What is Assistive Technology
advertisement

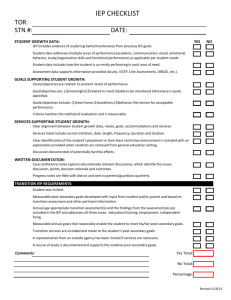
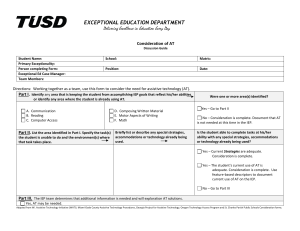
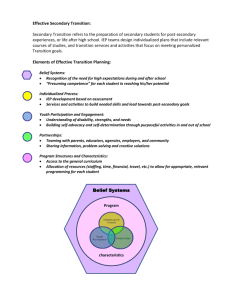
Candy Tavernier, Transition Specialist Capital Region/North Country Regional Special Ed Technical Assistance Support Center (RSETASC) What is Assistive Technology (AT)? • “Any item, piece of equipment, or product system, whether acquired commercially or off the shelf, modified, or customized, that is used to maintain, or improve functional capabilities of individuals with disabilities” -IDEA 2004 (§ 602) Transition Planning Federal Guidelines Transition Requirements • Measurable post-secondary goals and recommendations for transition services and activities must be included in each student's IEP beginning not later than the first IEP to be in effect when the student is age 15 (and at a younger age, if determined appropriate), and updated annually. The IEP must include: • measurable post-secondary goals in the areas of training, education, employment and, where appropriate, independent living skills. These goals must be based on age-appropriate transition assessments1; • the student’s needs as they relate to transition from school to post-school activities, including the courses of study to be provided to the student to reach those goals; • annual goals that document the knowledge/skills the student is expected to achieve that will incrementally prepare him/her to meet the postsecondary goals; and • transition services/activities the student will need to facilitate his/her movement from school to post-school activities. Transition services are a coordinated set of activities developed for a student with a disability, designed to improve his/her academic and functional achievement in order to facilitate the student's movement from school to post-school activities. Coordinated means the CSE has recommended a combination of activities that will lead the student to reach his/her post-secondary goals, including instruction, related services, community experiences, development of employment and other post-school adult living objectives and, when appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills and a functional vocational evaluation. • Students must be invited to CSE meetings when transition goals and services will be discussed. If a student does not attend, the district must take steps to ensure the student’s preferences and interests are considered. The school district must also invite a representative of a participating agency that is likely to be responsible for providing or paying for transition services. Parental consent (or the consent of the student who is age 18 or older) must be obtained prior to inviting other agency representatives. If the invited agency does not attend, the school must take steps to involve the agency in the planning of any transition services. • • • • • In short Individualized process Increased focus at 15 Based on Measurable PostSecondary determined through age-appropriate assessment Student Voice evident Activities that move the student toward their Measurable Post-Secondary Goals. Truth or Myth? 1. AT provides a substitute for classroom instruction 2. AT teaches a basic skill 3. AT provides an unfair advantage 4. AT does all of the work for the student 5. All AT is expensive Stachowiak, University of Iowa 6. AT use is the goal 7. AT can be chosen based strictly on disability 8. Once AT is chosen, the student is all set 9. Student will always use AT 10. The newest AT is always the best BIGGEST MYTH If AT worked for the Transition Age Student, they would have it by now. • Around the ages of 12-14, technology interventions in schools tend to stop • Need to consider – What technology was available 12-14 years ago – How available was AT training/ education to those working in the school districts (service providers) in the past and what is their knowledge/ comfort level with AT – What NEW technology is there to try – General funding/ policy issues – Student and family comfort level/ readiness Cathy Bodine, PhD. (2009) Based on a study in Colorado Schools AT = Independence • Many Americans with disabilities rely on assistive technology, and 35% say they would lose their independence without this technology – 2004 N.O.D./Harris Survey –Slide developed by Cornell ADA Trainer Network Do we continue to focus on skills(reading, math, writing) that the student has been unable to master in the past... OR Do we focus on allowing individuals to begin to use assistive technology to compensate for their disability and become a more independent adult? At and Transition Planning Measurable Post Secondary Goals should be driving the process Transition and AT Consideration…. • Where does the student see themselves in the future? – Education/ Training – Employment – Independent Living • What are the requirements of the setting? – What will the student need to be able to do? • Current skills/ abilities vs. requirements • How available is the AT? Measurable Post-Secondary Goals should be driving the process…. The SETT Framework Step 1 Student’s (Zabala, 1995) present levels of academic and functional performance and evaluation data Step 2 Environment where the student will make progress toward goals and objectives Step 3 Step 4 Tasks and objectives that address the student’s needs Tools/ AT devices and services required for the student to make progress toward the objectives SETT Process Tool Student • What does the student need to be able to do? • What are the student’s current abilities and skills? • What are the student’s functional limitations? • What are the student’s special needs? • What is the student’s comfort level with technology? • How does the student perform with and without a piece of assistive technology? (DATA!!!) Environment • What materials and equipment are currently available in the environment? • What resources and equipment will be available to the student in their future, chosen environment? • What is the physical arrangement? Are there special concerns? • What is the instructional arrangement? Are there likely to be changes? • What supports are available to the student? • What resources are available to the people supporting the student? Entitlement Eligibility Adult Services School-aged Services Entitlement • Based on IDEA • Guarantees access to education • Services/supports determined by CSE Eligibility • • • Based on ADA Must apply for services/supports Determinations made on case by case basis Tasks • What activities take place in the environment? (future or current) • What activities support the student’s curriculum or postsecondary goals? • How might these activities be modified to meet the student’s needs? • How might technology support the student’s active participation in this activity? • Is technology already available in the environment they are going into? • Will the technology be considered a reasonable accommodation? • How do you advocate for reasonable accommodations in this/these setting(s)? Tools • What tools might be used to invite increased student performance? • What tools might be considered when developing a system with special needs to carry out tasks? • How might these tools be tried in the customary environment? • What tools will the student need to learn to use to enter into the adult world of living, learning, and earning. http://askjan.org/soar/disabilities.html Quality Indicators for Assistive Technology http://www.qiat.org/index.html Tech Matrix http://techmatrix.org/ At Resource Guides IEP Overarching planning tool for the school year. Assistive Technology should be included in an IEP when: • It enables students to perform functions that can be achieved by no other means • It enables students to approximate normal fluency, rate, or standards--a level of accomplishment which could not be achieved by any other means • It provides access for participation in programs or activities which otherwise would be closed to the individual • It increases endurance or ability to persevere and complete tasks that otherwise are too laborious to be attempted on a routine basis • It enables students to concentrate on learning tasks, rather than mechanical tasks • It provides greater access to information • It supports normal social interactions with peers and adults • It supports participation in the least restrictive educational environment Stachowiak, University of Iowa Where does AT fit in Transition Planning Process? • Measurable Post-Secondary Goals • Present Levels of Academic Performance – – – – – Evaluation Results Academic Achievement, Functional Performance and Learning Characteristics Social Development Physical Development Special Considerations • Transition Needs • Annual Goals • Programs and Services • Coordinated Set of Activities IEP and AT Quality Indicators Adult Services • Students who will be accessing adult services (ACCES-VR, OPWDD, College Accommodative Support Services) should have clear support in their IEP for WHY ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY WORKS for them. – Helps ensure continuation of services – Helps agencies assist students in advocating for accommodations Remember Assessment is the key to this process. Foster as much independence as possible! Coordinate the effort so the device usage is maximized. Do not assume that the student will have help when they exit. Develop a relationship with the agencies or assist the student with learning how to navigate the adult world. Contact me! Candy Tavernier 23 Huskie Lane Malone, NY 12953 ctaverni@mail.fehb.org