Waves, Light, and Sound Study Guide
advertisement
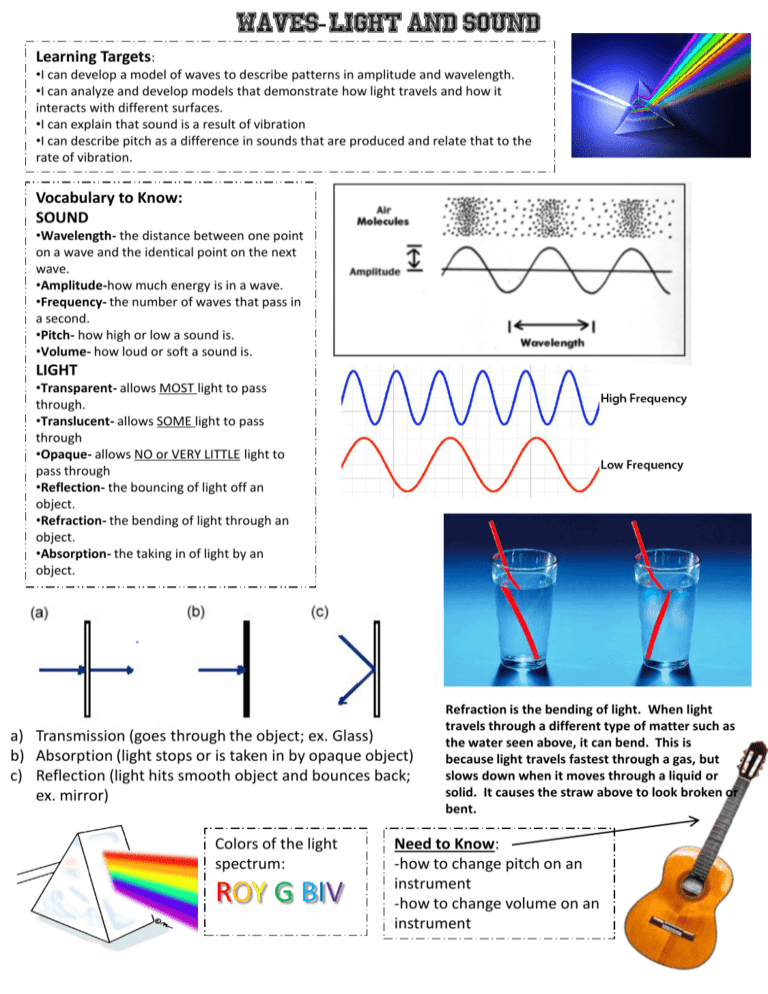
Learning Targets: •I can develop a model of waves to describe patterns in amplitude and wavelength. •I can analyze and develop models that demonstrate how light travels and how it interacts with different surfaces. •I can explain that sound is a result of vibration •I can describe pitch as a difference in sounds that are produced and relate that to the rate of vibration. Vocabulary to Know: SOUND •Wavelength- the distance between one point on a wave and the identical point on the next wave. •Amplitude-how much energy is in a wave. •Frequency- the number of waves that pass in a second. •Pitch- how high or low a sound is. •Volume- how loud or soft a sound is. LIGHT •Transparent- allows MOST light to pass through. •Translucent- allows SOME light to pass through •Opaque- allows NO or VERY LITTLE light to pass through •Reflection- the bouncing of light off an object. •Refraction- the bending of light through an object. •Absorption- the taking in of light by an object. a) Transmission (goes through the object; ex. Glass) b) Absorption (light stops or is taken in by opaque object) c) Reflection (light hits smooth object and bounces back; ex. mirror) Colors of the light spectrum: ROY G BIV Refraction is the bending of light. When light travels through a different type of matter such as the water seen above, it can bend. This is because light travels fastest through a gas, but slows down when it moves through a liquid or solid. It causes the straw above to look broken or bent. Need to Know: -how to change pitch on an instrument -how to change volume on an instrument