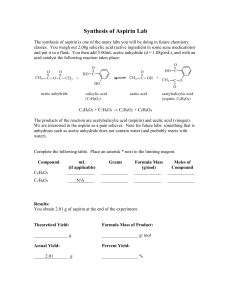
document
advertisement
Acid-Base Titration An Analysis of Aspirin Tablets Limitation in this experiment: Assume that all the acidic ingredients come from acetylsalicylic acid(aspirin) Introduction: Aspirin is widely used as pain killer and lower body temperature. The main constituent of aspirin tablets is acetyl-salicylic acid(CH3COOC6H4COOH). Aspirin passes unchanged through the acidic conditions in the stomach but is hydrolysed to ethanoate ions and salicylate ions by the alkaline juices in intestines. Over doses of aspirin may even causes death. CH3COOC6H4COOH + 2OH- CH3COO- + HOC6H4COO- + H2O Principle: The object of this experiment is to determine the percentage of acetyl-salicylic acid in aspirin tablets. A known amount of standard sodium hydroxide solution is used in excess to hydrolyses a known mass of aspirin tablets. CH3COOC6H4COOH + 2NaOH CH3COONa +HOC6H4COONa +H2O The unused sodium hydroxide which remains is then titrated with standard acid. The amount of alkali required for the hydrolysis can now calculated. The number of moles of acetylsalicylic acid which have been hydrolysed can be found. Brands of aspirin: Brand 1: Disprin ($13 each pack, 24 tablets per pack) Brand 2: Fuse ($10 each pack, 10 capsules per pack) Chemicals: 1M sodium hydroxide 0.10375M hydrochloric acid 3 tablets of Disprin aspirin (1.44g) 5 capsules of Fuse aspirin (0.72g) Phenolphthalein (act as indicator) Apparatus list: burette x2 pipette x2 conical flask x6 volumetric flask x2 beaker x4 measuring cylinder x 1 funnel x2 Experimental setup 1 (Hydrolysis of aspirin) Procedure 1 Hydrolysis of aspirin: 1.Record the weight of aspirin tablets 2.Transfers the crushed aspirin tablets into a clean conical flask. 3.Pipette 25 cm3 of NaOH in to the aspirin- containing conical flask. 4.The same volume of distilled water is added to form a mixture. 5.Leave the mixture to react for 10 minutes. 6.Transfer the mixture to a volumetric flask and make up to the mark with distilled water. Experimental setup 2 (Back titration): Procedure 2 Back titration with hydrochloric acid: 1. Pipette 25cm3 of hydrolyzed solution into a conical flask. 2. Phenolphthalein is added as indicator. 3. Back titrate the hydrolyzed solution with hydrochloric acid. 4. Record the volume of hydrochloric acid. 5. Repeat the above experiment for a least 4 times. Data and results: Brand name: Disprin No. of tablets used: 3 Weight: 1.44g Average volume of hydrochloric acid : 14.73cm3 Brands name: Fuse No. of capsules used: 5 Weight: 0.72g Average volume of hydrochloric acid: 17.85cm3 Observation Aspirin + NaOH Phenolphthalein added Aspirin + NaOH + phenolphthalein Titrate with hydrochloric acid and the endpoint is reached. Source of errors: • The aspirin tablets may contain more than one kind of acid other than aspirin. • The aspirin may not fully dissolve in the distilled water. • The mixture of aspirin solution may not be wellshaken. • Extra drops of hydrochloric acid may added while the end-point is reached. • It was not easy to get a good estimation to 0.05 cm3 from the burette. Precautions: • NaOH is corrosive. We should avoid contacting the solution with our skin. • Safety goggles must be put on during heating and titration. • We should wash our hands after the experiment Remarks: • The pH of the mixture should be checked by a pH paper before carrying out the titration. • Slightly heated the mixture to ensure all aspirin dissolved. • We should label the containers of both sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid as they are colorless solution. Improvement: As some acidic impurities presents in the aspirin tablets, the accuracy of the above experiment to determine the concentration of aspirin is low. However, the acetylsalicylate ions (ionized aspirin) is an ester and esters are formed from combination of an acid and an alcohol. By reacting the ester with NaOH, alcohol is formed. Determining the alcohol concentration by carrying fractional distillation. Therefore the concentration of the aspirin can be calculated. Calculation: BRAND 1 BRAND 2 No. of moles of HCL used =14.73/1000*0.10375 =0.00153mol Initial no. of mole of NaOH =1*25/1000=0.025mol No of moles NaOH reacted =0.025-0.00153 =0.0248mol ∴No. of mole of aspirin reacted =0.0248mol ∴No. of mole per aspirin tablet =0.0248/3=0.008mol / tablet ∵the mixture has been diluted 10 times 0.008*10=0.08mol / tablet Cost of aspirin per mole =13/(0.08*24)=$6.78/mol No of moles of HCL used. =17.85/1000*0.10375 =0.00185 Initial no. of mole of NaOH =1*25/1000=0.025mol No of moles reacted =0.025-0.00185 =0.0232mol ∴No. of mole of aspirin reacted =0.0232mol ∴No. of cost per aspirin capsule =0.0232/5=0.0046 ∵the mixture has diluted 10 times 0.0046*10=0.046mol / capsule Cost of aspirin per mole =10/(0.046*10)=$21.8/mol Conclusion: Disprin is the best buy Reference: Chemistry in context (G.C Hill J.S Holman Nelson) Websites: http://capital2.capital.edu/faculty/wbeckte l/PAsprinL.htm http://chemlabs.uoregon.edu/Classes/Exton /CH229/AspAnalysis/AspAnalysis.pdf http://web.esf.edu/dljohnson/fch380net/la bs/seventh.htm Member List 6A *Wong Man Fong (26) Chan Wai Kin (2) Yum Kee Him (30)