Light and Sound
advertisement

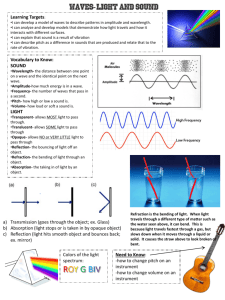
Light and Sound Sound • Sound is a longitudinal wave • Sound causes compressions and rarefactions in the air molecules • Sound must travel through a material • Sound can not travel through empty space • Decibels – how loud the sound is • Decibels are determined by amplitude (energy) Pitch of sound • The pitch of the sound wave depends on the frequency of the wave • High frequency is high pitch • Low frequency is low pitch Doppler Effect • Sound • Change in frequency and pitch of a sound that is caused by either the movement of the object or the listener • Ambulance • Race car Speed of Sound • Sound travels at 340 m/s in air • Changes speed depending on how close together the atoms in the material are • The speed of sound is different in different materials – Travels fastest in solids (steel – 4512 m/s) – Travels in between in liquids (water – 1483 m/s) – Travels slowest in gases • Speed also depends on the temperature – Travels faster in warm air (100⁰F – 354 m/s) – Travels slower in cold air (0⁰F – 320 m/s) Supersonic • Caused by motion that is faster than the speed of sound • Silence as the object is approaching • Loud boom after the object passes • Sound is racing to catch up Light • Light is created when electrons move energy levels inside of the atoms • When energy is added to an atom the electrons jump to higher energy levels • When electrons fall back to lower energy levels, energy is released in the form of light Light • • • • Does not need a medium to travel through Can travel through empty space Speed is fastest in gas, slowest in a solid As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases Theories of Light • Particle theory – light travels as streams of particles or photons in a straight line – reflection • Wave theory – light travels as waves – light travels through openings and spreads out • Quantum theory – a bundle of light energy (quantum) that travels in waves Particles, Waves or Quantum Speed of Light • Speed of light is 300,000,000 m/s • Light can circle the earth 27 times in 1 second • Why do we see lightening before we hear thunder? Photoluminescence • Glow in the dark • Atoms in certain materials can store energy when they exposed to light • When the light is turned off they are no longer storing energy and energy is given off as light Electric Light • Electricity is used to cause the electrons to jump and fall between levels • Incandescent bulbs heat metal to give off lightthey also give of heat – less efficient • Fluorescent bulbs heat gases to give off light – give off less heat – more efficient Colors of Light • White light is composed of all the colors of the spectrum – ROY G BIV – Light from the sun is white – what happens when it travels through a raindrop? • Black light is the absence of all color – Shut yourself in the bathroom with no light – can you see any color? Colors of Light • Photoreceptors in the eye detect visible light • The light we see is reflected light • Why do we see color? – Light that hits the shirt from the sun or a light bulb is white – The color of an object depends on the light wave that is sent to our eye – A blue shirt looks blue because blue light waves are sent to our eye Color in Art • Do pigments mix the same way that light mixes • If I mix all the colors of pigment do I paint with white paint • How do I make white paint or have white paper? Optics • Lenses – use refraction to bend light • Mirrors – reflect light • Prisms – uses refraction to separate light into the colors • Telescope – collection of lenses used to magnify an object • Laser – one specific wavelength of light that is concentrated and organized