4th lecture
advertisement

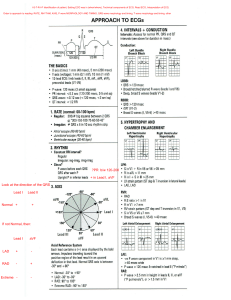
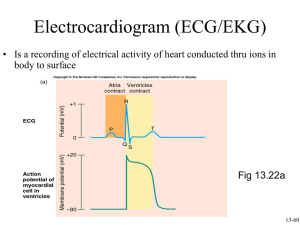
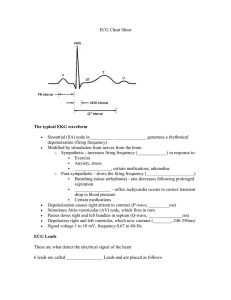
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) • Is a recording of electrical activity of heart conducted thru ions in body to surface Normal conduction pathway: SA node -> atrial muscle -> AV node -> bundle of His -> Left and Right Bundle Branches -> Purkinje fibers -> Ventricular muscle Types of ECG Recordings • Bipolar leads record voltage between electrodes placed on wrists & legs (right leg is ground) • Lead I records between right arm & left arm • Lead II: right arm & left leg • Lead III: left arm & left leg Normal ECG graph The 12-Lead System The most commonly used clinical ECG-system, the 12-lead ECG, consists of the following 12 leads, which are: 3 Augmented Leads 3 Limb Leads 6 Chest Leads I , II , III aVR , aVL , aVF V1 ,V2 ,V3 ,V4 ,V5 ,V6 Chest Leads Adapted from: www.numed.co.uk/electrodepl.html Elements of the ECG: 1) P wave: Depolarization of both atria; Shape and duration of P may indicate atrial enlargement 2) 3) PR interval: from onset of P wave to onset of QRS 1) Normal duration = 0.12-2.0 sec (120-200 ms) (3-4 horizontal boxes) 2) Represents atria to ventricular conduction time (through His bundle) 3) Prolonged PR interval may indicate a 1st degree heart block QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization • Larger than P wave because of greater muscle mass of ventricles • Normal duration = 0.08-0.12 seconds • It is useful in diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular hypertrophy and myocardial infarction. 4) ST segment: • Connects the QRS complex and T wave • Duration of 0.08-0.12 sec (80-120 msec) 5) T wave: • Represents repolarization or recovery of ventricles 6) QT Interval • Measured from beginning of QRS to the end of the T wave • Normal QT is usually about 0.40 sec • QT interval varies based on heart rate Fig. 13.24b Fig. 13.24c Fig. 13.24d Fig. 13.24g The normal electrocardiogram