Reading and Interpreting EKG
advertisement

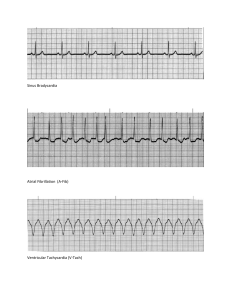
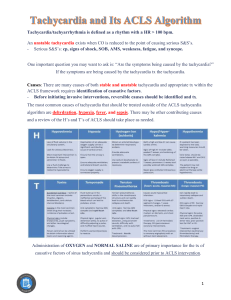
Reading and Interpreting EKG T Petrillo-Albarano, MD Division of Pediatric Critical Care Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta The EKG P wave – Depolarization atria QRS – Depolarization ventricle T wave – Repolarization Ventricle EKG (pic of QRS) Normal Rates O-3 months 3m-2years 2-10years > 10years 85-205 (140) 100-190 (130) 60-140 (80) 60-100 (75) Determining Rates (counting boxes) Identifying Rhythm Too Slow – bradycardia Too Fast – tachycardia Absent – Pulseless arrest Bradycardia (strip) Bradycardia HR less than 60 Associated with poor perfusion Can be caused by many factors – Hypotension, hypoxemia, acidosis, ingestion In children Hypoxemia is often culprit – Support the airway Bradycardia Algorithm Tachy-arrhythmias ABC – Adequate airway – Respiratory effort Does the child have a pulse? – No Pulse: CPR; define rhythm – Positive pulse.. Define rhythm Assess QRS duration Sinus Tachycardia Causes? – Hypovolemia – Fever – Anxiety – Pain – Metabolic stressors – drugs Sinus Tachycardia P waves present and normal Variability to rate Constant PR interval Infants usually less than 220; children usually less than 180 Treat the cause Sinus Tachycardia (strip) Supra-ventricular Tachycardia Usual sudden onset No history to support ST P waves are often absent ( but can be present) Abrupt changes Usually greater than 220 or 180 SVT Assess Perfusion Good perfusion: – Call cardiology – Vagal maneuvers – Adenosine Poor perfusion – Cardioversion – Adenosine – Beta blockers SVT (strip) V Tach with pulse Most will have underlying congenital heart disease or myocarditis/ cardiomyopathy Can be related to electrolyte imbalance, toxin, drugs Cardioversion Consider Amiodirone V Tach Tachycardia Algorithm Pulseless Rhythms VT V-fib PEA Asystole V Fib V Tach PEA Asystole Pulseless Algorithm