Sensory Receptors

Sensory Receptors
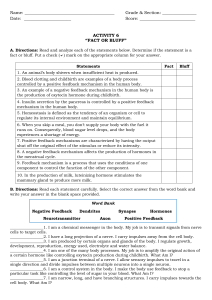
D.S.Q.
• 1. What is getting ready to happen to the foot in the picture?
• 2. What will most likely happen as soon as the feather rubs against the foot?
• 3. What causes different reactions to this kind of stimulation?
Discussion Questions
• 1. How many senses do we have?
• 2. When we sense something by touch, our bodies receive a mechanical input. What kind of input are we receiving with our sense of taste or smell?
• Chemical input
• 3. What kind of input are we receiving with our sense of sight or hearing?
• Electromagnetic Input
• 4. What allows us to hear a sound?
How do we receive signals?
• Which system helps us receive signals?
• Nervous system
• Any change or signal in the environment that an organism can recognize and react to is called a stimulus.
• After the nervous system analyzes a stimulus, it directs a response.
What do our senses do?
• Your eyes, ears, nose, mouth and skin are specialized sense organs that enable us to get information from the outside world.
• Each organ contains sensory neurons that send impulses to the brain
• Your brain interprets them, which enables us to understand more about the environment.
How do we see?
• Our eyes respond to the stimulus of light
• WE convert that stimulus into impulses that our brain interprets, which lets us see
• First, the light rays enter through the pupil
• Second, they pass through the lens and the muscles in the lenses adjust the shape and focus the light rays on the retina
• Third, the lens bend the light rays, and produce an upside down image
How do we see cont.?
• Fourth, the nerve impulses then travel through the brain and the brain turns the image right-side up
Taste and Smell
• Taste and smell work together
• They both depend on chemicals in the air or in food
• The chemicals trigger responses in receptors in the nose and mouth
• Then the nerve impulses travel to the brain and helps us interpret the smells and tastes
How do we hear?
• Sounds are caused by the vibrations of air particles
• Ears convert sound waves into nerve impulses that your body interprets
• 3 main parts of the ear—outer ,middle, & inner
How do we hear cont?
• 1. Sound waves enter your outer eat through the canal
• 2. When the sound waves reach your eardrum, they cause it to vibrate
• 3. The vibrations pass the 3 tiny bones in the middle of your ear, and takes them to the inner ear.
• 4. These vibrations turn into nerve impulses and then are interpreted by the brain
Touch
• Sense of touch is found all over your skin.
4 types of nerves that respond to specific kinds of changes
• 1. Mechanical Changes (Mechanoreceptors)
• Enables us to detect touch, sense the position of our muscles, bones and joints and detect sounds and the motion of the body
4 types of nerves that respond to specific kinds of changes
• 2. Chemical Changes (Chemoreceptors)
• The chemical processes of smelling and tasting begins when molecules go into the nose or mouth where they dissolve and stimulate special chemical receptor cells.
• The cells then send the messages to the brain and that detects the odors and flavors.
4 types of nerves that respond to specific kinds of changes
• 3. Temperature Changes (Thermoreceptors)
• Humans and animals sense hot and cold temperatures on their skin and inside their bodies
• Thermoreceptors are in the brain and are used to monitor internal body temperatures
4 types of nerves that respond to specific kinds of changes
• 4. Light Changes (Photoreceptors)
• Eyes are the only organs that detect light using different receptors in the retina for color (cones) and brightness (rods)