ECG Cheat Sheet - DVUSDMedicalScience
advertisement

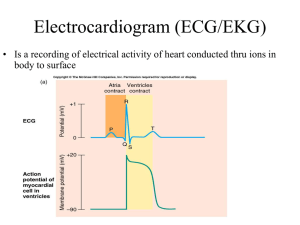
ECG Cheat Sheet The typical EKG waveform Sinoatrial (SA) node in __________ ______________ generates a rhythmical depolarization (firing frequency) Modified by stimulation from nerves from the brain o Sympathetic - increases firing frequency (_____________) in response to: Exercise Anxiety, stress ________________, certain medications, adrenaline o Para-sympathetic - slows the firing frequency (_____________________) Breathing (sinus arrhythmia) - rate decreases following prolonged expiration ________________ - reflex tachycardia occurs to correct transient drop in blood pressure Certain medications Depolarization causes right atrium to contract (P-wave, _________ms) Stimulates Atrio-ventricular (AV) node, which fires in turn Passes down right and left bundles in septum (Q-wave, _______________ms) Depolarizes right and left ventricles, which now contract (________, 240-350ms) Signal voltage 1 to 10 mV, frequency 0.67 to 40-Hz ECG Leads These are what detect the electrical signal of the heart 6 leads are called ________________ Leads and are placed as follows: The additional 6 leads are called __________________ Leads and are placed in different areas according to what is going on with the heart. They make be placed on the arms and legs, or chest. Disorders of the Heart Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) _______________ of coronary arteries supplying the myocardium (heart muscle) Caused by smoking, high fat diet, _____________ (high blood pressure), diabetes EKG shows ________ depression Can be treated by angioplasty, coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) Angina Spasm of sclerotic coronary artery Causes chest pain reversed by nitroglycerine (nitro spray under tongue) Unstable (recurring) angina indicates impending ____________________ Myocardial Infarction (MI, heart attack) _____________________________ of coronary artery Causes chest pain which is ______ reversed by nitro Diagnose by EKG (ST _________________, T-wave inversion) Complications: arrhythmia, cardiac failure Treatment: morphine, aspirin, monitor for complications, thrombolysis ________________________________ Irregular heart rhythm, e.g. atrial fibrillation (AF), heart block, ventricular fibrillation (VF), supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Treatment o digoxin for AF o atropine, pacemaker for bradycardias o VF (may cause sudden death) - treat quickly with electroshock (defibrillator) and chest compressions Cardiac Failure (heart failure) Reduced cardiac output (pump failure) due to weakened ____________________ May be acute (complicating myocardial infarction) or chronic (chronic IHD) Kidneys retain sodium and water - results in pulmonary ________ (fluid in lungs) Treated with diuretics Normal ECG Heart Blockage – long ___________ interval Severe Heart Blockage – two _____ Waves per QRS Complex ________________________ – flat line Bradycardia -- Normal P, QRS, T, rate < _________________ Hypercalcemia -- Short/absent _______ segment Hyperkalemia -- _____________-shaped Twave Idioventricular Rhythm (IVR) -- No ____________, bizarre QRS, rate 20-40 Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) -- ______________ Pwave, irregular P-P interval Premature Ventricular Contraction (VAC) – Wide ____________, unrelated to Pwave Tachycardia -- Normal P, QRS, T, rate > _________________ Ventricular Fibrillation (VFIB) -- _______________ waves Ventricular Tachycardia (VTAC) -- Bizarre, wide QRS, no __________, rate > 100 To help you study these: http://www.gwc.maricopa.edu/class/bio202/cyberheart/ekgqzr0.htm For a really cool website of heart sounds: http://www.med.ucla.edu/wilkes/inex.htm