How the NERVOUS SYSTEM works?
advertisement

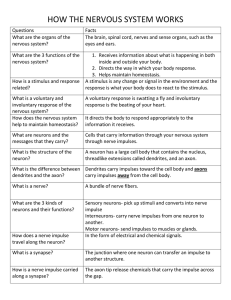
HOW DOES THE NERVOUS SYSTEM WORK? Chapter 12 Section 1 Functions of the nervous system Receives information from inside and outside of the body Directs the way the body responds to information Helps maintain homeostasis Stimulus: change or signal in the environment causing a reaction Response: Reaction to stimulus Neuron = Nerve cell Carries nerve impulses/information through the body Parts of Neuron Axon: carries impulses away from the cell body Dendrites: carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body Three kinds of neurons Sensory Neuron: picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment (also turns stimulus N2 nerve impulse Interneuron: carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another Motor Neuron: sends impulse to muscle or gland— then muscle or gland reacts Synapse: junction where one neuron can transfer an impulse to another structure Nerve impulses must cross the gaps between the axon and next structure in order for the impulse to be carried. Axon tips release chemicals that carry the impulses across the gap.