Light and Sound Science Test
advertisement

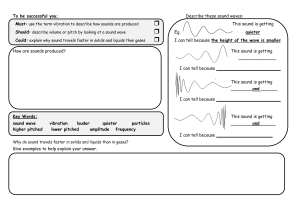
Name: ______________________________ Test Date: _________________ Sound Study Guide 1. Be able to match the following words with their definitions: Amplitude - the height of a sound wave; the distance between the resting point and a crest Frequency- The number of crests or troughs in a certain amount of time intensity - the amount of force applied to an object pitch - how high or low a sound is (depends on frequency) sound wave - a change that carries energy (sound) from one place to another vibration -the back and forth motion of an object volume- loudness of a sound; it’s determined by its amplitude wavelength- distance between one crest or trough or another 2. How are light and sound alike? They are both forms of energy and travel in waves. 3. Know the relationship between frequency and pitch & amplitude and volume. Frequency (number of crests in a period of time) changes the pitch. Higher number of waves = higher sound (tone) Amplitude (height of crests) changes the volume. The higher the waves , the louder the sound. 4. How would you describe how sound travels? Think about direction. Sound travels in waves that travel in all directions. 5. How does sound travel? What medium does it travel the fastest through? What medium does it travel the through the slowest? Sound requires matter to travel. The matter is the medium of the sound. Sound travels fastest through solids and slowest through gases. 6. How does temperature affect how sound travels? Sound travels faster at warmer temperatures. 7. Be able to discuss an activity done in class that demonstrated VIBRATIONS (sound). Rice experiment, tuning forks, slinky, coat hanger experiment, straw experiment 8. Be able to draw a wave for each type of sound: (use the line provided as a resting point for your wave) High Amplitude Sound Low Amplitude Sound High Frequency Sound Low Frequency Sound ------------------- ------------------- ------------------ ------------------ 9. Explain how sound is produced and how you can change sound with instruments. Instrument How sound is produced? How can you change the pitch? How can you change the volume? Plucking the strings Making the strings longer or shorter Plucking the strings harder or softer. Drum Hitting or tapping the drum skin Making the skin tighter or looser. Hitting the skin harder or softer. Bottles Blowing across the bottle’s top Shortening or lengthening the air column by adding something such as water. Blowing across the top harder or softer Guitar