IN CASE YOU ARE NOT CONSIDERING: During our review days I
advertisement

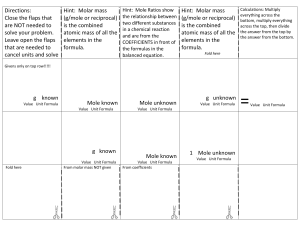
IN CASE YOU ARE NOT CONSIDERING: During our review days I forget to point out that you need to study the “mole road” please revise it. mass # mole # particles mass to # mole divide by MM & # mole to mass multiply by MM MM is molar mass & it is the sum of atomic masses We get atomic mass from periodic table. The unit of MM is g/mole. If it is an element its molar mass is the same as its atomic mass. For diatomic elements (H,N,O,F,Cl,Br & I ) their molar mass is double of their atomic mass (if they are in their natural state). # mole to # particle multiply by Avog.# & #particle to # mole divide by Avog. # Avog. # is 6.02*1023 The other important point is Limiting Reactants (LR) : If the mass or # moles of two reactants is given do not forget first to figure out the LR by comparing the # moles for the given mass with the mole ratio from balanced equation, Once you know the LR use that amount to find the theoretical yield and other related question. (Please revise stoichiometric calculations). Also remember the Hf & Gf for elements in their natural state is zero. Hf is Heat of formation. STUDY significant # in calculations & chemical equilibrium GOOD LUCK