Cavity – Between parietal and visceral layer – Contains pericardial fluid -> reduces friction between membranes as heart moves Heart Wall • Epicardium – also visceral layer of serous pericardium – Thin transparent outer layer of the heart wall • Myocardium – Consists of cardiac muscle tissue -> only found in the heart – Makes up the bulk of the heart – Responsible for pumping action of the heart Heart Wall • Endocardium – Thin epithelial layer that lines the inside of the heart – Covers the valves and tendons inside the heart – Continuous with epithelial lining of large blood vessels Parts of the Heart The Heart: Chambers • Right and left side act as separate pumps • Four chambers – Atria • Receiving chambers – Right atrium – Left atrium – Ventricles • Discharging chambers – Right ventricle – Left ventricle Figure 11.2c Blood Circulation Figure 11.3 The Heart: Valves • Allow blood to flow in only one direction • Four valves – Atrioventricular valves – between atria and ventricles • Bicuspid valve (left) • Tricuspid valve (right) – Semilunar valves between ventricle and artery • Pulmonary semilunar valve • Aortic semilunar valve The Heart: Valves • Valves open as blood is pumped through • Held in place by chordae tendineae (“heart strings”) • Close to prevent backflow The Heart: Associated Great Vessels • Aorta – Leaves left ventricle • Pulmonary arteries – Leave right ventricle • Vena cava – Enters right atrium • Pulmonary veins (four) – Enter left atrium