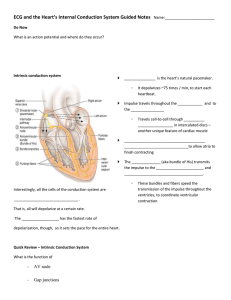
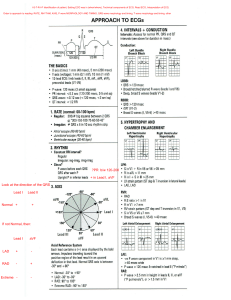
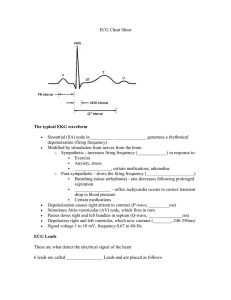
specialized myocardial cells Automacity Extitability conduitivity contractility positive chronotropy T heart rate positive inotropy myocardial contraction positive dromotropy conduction throughAV node cardiac conduction system sinoatrialnode sinus Node electrical impulses 60 100 bpm Pwave on ECG Atrioventricular function PR segment onECG contraction known a atrialkick Bundle OfHis R bundle branchsystem L bundlebranchsystem Purkinje fibers Cardiac electrial altivity can be monitored by using ECG 12lead ECG restingECG Ambulatory ECG holter monitoring continuous cardiac monitoring Telemetry Lardial monitoring is usedto diagnose dysthythmias chamber enlargement myocardial ischemia injury or infarction To monitor effects of electrolyte imbalance medication administration cardiac dysrhythmias are heartbeat disturbances Sinus Bradycardia SB symptomatic if HR 2601min Manifested by dizziness syncopechestpain hypotension Causes Drugs BBs Bs digoxin consider withholding bb if systolic bp 400 notify provider or HR 260bpm vagal stimulation Diseases hypothyroidism M1 increased IP esymptomatic bradycardia SB treatment atropine 0.5 mg WB every 3 5 mins until max dosage of 3m 2 IF ATROPINE IS INEFFECTIVE transcutaneous pacing or an infusion of dopamine or epinephrine is considered 3 permanent pacemaker for electrical management 1 HR HeartRate on ECG OfRB intervals 70s 5 10 50 bpm Brady Sinustachycardia St ormalrate occurswhen the sinusnode createsan impulse at a fasterthan Regular rhythm 100 150min Normal Pwave PRinterval 0.10 0.20s QRS 20.12 sinus Arrhythmias Respiratory sinus arrhythmias Benign Whenthe person breathes in the HR when they breathe out HR More common in children than adults Tends to disappear as they grow The RP interval will often be longer than 0.16s when person breathes out Assessment Of Pts with arrhythmias Physical Assessment paleand cool skin signs of fluid retention JUD rate rhythm of apical peripheral pulses Heartsounds BP pulse pressure Potential complications cardiac arrest I Infomboembolic event PlanningGoals Eradicating decreasing occurance of arrhythmia to maintain co Minimize anxiety Evaluation MAINTAIN CO Experience stable v5 no signs of arrythmias YEAHFIFTH our 1 1 Tac whenweIannotstepwave cardioversion stoppingtheheart Needs informed tonsent famewaves EMILY 8m mmmmm FIFIES g v Fib b shocking Pt ftp.fnepnrine E.EE i.ieiiiiii iii n'outaiium iiiventrille T Thigh 144 4th contract repolarization E.itEE i iii ii OMNI is atrium.no intrans EITHER Atrium contractingMore Antiarrhythmicmeds s Repolarization Relax SA Node depolarization contract wave tellshowthe atrium is contracting Atrial relaxationhappens when veriff RS how the ventricle is lontracting wave Relaxation of ventricle ventricle relaxation Arrhythmias 7 Disorders of formation or conduction of electrical impulses within heart 2 Can cause disturbance of Rate Rhythm or both 3 Potentially can alter bloodflow 4 Diagnosed byanalysis of ECG cause hemodunamic changes DYSRHYTHMIAS Classified by site of origin Sinoatrial NodeSA Atria Atrioventricular AV node ventricle Effect on rate and rhythm bradycardia tachycardia heart block Premature beat Flutter E's stole PREMATUREATRIALCONTRACTION Causes Caffeine Alcohol Nicotine Stretched atrialmyocardium HYPERVOLEMIA Anxiety HYPOKALEMIA Hypermetabolicstates leg Pregnancy atrial ischemia injury infarction OFTENSEEN IN SINUS TACHYCARDIA TX NOtreatmentnecessary If morethan a in I min mayindicate worseningdisease or onsetof fibrillation VENTRICULARFibrillation lethal dysthythmia mechanically theventricleis quivering wt no effective contraction and CO PULSELESS UNRESPONSIVE APNEICSTATE LO 20 3090 Treatment ActivationOFEMERGENCY RESPONSE CPR and ACLS Airway intubation placement Establish Ix access Epi Amiodarone Defibrillation Shock Mmmmm VENTRICULAR V Fib FIBRILATION fY If in shocking Pt ASYSTOLE Flatline ventricular Asystole Total absence of ventricular electrical activity in the heart NO VENTRICULAR CONTRACTION PULSELESS UNRESPONSIVE APNEICSTATE Fishowality CPR ALLS Epi andor vasopressin Advanced airway intubation Establish 14access Treatment for any irreversible causes Notshockable bc theelectricalsystem oftheheart is working properly VENTRICULARTACHYCARDIA Rhythm is often regular butcan be irregular 100 250BPM QRS complex wider than 0.12s Pwave buried in the QRS tomplex TIntiarrhythmic meds lidocaine Epi amiodarone synchronized cardioversion if pulse is present IF Pulseless PEA TREATED w CPR and d Fib ConductionAbnormalities First degree AV Node block Seconddegree AV block type I Seconddegree AV block type11 Thirddegree AV block First degree AV Node Block Normal HR AV conduction is prolonged evidenced by PR interval 0.20s or 5 small offs Second Degree AV Block Pnormal wave wtmissed QRScomplexes a Second DegreeAV block typ11 Mobitz we PRinterval progressively longer until QRS complex is missed bSeconddegreeAVBlockType11Mobitz11 usually associated withelectrolyte disturbances but more oftenassc w CCB conduction system ordrug toxicityBB MORE P WAVESTHAN QRS Complete Heart Block 3rd Degree AV Node Block The atria and ventricles are stimulatedand contract independently F the pt is stable no symptoms no treatment may be indicated or simply decrease eliminating the laude e 9 stoppind med 2 IV bolus of Atropine 2nddegree AV blocktype11 3 temporary transcutaneous pacing 4 permanent pacemaker pacemakers Étemporary or permanent Conduction ofelectrical impulses through SAnode can be slowed w aging causing bradycard and conduction defects A paper spike or pacemakerartifact will be seenon a ECG the Pacer spike a vertical line should be followed by a P wave atrial Pacing or QRS complex ventricular pacing ICD Implantable cardioverterDefibrillator monitor for a life threatening changes in card rhythm automatically delivers an electricalshockdirectly to theheart in an attempt to restorenormalrhythm Temporary pacemakers energy source is providedbyexternalbatterypack cutaneous DExternal trans pacingenergy isdelivered trancut requires largeamounts of electricity can be painful to patients USED WHEN SYMPTOMATIC BRADYCARDIA IS UNRESPONSIVE ATROPINE OROTHERTO HR Epicardial leads aredirectly totheheart during openheart surgery DEndocardial transuenous Pacingwires arethreaded through a large centralvein lodgeinto thewall ofthe Rventricle R atrium or both Permanent pacemaker ICD contain internal pacingunit indicated for chronic or recurrent dysthythmias dueto sinus or AV node malfunction canbe programmed Pacemaker modes Fixed rate asynchronous Fires at a constant rate w o regard for heart's electricity Demandmode synchronous Detects heart's electrical impulses fires at a preset rate only if the heart's intrinsic rate is below a certain level aspacemaker responsemodes Inhibited pacemaker activity is inhibiteddoes not fire Triggered Activity is fired when intrinsic activity is sensed Tachydysrhythmia function implantable cardioverter Defibrillator indicated for survivors ofsudden cardiac death at risk of symptomatic ventricular tachycardia PostProcedure ClientEducation Carry a device ID Prevent wire dislodgement weara slingwhen outof bed DONOT RAISE SHOULDERS FOR 1 2 WEEKS Take pulse at the sametime for those w pacemakers or combination devices Never place items that generate a magnetic field directly over pacemaker In cardioVERSION Patient conscious awake usually sedated used in emergencies FOR UNSTABLE VENTRICULARtachydysrhythmias Defibrillation patient unconscious life threatening condition