Alcohol Lab
advertisement

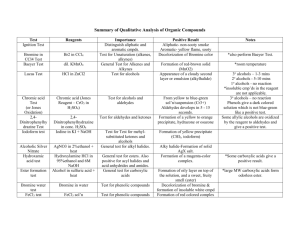
Properties of Alcohols Isomers of Butanol and Properties of n-alcohols Classification of Alcohols Primary (1º) H Secondary (2º ) CH3 CH 3-C-OH CH 3-C-OH H H 1C attached to C-OH 2C attached to C-OH Tertiary (3º) CH 3 CH 3-C-OH CH 3 3C attached to C-OH Oxidation vIs a gain of oxygen (O) or vA loss of hydrogen (H) Alcohols 1Ealcohols are oxidized to aldehydes and 2E alcohols are oxidized to ketones Alcohols 1E 2E aldehydes ketones Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Primary alcohol aldehyde OH O [O] CH 3-C-H ; CH3-C-H H Ethanol (ethyl alcohol) Ethanal (acetaldehyde) Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Secondary alcohol OH ketone O [O] CH3-C-CH 3 2-Propanol (isopropyl alcohol) ; CH 3-C-CH 3 2-propanone (dimethyl ketone, “acetone”) Oxidation of Alcohols [O] Tertiary alcohols OH CH3-C-CH 3 CH3 no reaction [O] no product no H on the C-OH to oxidize 2-Methyl-2-propanol (tert-butyl alcohol) Oxidation of Ethanol in the Body l Enzymes in the liver oxidize ethanol l Aldehyde product impairs coordination l Blood alcohol over 0.4% can be fatal. O O ; CH3CH2OH ethyl alcohol ; CH3CH CH3COH 2CO2 + H2O acetaldhyde acetic acid Synthesis of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols. R-OH + HX à R-X + i) HX = HCl, HBr, HI ii) may be acid catalyzed (H+) iii) ROH: 3o > 2o > CH3 > 1o iv) rearrangements are possible except with most 1 o ROH H2O CH3 CH3CCH3 OH + tert-butyl alcohol 2-methyl-2-propanol HCl à CH3 CH3CCH3 + H2O Cl tert-butyl chloride 2-chloro-2-methylpropane 3o alcohol can form H-bonds from hydroxyl Alkyl halide is less polar,can’t form H bonds and is not soluble in water produced (cloudy) CH3 CH3CCH3 OH + tert-butyl alcohol 2-methyl-2-propanol HCl à CH3 CH3CCH3 + H2O Cl tert-butyl chloride 2-chloro-2-methylpropane Hydroxyl Hydrogen is the most polar in a 3o alcohol Halogenation is fastest in tertiary alcohols CH3-OH + methyl alcohol methanol HCl à CH -Cl3 + H2O methyl chloride Chloromethane Hydroxyl Hydrogen is the least polar in a 1o alcohol Halogenation is slowest in primary alcohols butan-1-ol 2-methylpropan-2-ol butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-1-ol SOLVENT PROPERTIES OF ALCOHOLS Solubility Low molecular mass (short chain) alcohols are miscible with water due to hydrogen bonding between the two molecules Longer chain alcohols are less miscible since the carbon chain is nonpolar and is unable to H-bond with water