Energy NOTES
advertisement

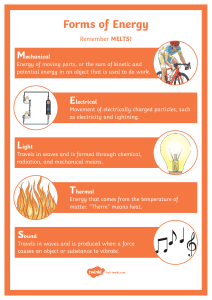
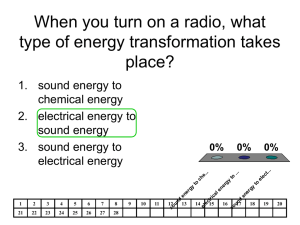
Energy NOTES Energy – the ability to do WORK Energy is a property of matter (all matter has energy) *It is easier to describe what energy does than what energy is* Law of Conservation of Energy – States that energy can be transferred from one object to another, but energy cannot be created or destroyed. Forms of ENERGY 1. Mechanical Energy – energy an object has because of its motion or position a) Kinetic Energy – energy of motion (the greater the speed and mass the greater the kinetic energy b) Potential Energy – energy of position (stored energy) -gravitational = stored energy due to height - elastic = stored energy due to stretching or compressing - chemical = stored energy in the chemical bonds of matter 1 Gravitational potential energy Elastic potential energy Chemical potential energy Examples of Potential and Kinetic Energy being Transferred 2 Forms of ENERGY 2. Thermal Energy – the energy related to the temperature of a substance (heat energy) Temperature vs. Heat Temperature = a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. Heat = the transfer of thermal energy between substances from the warmer substance to the cooler substance Thermometer = measures temperature * Heat flows from a warmer substance to a cooler substance. Methods of Heat Transfer A. Conduction = transfer of heat by direct contact. Heat from the end of the metal rod travels to the hand 3 B. Convection = transfer of heat in a fluid through currents. (Heat rises) C. Radiation = transfer of energy as electromagnetic waves. *Can travel through empty space as well as through solids, liquids, and gases. through empty space 4 Examples of heat transfer Forms of ENERGY 3. Light Energy – the energy carried by light and other kinds of electromagnetic waves Properties of light •Light spreads out in all directions from its source. •Light travels in straight lines called rays. Decreasing wavelength Increasing frequency •Light travels “at the speed of light” 186,282 miles per second •Light can travel in a vacuum (empty space) as well as through matter. 5 Forms of ENERGY 4. Sound Energy – the energy carried by sound waves Sound is produced when an object vibrates. The vibrating object pushes the particles of matter next to it and causes them to compress (squeeze together). The compressed matter squeezes the matter next to it. The compression travels through the matter as a wave of energy. Sound waves travel in all directions away from their source. Sound travels more slowly than light. (761 miles per hour) Sound waves must travel through a medium. (solid, liquid, or gas) Forms of ENERGY 5. Chemical Energy – the energy stored in chemical bonds gasoline food battery 6 Forms of ENERGY 6. Electrical Energy – the energy produced by electric charges Forms of ENERGY 7. Nuclear Energy – the energy contained in the nuclei of atoms Nuclear Power Plant Nuclear Fission = splitting atoms to produce ENERGY 7