US Diplomacy in Asia: Presidential Policies Worksheet
advertisement

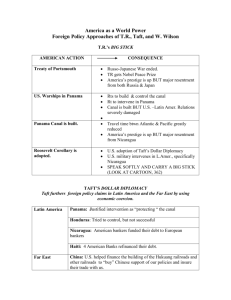
Presidential Policies – A New American Diplomacy American Diplomacy in Asia (p 190) Identify the 3 strategic advantages the US had in Asia that made it a major power. 1. 2. 3. Unlike many of its imperial competitors who were motivated by conquest, the US was motivated by ________________. Open Door Policy (pp. 190-191) Define “sphere of influence”: Identify the countries that were aggressively trying to establish spheres of influence in China in the 1890s. What country appears to have been the most aggressive in China? What was the American concern about these foreign spheres of influence in China? President McKinley’s Secretary of State, John Hay, came up with a plan called the _________ __________ _________. In this new policy, what did the US demand of the other imperial powers in China? Review the definition of imperialism. Given the goals of the Open Door Policy, would it be accurate to say that the US was engaged in imperialism in China? Explain your answer. President Roosevelt’s Foreign Policy (pp. 192-194) Theodore Roosevelt became president in September of 1901 after ________________________ was assassinated. While Roosevelt worked to balance the power between the rival imperial powers in Asia, it became well known that ____________________ was the United States’ biggest rival for influence in Asia and the Pacific. President Roosevelt expressed his attitude about US power were expressed in an African proverb ___________________. On p.192, look at the photo and read the caption. How were the events in this photo an example of Roosevelt’s attitude about US power? The Panama Canal What was the motivation behind US construction of the Panama Canal? Identify the events that happened on the following dates before construction on the canal: 1889 1902 1903 Nov 1903 1904 Construction on the canal begins. Explain how the physical geography of Panama made construction of a canal difficult. The tropical diseases ______________ and _______________ were also challenges to building the canal. How long did it take to complete the Panama Canal? ____ years What was the goal of the Roosevelt Corollary? How did the Roosevelt Corollary obligate the United States to become the “police man” for Latin America? President Taft’s Foreign Policy (p. 194) Describe Taft’s “Dollar Diplomacy” What was the goal of Dollar Diplomacy? After reading about Taft’s experience in Nicaragua, make an inference as to how effective the policy was in other countries in Latin America. President Wilson’s Foreign Policy (pp. 194-195) Define moral. (Use your phone) Explain why Wilson’s foreign policy was often called “moral diplomacy”. (Think about Wilson’s goals.) What was happening to destabilize Mexico during Wilson’s presidency? In response to events in Mexico, Wilson announced a new policy for groups that seize power in a country in Latin America. The receive US recognition, these groups would have to establish a government based on the rule of _______, and not force. Explain how this was in keeping with Wilson’s Moral Diplomacy. What motivated Wilson to order American warships and Marines to seize the Mexican port city of Veracruz in 1914? In 1916, Wilson again ordered US troops into Northern Mexico in response to what event? Presidential Diplomacy – Who got it right? What slogan captures Roosevelt’s What slogan captures Taft’s diplomatic style: diplomatic style: What slogan captures Wilson’s diplomatic style: Make an argument for the president you think had the most successful at protecting American interests. I claim that President______________did the best job protecting American interests. I made this judgment based on this reason: __________________________________________________________________________________________, which I base on this evidence:________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________.