Alcohols
advertisement

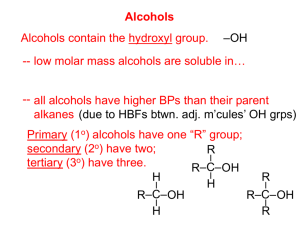
Compounds with Oxygen Atoms Alcohols -OH hydroxyl CH3-OH CH3CH2-OH OH OH Phenols Ethers -O- CH3-O-CH3 Learning Check Classify each as an alcohol (1), phenol (2), or an ether (3): A. _____ CH3CH2-O-CH3 C. _____ CH3CH2OH OH B. _____ CH3 Solution Classify each as an alcohol (1), phenol (2), or an ether (3): A. __3__ CH3CH2-O-CH3 C. __1__ CH3CH2OH B. _ 2__ OH CH3 Naming Alcohols A carbon compound that contain -OH (hydroxyl) group In IUPAC name, the -e in alkane name is replaced with -ol. CH4 methane CH3OH methanol (methyl alcohol) CH3CH3 ethane CH3CH2OH ethanol (ethyl alcohol) Alcohols How is the -OH group different from the hydroxide ion? -OH group forms covalent bond with the carbon Hydroxide ion forms ionic bond with a metal Ethanol CH3CH2OH Acts as a depressant Kills or disables more people than any other drug 12-15 mg/dL ethanol metabolized by a social drinkers in one hour 30 mg/dL ethanol metabolized by an alcoholic in one hour. Alcohol in Some Products % Ethanol Product 50% 40% 15-25% 12% 3-9% Whiskey, rum, brandy Flavoring extracts Listerine, Nyquil, Scope Wine, Dristan, Cepacol Beer, Lavoris More Names of Alcohols IUPAC names for longer chains number the chain from the end nearest the -OH group. CH3CH2CH2OH 1-propanol OH CH3CHCH3 CH3 2-propanol OH CH3CHCH2CH2CHCH3 5-methyl-2-hexanol Some Typical Alcohols OH “rubbing alcohol” CH3CHCH3 2-propanol (isopropyl alcohol) antifreeze HO-CH2-CH2-OH 1,2-ethanediol (ethylene glycol) OH glycerol HO-CH2-CH-CH2OH Classification of Alcohols Primary (1º) H Secondary (2º ) CH3 CH3-C-OH CH3-C-OH H H 1C attached to C-OH 2C attached to C-OH Tertiary (3º) CH3 CH3-C-OH CH3 3C attached to C-OH Learning Check Classify the following as 1º, 2º, or 3º alcohols: OH A. CH3CH2CH2OH C. OH B. CH3-CH-CH2CH3 D. OH CH3-C-CH2CH3 CH3 Solution Classify the following as 1º, 2º, or 3º alcohols: OH A. CH3CH2CH2OH 1º C. OH 2º B. CH3-CH-CH2CH3 2º D. OH 3º CH3-C-CH2CH3 CH3 Properties of Alcohols Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) used in the intoxicating beverages; an important industrial solvent Many aliphatic alcohols used in laboratories, clinics, and industry – Isopropyl alcohol (2-propanol) is rubbing alcohol; used as antiseptic, and a base for perfume, creams, lotions, and other cosmetics Properties of Alcohols Glycerol (1,2,3-propanetriol) - used as a moistening agent in cosmetics, foods, and drugs; also a component of fats and oils Learning Check Name the following alcohols: A. OH CH3CHCHCH2CH3 CH3 OH B. Solution Name the following alcohols: A. OH 3-methyl-2-pentanol CH3CHCHCH2CH3 CH3 OH B. cyclobutanol Properties of Alcohols Much like water, alcohols are capable of hydrogen bonding between molecules –this means they will boil at a higher temp. than alkanes and halocarbons with a comparable number of atoms Properties of Alcohols Alcohols of up to 4 carbons are soluble in water in all proportions; more than 4 carbons are usually less soluble, because…? Properties of Alcohols Denatured alcohol- means it has been made poisonous by the addition of other chemicals, often methyl alcohol (methanol, or wood alcohol). As little as 10 mL of methanol has been known to cause permanent blindness, and 30 ml has resulted in death!!! Reactions of Alcohols Combustion CH3OH + 2O2 Dehydration H OH H-C-C-H H H alcohol CO2 + 2H2O + Heat H+, heat H-C=C-H + H2O H H alkene Oxidation Is a gain of oxygen (O) or A loss of hydrogen (H) Oxidation of Alcohols 1°alcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and 2° alcohols are oxidized to ketones Alcohols 1° 2° aldehydes ketones Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Primary alcohol OH [O] CH3-C-H aldehyde O CH3-C-H H Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) Ethanal (acetaldehyde) Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Secondary alcohol OH [O] CH3-C-CH3 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) ketone O CH3-C-CH3 2-propanone (dimethyl ketone, “acetone”) Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Tertiary alcohols OH no reaction [O] CH3-C-CH3 CH3 no product no H on the C-OH to oxidize 2-Methyl-2-propanol Oxidation of Ethanol in the Body Enzymes in the liver oxidize ethanol Aldehyde product impairs coordination Blood alcohol over 0.4% can be fatal. O O [O] [O] CH3CH2OH CH3CH CH3COH 2CO2 + H2O ethyl alcohol acetaldehyde acetic acid Learning Check Select the product for the oxidation of CH3CH2CH2OH: 1) CH3CH=CH2 O 2) CO2 + H2O 3) CH3CH2CH Solution Select the product for the oxidation of CH3CH2CH2OH: [O] O 3) CH3CH2CH Reduction Is a loss of oxygen (O) or gain of hydrogen (H) Reduction Aldehydes are reduced to 1° alcohols and ketones are reduced to 2° alcohols Alcohols 1° aldehydes 2° ketones Phenols IUPAC name for benzene with a hydroxyl group Many are used as antiseptics and OH disinfectants Phenol Phenols in Medicine OH OH OH OH OH CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 Phenol Resorcinol (antiseptic) 4-Hexylresorcinal (antiseptic) Ethers Contain an -O- between two carbon groups Simple ethers named from -yl names of the attached groups and adding ether. CH3-O-CH3 dimethyl ether CH3-O-CH2CH3 ethyl methyl ether Ethers as Anesthetics Anesthetics inhibit pain signals to the brain CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 used for over a century; commonly called just ether (Morton, 1846) Causes nausea and is highly flammable 1960s developed nonflammable anesthetics Cl F F Cl F H H-C-C-O-C-H F F F Ethane(enflurane) H-C-C-O-C-H HF H Penthrane MTBE Methyl tert-butyl ether CH3 CH3-O-C-CH3 CH3 Second in production of organic chemicals Additive to improve gasoline performance Use in question with discovery of contaminated water supplies Learning Check Write the structure of the following: A. 3-pentanol B. Dimethyl ether C. 3-methylcyclobutanol Solution Write the structure of the following: OH | A. 3-pentanol CH3CH2CHCH2CH3 B. Dimethyl ether CH3-O-CH3 CH3 C. 3-methylcyclobutanol OH Thiols Contain the functional group -SH Named by adding thiol to the name of the longest carbon chain Number the -SH group in longer chains CH3-SH methanethiol CH3-CH2SH SH ethanethiol CH3-CH-CH3 2-propanethiol Thiols Many thiols have disagreeable odors Used to detect gas leak Found in onions, oysters, garlic and oysters Onions CH3CH2CH2-SH Garlic CH2= CHCH2-SH Skunk spray CH3 1-propanethiol 2-propene-1-thiol trans-2-butene-1-thiol CH = CH CH2SH