12 Lead EKG Review
advertisement

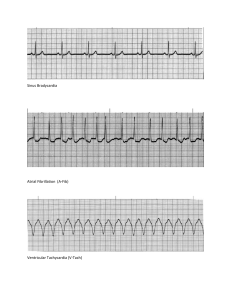
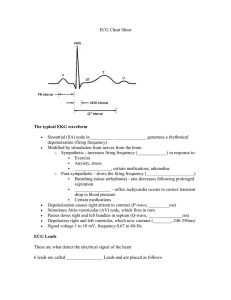
Procedural Skills for Medical Students 12 lead Electrocardiogram (ECG) Interpretation Objectives: 1. Understand the principles of ECG tracings in relation to the electrical activity of the heart. 2. Understand how to properly place the electrodes and differentiate between leads. 3. Be able to interpret common abnormal rhythms including sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, pulseless electrical activity, asystole, ST elevation and ST depression. Material to review prior to lab: Dynamic Cardiac Rhythm Simulator Indications for obtaining a 12 lead ECG: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Chest pain or discomfort Shortness of breath Syncope or near syncope Palpitations Any heart rate less than 50 or greater than 150 A feeling of impending doom Diaphoresis unexplained by ambient temperature, unexplained general weakness, or unexplained nausea and vomiting. 8. Suspected diabetic ketoacidosis 9. Any suspected drug overdose or metabolic derangement 10. An unconscious patient (excluding cardiac arrest) 11. Return of spontaneous circulation, post cardiac arrest Contraindications: 1. There are no identified contraindications for obtaining a 12 lead ECG. However, the practitioner should ensure that someone who is trained to interpret the tracing is available for accurate and reliable interpretation. Equipment: HPS, electrodes Instructional Procedure & Endpoints: 1. Learners will be oriented to Human Patient Simulator (HPS) and equipment in ASTEC. 2. Instruction will be given on lead placement and direction of electrical activity resulting in ECG tracings. 3. Learners will demonstrate correct lead placement on HPS. 4. Instructor will review common ECG tracings and characteristics with learners. 5. Learners will be able to identify 7 out of 10 of the following rhythms on the HPS: sinus rhythm, sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, sinus arrhythmia, atrial flutter, atrial 1 Procedural Skills for Medical Students fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and asystole. 6. Learners will be able to identify 3 out of 4 of the following EKG findings: cardiac ischemia (ST segment elevation versus ST segment depression), premature atrial contractions, and premature ventricular contractions. References: SkillStat Learning Inc. (2005). The six second ECG: Dynamic cardiac rhythm simulator. Retrieved from http://www.skillstat.com/Flash/ECGSim531.html White, R.D. & Harris, G.D. (2011). Office electrocardiograms. In J.L. Pfenninger, & G.C. Fowler (Eds.), Procedures for Primary Care, 3rd Ed (579-584). Philadelphia: Elsevier Mosby. 2