Best Buy Corporate Governance Analysis Management and
advertisement

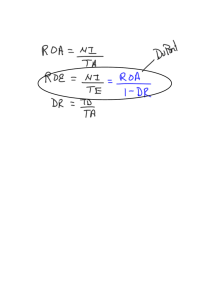
Best Buy I. Corporate Governance Analysis A. Management and Stockholders Balance of Power Best Buy is run by its management which is led by the CEO, Hubert Joly. The power on the board comes from their position and not their ownership of stock. The board members themselves own very little stock. In fact, the CEO sold $17 Million worth of stock to help settle a divorce. (See Huffington Post Article) A large majority of the power comes from the owner and founder of Best Buy, Richard Schulze. Richard Schulze owns 62,920,813 shares or 18.1% of outstanding shares. (See Bust Buy Ownership Summary) He also helped hand –pick the board. (See Fortune article)This makes him the top holder of shares at best Buy. Moreover, Richard attempted to take over Best Buy in August 2012. However, he was unable to secure the private funding in order buy the board seats. Richard lost power in the company in May 2012 because he was forced to step down as Best Buy chairman when an investigation found out he knew the CEO was having a relationship with an employee. However, in March 25, 2013 Richard was reinstated with a new title chairman emeritus. This allowed him to hold a non advisor position on the board. He was also allowed to add two former executives, Brad Anderson and Al Lenzmerier, to the board on his behalf. This along with his share ownership gives him a great amount of power at Best Buy. Both Hubert Joly and Richard Schulze have many relationships with the board. Hubert has 23 relationships while Richard has 28 relationships. (See Businessweek Profile). Manifestations Best Buy has compensated very well this past year for the boars performance. In 2013 executives were compensated 63.66 million which is almost three times the 2012 compensations of 23.33 million. In 2013 Hubert Joly was compensated $19,550,692 million dollars. (See MorningStar profile) Source: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/09/11/best-buy-ceo-divorce_n_3907685.html http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=83192&p=irol-ownershipsummary http://investing.businessweek.com/research/stocks/people/board.asp?ticker=BBY http://insiders.morningstar.com/trading/executive-compensation.action?t=BBY http://finance.fortune.cnn.com/2012/08/22/best-buy-shareholders-caught-in-the-crossfire/ Managerial Performance Under Hubert Joly’s new strategy management was able to increase gains on Best Buy stock by237% in 2013. This made Best Buy one of the top performing stocks in the S&P 500 in 2013. (See Fool) However, in the beginning of 2014 the stock dropped 29 percent because of a decline in holiday sales. Hubert Joly’s price math strategy failed to boost holiday sales and revenue fell .9%. Profits fell by 1.85% and revenue declined by 2.6%. Currently the entire retail industry is suffering and Best Buy seems to have taken a considerable hit by the slow winter retail sales. (See Bloomberg article) Source: http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-16/best-buy-u-s-holiday-sales-fall-as-shoppers-spurnprices.html http://www.fool.com/investing/general/2014/01/07/todays-3-worst-stocks-in-the-sp-500.aspx Stockholder Reaction Stockholder reaction was a large issue in 2012 when Richard Schulze attempted to buy back the company. He issued a public letter and a price to buy the company when he felt that the board refused to allow due diligence for earnings. The entire process ended with both parties being disappointed and with Best Buy appointing an outsider as the new CEO. Stockholders suffered since the stock price decreased significantly and talks of Schulze buying the company were halted by the board. The board refusing to hear Schulze’s demands during the holiday season hurt both the company and the stockholder’s chance of seeing the company be acquired. (See Fortune article) Source: http://finance.fortune.cnn.com/2012/08/22/best-buy-shareholders-caught-in-the-crossfire/ B. Firm and Financial Markets Best buy is a widely followed firm and one of the largest electronic retailers. The company is used to distinguish performance between online retailers such as Amazon and box retailers like Best Buy. Best Buy provides information about its strategies and financial information in their earnings reports. A large amount of information is also available from external sources such as equity research analysts. This reduces the amount of bias in information. (See Reuters) Source: http://www.reuters.com/finance/stocks/analyst?symbol=BBY.N C. Firms and Society Best Buy was forced to make some difficult decisions because of a scandal between CEO Brian Dunn and founder Richard Schulze. Best Buy handled the situation poorly and caused the entire situation to blow out of control. Richard confronted Dunn about the affair but did not report it to anyone. When an audit committee was formed Dunn left but Best Buy made the poor decision to not explain why. This lack of transparency resulted in a media frenzy that caused Best Buy to create its own PR crisis. (See Business Indsider) Best Buy is doing an excellent job with social responsibility. The company has won awards for recycling and helping reduce energy consumption. (See Best Buy CSR Report) Source: http://www.businessinsider.com/best-buys-pr-crisis-turned-into-a-bloodletting2012-5 http://www.bby.com/category/sustainability/ Financial Information Best Buy wants to transition into appealing more customers to the box retailer experience. In the past year Best Buy has done that by providing price matching against its competitors. Although this has made 2013 a successful year for Best Buy it has also reduced profit margins. Best Buy is currently struggling with competing with companies like Amazon who make it difficult to match prices when they have no overhead. The industry is currently wondering if Best Buy will simply just be a Amazon showroom. II. Stockholder Composition In order to analyze stockholder compensation we looked at which types of groups owned sotck in Best Buy. This information was broken down into a table shown below. Breakdown Percent % of Shares Held by All Insider and 5% Owners: 21% % of Shares Held by Institutional & Mutual Fund Owners: 75% % of Float Held by Institutional & Mutual Fund Owners: 94% Number of Institutions Holding Shares: 418 We then looked at how the stocks were broken down by individual shareholders. The major shareholders are listed below. Major Holders Shares Richard Schulze 1,735,500 Allen Lenzmeier 6,327 Joly Hubert 476,629 Stephen Gillett 344,840 James Muehlbauer 205,697 Finally we looked at the institutions and mutual funds with the largest shareholders. They are listed below. Largest Stockholders Shares FMR LLC 42,499,249 Fidelity Low-Priced Stock Fund 23,670,000 Vanguard Group 19,270,786 Wellignton Management Company LLC 12,804,683 State Street Corporation 11,756,849 (See Yahoo finance) Best Buy is owned by mainly well diversified funds. The company has a large number of insider holdings because of the shares from the owner Richard Schulze. Approximately 21% of shares are owned by insiders at Best Buy. However, in the electronics industry 23.34% of shares are owned by Insiders. The average investor is either an insider or a large institution. (See Macroaxis) Source: http://finance.yahoo.com/q/mh?s=BBY+Major+Holders http://www.macroaxis.com/invest/ratio/BBY--Shares_Owned_by_Insiders III. Risk Profile An analysis of Best buy’s stock prices for the past 5 years shows that the price had a downward until the end of 2012. However, in 2013 the price rebounded back to its original price of $40. IN 2014 the price plunged more than $10 because of the slow winter retail sales. A. Market Analysis of Risk and Return To analyze the volatility from market forces we ran a regression of Best Buy’s stock prices against the S&P 500. . reg var1 var2, beta Source SS df MS Model Residual 9721.48435 87011.2703 1 1257 9721.48435 69.2213765 Total 96732.7546 1258 76.8940816 var1 Coef. var2 _cons -.0110323 45.19707 Std. Err. .0009309 1.265193 t -11.85 35.72 Number of obs F( 1, 1257) Prob > F R-squared Adj R-squared Root MSE = = = = = = 1259 140.44 0.0000 0.1005 0.0998 8.3199 P>|t| Beta 0.000 0.000 -.3170148 . We interpreted the following from the regression: A. Slope of the regression: -.32. This is Best buy’s beta. B. Intercept of the regression: -.01% This shows Best Buy’s performance. When compared with the Rf (1-b) we can see the estimated performance. Rf (1-b) = 0.6% (1--.32) = .08% Intercept - Rf (1-b) =-0.01% - (0.08%) = -.09% This shows the Best Buy performed -.09% worse than expected based on the CAPM for the past 5 years. C. R squared of the regression: 10.05%. This shows that 10.05% of the risk for Best Buy comes from the market and the remaining 89.95% of the risk comes from the firm. This means that Best Buy is a risky investment in the market (Source: Google Finance and Yahoo Finance Historical Stock Prices) Levered beta In order to find the levered beta we first estimated the market value of equity and debt. Market Value of Equity= Share price * Number of Shares = $24.48 * 341.5 million = 8359.2 Million To find the market value of the debt we used the book value of debt $ 1612 million, the interest expense of $100 million and the face-value weighted average maturity of 4 years with the cost of borrowing at 5% (See Best Buy 10k Long Term Debt) to find an estimated value of debt to be $2224 Million. Estimated Market value of debt= 100 [(1-1/(1.05)^4 / .067] + 1612/(1.05)^4 = $2,224 So the levered Beta for Best buy = -0.32(1+(1-0.367*(2224/8359.2)) = -.374 Beta to Cost of Equity In order to find the cost of equity we used a long term treasury bond rate for the risk free rate and for the risk premium we used the historical risk premium for stocks of 5.5%. Expected Return = 7% + -.374 (5.5%) = 4.94% Best Buy’s Cost of Debt Based on Best Buy’s long term treasury rate , default spread , and pre-tax borrowing to find the after-tax cost of debt. After-tax Cost of debt = 7.5% (1-.367) = 4.74% Best Buy Weights for Debt and Equity Equity Ratio= 79% Debt Ratio = 21% Best Buy’s Cost of Capital Using the cost of equity and the after-tax cost of debt to cost of capital is as follows: Cost of Capital = 4.94%(.79) + 4.74%(.21) = 4.90% (See Best Buy’s 10k) Currently Best Buy’s debt to equity ratio is .4157. This shows that Best Buy has a considerable amount of debt on the books which is not good. (See Standard and Poor’s Capital IQ Net Advantage) IV. Investment Return Analysis A Typical Project Typical projects at best Buy depend on management and the direction and strategy the CEO has planned for the company. Projects at Best Buy are long term projects planned out for the entire year and have a large impact on the company’s financial. Projects are likely to cost a lot of money and follow the industry’s forecasts. Projects mainly deal with increasing revenue and enhancing the consumer experience. Other projects deal with shifting real estate needs in order to align with customer interest. So for example Best Buy has begun to close large big box stores and Best Buy Mobile Stores. (See Standard and Poor’s Capital IQ Net Advantage Best Buy Business Strategy) A. Measuring Past Returns In order to determine the returns on Best Buy’s past projects we need to assume that the earnings after the project can be attributed to the project. Since Best Buy focuses on high budget financial projects we can assume this assumption will allow us to determine the success of the project. The project we will be focusing on is the new price matching strategy introduced early 2013. Return on Equity= Net Income 2014/ Average BV of Equity for 2013 and 2014 = $532 million/$3852 million = 13.81% (Average BV of equity =Feb 2013 BV of equity $3715 + Feb 2014 BV of Equity $3989 /2= $3852) Net Income February 2013: -441 Million Net Income February 2014: 532 Million Return on Capital= EBIT2014(1-t) / Average BV of Capital from 2013 to 2014 = 1087(1.37)/(5234.5) = 13.08% (2014 BVE 3989+ BVD1612 = 5601 2013 BVE3715+BVD 1153= 4868 Average = 5234.5) (See Best Buy’s 10k) B. Evaluation of Past Returns In order to determine if the returns have an impact on Best Buy’s financials we must look at the return on equity and cost of equity. Return on Equity = 13.81% Cost of Equity = 4.94% Equity Return Spread= 13.81%-4.94%= 8.87% The spread is used to determine the value of the project after it is multiplied by the book value of equity. Equity EVA= (Return on Equity – Cost of Equity) (BV of Equity) = (.1381-.0494)(3852) = $341.7 million In addition, looking at the return on capital shows the following: Return on Capital= 13.08% Cost of Capital = 4.90% EVA= (.1308 -.0490)( 5234.5)=428.18 Million This shows that Best Buy created 428.18 Million dollars because of the projects. (See Best Buy’s 10k) C. Assessments for the Future We believe that Best Buy’s new projects will continue to create value for the company year by year. The price matching strategy reduces profits but helps them generate enough revenue to compete with online competitors like Amazon. In addition, the shift of reducing the amount of Big box stores and focusing on smaller mobile stores has allowed them to cut operating expenses. These projects have generated significant value for Best Buy throughout 2013. (See Standard and Poor’s Capital IQ Net Advantage Best Buy Business Strategy) V. Capital Structure Choices Current Financing Mix Best Buy currently has the following debt. Amount $349 Million $500 Million $649 Million $1 Million (See Best Buy’s 10k) Maturity 2 4 7 3 Percent 5.5% 5.0% 5.5% 6.7% This shows that Best Buy has a large amount of debt on their balance sheet. The debt all matures at different years and have appropriate interest rates. Trade Off on debt versus Equity When we look at Best Buy’s debt we see the following. Added Discipline of Debt Bankruptcy Risk When we look at Best Buy’s institutional stockholders we see that the owner owns a large amount of the firm. Because he has a large say in what goes on for management Best Buy should be cautious with their debt. This is why Best Buy’s debt was recently rated as junk by Standard and Poor recently. The risk involved and the poor company performance made the debt a risky investment (See Standard and Poor’s Capital IQ Net Advantage) A large amount of the cash flow is volatile because the company depends on day to day retail sales. They are at the point where the company needs to price match to lure in customers so the company is a risk for bankruptcy. However, this risk is low because of the large amount of assets Best Buy can sell to pay off debt. We believe that Best buy has a significant debt capacity. The only benefit from the debt is the slight tax benefit but the cash flows help sustain the amount of debt they have. Best Buy should focus on lowering their debt to equity ratio. VI. Optimal Capital Structure Current Cost of Capital/ Financing Mix To determine the cost of capital we used the market value equity and debt from the previous sections. Cost of Capital = 4.94%(.79) + 4.74%(.21) = 4.90% An optimal debt ratio would be An AAA to A- rating which means the debt ratio needs to be under 30%. Because Best buy has a debt ratio of 21% it is optimal. VII. Mechanics of Moving to the Optimal A. Path to the Optimal Intuitive Analysis Business Retail Stores Project Cash Flow Characteristics Projects are short term. Type of Financing The cash flows are in dollars. Short term. New cash flows are driven by electronics sales Primarily dollar Debt should be Tied to strategies. Real Estate Projects are likely to be Debt should be long term Long term. Primarily in dollars. Rely on market value VIII. Dividend Policy Best Buy uses dividends in order to payback shareholders. In the past they five years they have bought back very little stock. The dividends in the past year are shown below. 2013: 17 cents per quarter 2012: 16 cents per quarter 2011: 15 cents per quarter 2010: 14 cents per quarter 2009: 14 cents per quarter (See Google Finance) Based on the stock price of $24.48 today the dividend yield is .17/2.78. It is interesting to note that Best Buy has been increasing the dividends even though the stock price has been really volatile. This shows that under new leadership the company believes they should send a strong message to stockholders to keep paying out dividends. IX. Dividend Policy: A Framework How much should Best Buy have paid as dividends from 2009 to 2013. To analyze this we need the estimate the free cash flows to equity at Best Buy each year. The table below summarizes the results. Year 2014 2013 2012 2011 Net income $42410 $45085 $46064 $49747 Dividends .68 .64 .60 .56 This shows that regardless of the net income Best Buy continues to increase the amount of dividends giving out every year. This is concerning because the dividends should reflect the financials and not what management see fit. X. Valuation