Geography: How do I study it? (8-30
advertisement

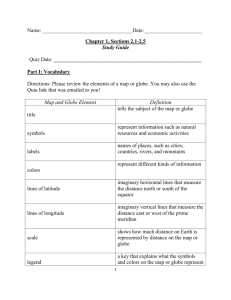
Geography: How do I study it? (8-30-10) • Geography is the study of the world’s people, places, and environments. • Everything you see, touch, use, and even hear is related to geography. • Does this seem like a large amount of information to study? • The FIVE THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY make it easy to understand all this information. The Five Themes of Geography • Location • Place • Human/Environment interaction • Movement • Regions Location • Location is the starting place for all geographers. • “Where is it?” PLACE • Place is those features and characteristics that give an area its own identity or personality. • These can be physical characteristics: Landforms, climate, plants, and animals. • Or they can be human characteristics: Language, religion, architecture, music, politics, and way of life. REGIONS • Regions are places grouped together because of one or more common characteristics. • Down East MOVEMENT • Movement is the continual movement of people, ideas, and goods. • How does the continual movement of humans help shape our world? HUMAN/ENVIRONMENT INTERACTION • Human/Environment interaction looks at how and why people change their surroundings. • These changes can be negative. • Our everyday lives affect our environment, and our environment affect our everyday lives. Notes 8/31/10 What is a Globe? • A globe is a model of the earth that shows the earth’s shape, lands, distances, and directions as they truly relate to one another. • A world globe can help you find your way around the earth. • By using one, you can locate places and determine distances. Hemispheres • To find places on the earth, geographers use a system of imaginary lines that crisscross the globe. • One of these lines is the Equator. The equator circles the middle of the earth like a belt. • It divides the earth into “half spheres,” or hemispheres . Everything north of the equator is in the Northern Hemisphere, and everything south of the equator is in the Southern Hemisphere. Notes (9-1-10) • Another imaginary line runs from north to south and helps divide the earth into half spheres in the other direction. • This line is called the Prime Meridian. Everything east of the Prime Meridian for 180 degrees is in the Eastern Hemisphere. • Everything west of the Prime Meridian for 180 degrees is in the Western Hemisphere. Which Hemisphere is North America located? Can you remember from class? Latitude and Longitude • The Equator and the Prime Meridian are the starting points for two sets of lines used to find any location. • Parallels circle the earth like stacked rings and show latitude. • Latitude is the distance measured in degrees north and south of the Equator. North pole is 90 degrees N (North) latitude, and the South pole is 90 degrees S (South) latitude • There are two important parallels in between the poles are Tropic of Cancer at 23 ½ degrees N latitude and the Tropic of Capricorn at 23 ½ S latitude. • Meridians run from pole to pole and crisscross parallels. Meridians show longitude. Longitude is the distance measured in degrees east (E) or west (W) of the Prime Meridian • The Prime Meridian, or 0 degrees longitude, runs through Greenwich, England. • On the opposite side of the earth is the 180 degree meridian, it is called the International Date Line. • Lines of latitude and longitude cross each other in the form of a grid system. You can find a place’s absolute location by naming the latitude and longitude lines that cross exactly at that place. Let’s try a couple……. The Parts of a Map • On a map you will find what geographers call a compass rose, which can look like a compass. • It shows the cardinal directions, which are north, south, east, and west. • Geographers sometimes use symbols to stand for certain things found on a map. • We call this a KEY or LEDGEND. The Earth in Space We will learn...... The Earth has life because of the sun. The earth has different seasons because of the way it tilts and revolves around the sun. Some terms to keep in mind..... solar system leap year orbit summer solstice atmosphere winter solstice axis equinox revolution Places we will locate..... Earth sun moon The Solar System The sun's heat provides life on our planet. Earth and all the planets revolve around the sun. Together with our sun, these bodies form our solar system. Each planet travels along an oval-shaped path around the sun called an _______. Each planet travels along its own orbit around the sun. Each planet also takes a different amount of time to complete one full trip around the sun. That’s all of today! Have a great weekend!