Unit 2
advertisement

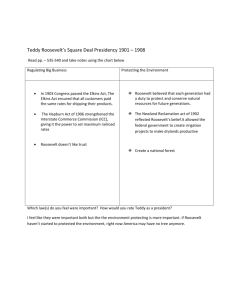
Unit 6 Callon’s definition… Empire: One group exerting political, economic, or military control over another Two reasons for an empire: • Barbarian hordes who have nothing better to do • To make money Trade takes something that is less valuable and turns it into something more valuable Hence, generation of wealth Provides an alternative to LAND = MONEY = POWER, but only slightly at first Empires are all about trade What makes for a successful empire? • Colonies Provide resources Provide a market for goods • Strong Navy Whoever has the strongest navy has the strongest empire By the 1800’s ALL the major world powers were empires Britain was the most successful The U.S. is outpacing Britain in industrial capacity and wants to become a major world power This means becoming an empire Wrote the influential book “The Influence of Sea Power upon History” Inspired Teddy Roosevelt (Undersecretary of the Navy) The U.S. began to modernize their navy Built dozens of new steel battleships and cruisers Seward’s Folly in 1867 William Henry Seward was Sec. of State Purchased Alaska from Russia for $7.2 million Scoffed at at the time, but extended U.S. influence in the Pacific Hawaii annexed in 1898 Annexation opposed by Queen Liliuokalani and native Hawaiians Queen forced to abdicate after coup by American planters in 1893 By 1897 the once mighty Spanish Empire was down to the lone island of Cuba Cubans revolted, started guerilla war Spanish cracked down, forcing Cubans into concentration camps American newspapers reported… Newspapers competed for circulation Especially notorious • William Randolph Hearst – New York Journal • Joseph Pulitzer – New York World Began to exaggerate and fabricate stories Hearst vs Pulitzer U.S. angry over Spanish treatment of Cubans Sent the U.S.S. Maine to Havana to protect Americans in Cuba Maine mysteriously exploded Spanish assumed guilty Americans demand war We now know it was an accident Oops… Teddy Roosevelt anticipated war with Spain Readied the U.S. Pacific fleet As soon as war declared Commodore George Dewey attacked the Spanish Philippines Stunning victory for the Americans Army forced to land in Cuba Target was Santiago After city taken, Spanish fleet forced to retreat Destroyed by American navy Spain forced to surrender U.S. paid $20 million in exchange for the Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam Cuba becomes a U.S. protectorate Cuba forced to cede land for a naval base, Guantanamo U.S. now has an established presence across the Pacific and Caribbean Filipinos were rebelling against the Spanish Switched to the U.S. when U.S. didn’t leave Long, bloody, expensive war for the U.S. Filipinos used guerilla tactics Ironically, the U.S. tried to force them into concentration camps Both sides used torture Eventually rebel leader Emilio Aguinaldo was captured in 1902 Thousands dead on both sides By the late 1800’s China was dominated by Europe Regions of China divided into spheres of influence Prevented others from trading in their territory The U.S. wanted to get involved, but no areas available to trade in U.S. proposed an “Open Door” policy to allow free trade throughout China Unpopular with Europeans, but ultimately unopposed after the Boxer Rebellion Helped protect Chinese sovereignty Allowed the U.S. trade access to China Teddy Roosevelt president in 1901 Reasserted the Monroe Doctrine • No new European colonies in the Western Hemisphere Added the Roosevelt Corollary • The U.S. would intervene to protect its interests in Latin America • Matched Roosevelt’s “Big Stick” diplomacy Best example of the “Big Stick” The U.S. and Europe wanted to build a canal through Central America Ideal location was Panama French company contracted to do the construction The problem was Panama was a province of Colombia, who refused the deal Roosevelt outraged French company conspired with Panama to overthrow the Colombian govt. Within hours Roosevelt recognized Panama’s independence and supported it with the U.S. Navy Triumph of modern engineering Took roughly 10 years to build After Roosevelt came Taft Taft disagreed with “Big Stick” diplomacy Tried to reform the relationship with Latin America Offered trade deals to bolster the economy After Taft came Wilson Wilson wanted to spread democracy into Latin America Refused to make agreements with nondemocratic governments Led to trouble with Mexico What is Progressivism? Progressivism = Reform Specifically, Progressivism means reform through government intervention Meant to solve the problems of the Gilded Age Reversal of Laissez-Faire Not restricted to one political party Applied to numerous areas from 1901- 1920 • Social Reform • Political Reform • Economic Reform • Environmental Reform • Labor Reform • And more… Investigative journalists who exposed social problems Thomas Nast helped expose Boss Tweed Jacob Riis exposed poverty in cities One of the most famous muckrakers was Upton Sinclair Wrote “The Jungle” depicting horrid conditions in meat packing plants in Chicago “It was too dark in these storage places to see well, but a man could run his hand over these piles of meat and sweep off handfuls of the dried dung of rats. These rats were nuisances, and the packers would put poisoned bread out for them, they would die, and then rats, bread, and meat would go into the hoppers together.” Almost turned Teddy Roosevelt into a vegetarian Doing more with less Business owners began to look for ways to operate more efficiently Soon spread to government Wasteful agencies soon removed or consolidated Would eventually lead to Henry Ford and the assembly line Roosevelt began attacking trusts Reasoned they were bad for the public good Only went after the worst offenders, many trusts left intact if they cooperated In 1902 Coal workers went on strike Wanted higher wages and shorter hours Roosevelt tried to intervene Invited owners and workers to talk Workers refused to negotiate Roosevelt infuriated and threatened to have the military take over the mine Workers relented with only minor gains Progressives also sought social justice Charities increased Cities cleaned up Sewers installed Child labor curtailed Temperance advocated One of the biggest influences was the WCTU, Women’s Christian Temperance Union Progressivism stalled in the South “Jim Crow” laws segregated blacks and kept them from voting Plessy v. Ferguson in 1896 legalized segregation and established “separate but equal” Doctrine was implicitly denied by the Gentleman’s Agreement with Japan in 1907 Booker T. Washington • Emphasized education • Founded numerous schools for blacks • Argued that over time blacks could prove themselves the equals of whites W.E.B DuBois • First black to earn a PhD from Harvard • Argued blacks should demand and immediate end to segregation • Eventually lost faith, supported Black Power, and moved to Africa Roosevelt one of the first presidents concerned with the environment Wanted long term resource management and wildlife protection for future Americans Founded 2 million acre Yellowstone Natl. Park Also founded dozens of wildlife preserves, parks, and national monuments, including the Grand Canyon Roosevelt at Yosemite, 1903 Roosevelt’s Secretary of War Groomed for the Presidency Elected in 1908 as a Republican Never comfortable as President Unpopular as President Reversed many of Roosevelt’s appointments Much more aggressive in anti-trust legislation Prompted Roosevelt to challenge Taft in 1912 Democrat elected President in 1912 Wanted to continue Progressive reform Worked to lower tariffs to damage trusts Passed legislation to further dissolve trusts Created the Federal Reserve (The Fed) in 1913 12 Regional Federal Reserve banks Intended to centralize and control the money supply Also passed next to the 16th Amendment, allowing for a federal income tax Most important event in modern history Completely changed the course of world history Affects Western politics, economics, religion, and society on profound levels Catastrophic in terms of damage Total Mobilized Forces ALLIED AND ASSOCIATED POWERS Russia 12,000,000 British Empire 8,904,467 France 8,410,000 Italy 5,615,000 United States 4,355,000 Japan 800,000 Romania 750,000 Serbia 707,343 Belgium 267,000 Greece 230,000 Portugal 100,000 Montenegro 50,000 TOTAL 42,188,810 ALLIED AND ASSOCIATED POWERS Germany 11,000,000 Austria7,800,000 Hungary Turkey 2,850,000 Bulgaria 1,200,000 TOTAL 22,850,000 GRAND 65,038,810 TOTAL Country Killed Wounded Prisoners and Missing Total Casualties Casualties as % of Forces 1,700,000 908,371 1,357,800 650,000 116,516 300 335,706 45,000 13,716 5,000 7,222 3,000 5,142,631 4,950,000 2,090,212 4,266,000 947,000 204,002 907 120,000 133,148 44,686 21,000 13,751 10,000 12,800,706 2,500,000 191,652 537,000 600,000 4,500 3 80,000 152,958 34,659 1,000 12,318 7,000 4,121,090 9,150,000 3,190,235 6,160,800 2,197,000 323,018 1,210 535,706 331,106 93,061 27,000 33,291 20,000 22,062,427 76.3 35.8 73.3 39.1 7.1 0.2 71.4 46.8 34.9 11.7 33.3 40.0 52.3 1,773,700 4,216,058 1,152,800 7,142,558 64.9 1,200,000 3,620,000 2,200,000 7,020,000 90.0 325,000 87,500 3,386,200 400,000 152,390 8,388,448 250,000 27,029 3,629,829 975,000 266,919 15,404,477 34.2 22.2 67.4 8,528,831 21,189,154 7,750,919 37,466,904 57.5 What does all this have to do with the U.S.? Not much Most people in the U.S. wanted to remain neutral Even if the U.S. joined it wasn’t clear which side they should be on U.S. selling supplies to France and Britain Would have sold to Germany, but British were blockading the coast Germany becoming increasingly desperate as supplies choked off Retaliated with U-boats in the Atlantic Germans eventually began attacking all ships off the coast of Great Britain U.S. merchants and passengers advised against travel 128 Americans killed in July 1915 Wilson demanded that Germany cease unrestricted submarine warfare Germany wanted to avoid U.S. involvement and agreed, despite its success The U.S. was happy to avoid the war Wilson re-elected in 1916 because: “He Kept Us Out of War” By 1917 Germany was increasingly desperate Decided to resume unrestricted submarine warfare In order to keep the U.S. out of the war Germany tried a scheme with Mexico Germany’s foreign secretary, Arthur Zimmerman, sent a telegram to the ambassador in Mexico Offered a deal that if Mexico would attack the U.S. then Germany would help them regain territory British intelligence intercepted the telegram and handed it off to the U.S. Resumption of unrestricted submarine warfare Germany conspired to attack the U.S. Bolshevik Revolution in Russia French Army on the verge of collapse Germany about to get major reinforcements at Russia drops out For the U.S. it was now or never The U.S. declared war on April 6, 1917 Still, the U.S. had virtually no standing army and would not deploy until 1918 Germany made two final pushes in 1918 Made it again to the gates of Paris The last push ultimately failed A faction in Germany revolted and forced the Kaiser to abdicate Germany asked for a cease-fire Went into effect Nov. 11 at 11am Germany bewildered and starving The British kept the blockade until the treaty was finally signed, 7 months later Wilson wanted to show mercy to Germany with easy terms to try and prevent another war France and Britain wanted payback Wilson’s peace plan to prevent another war Advocated: • No secret alliances • Free trade / oceans • Arms reductions • Self-determination for colonies and ethnic groups • A “League of Nations” Only the League of Nations was adopted, but U.S. failed to join Germany lost significant territory Germany prevented from keeping any significant army Territory on the Rhine occupied by Allies Germany forced to admit “war guilt” and pay enormous reparations Austria-Hungary dissolved and forbidden to join Germany Numerous new nations created