AP CHEMISTRY UNIT 1 REVIEW Packet AB
advertisement
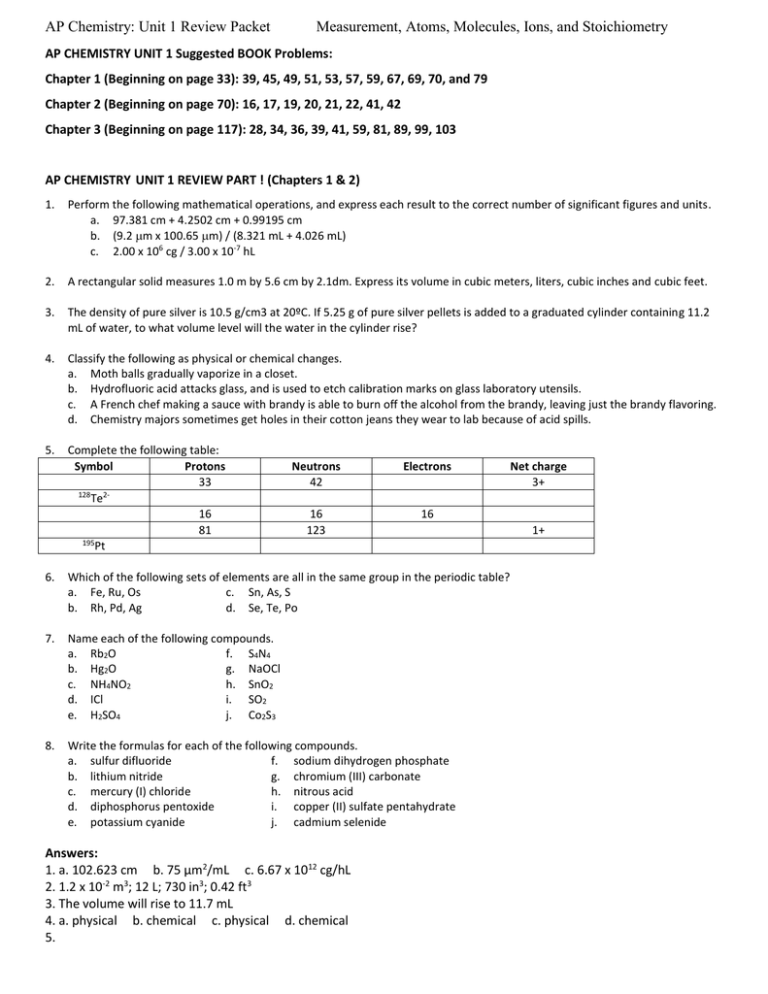
AP Chemistry: Unit 1 Review Packet Measurement, Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Stoichiometry AP CHEMISTRY UNIT 1 Suggested BOOK Problems: Chapter 1 (Beginning on page 33): 39, 45, 49, 51, 53, 57, 59, 67, 69, 70, and 79 Chapter 2 (Beginning on page 70): 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 41, 42 Chapter 3 (Beginning on page 117): 28, 34, 36, 39, 41, 59, 81, 89, 99, 103 AP CHEMISTRY UNIT 1 REVIEW PART ! (Chapters 1 & 2) 1. Perform the following mathematical operations, and express each result to the correct number of significant figures and units. a. 97.381 cm + 4.2502 cm + 0.99195 cm b. (9.2 m x 100.65 m) / (8.321 mL + 4.026 mL) c. 2.00 x 106 cg / 3.00 x 10-7 hL 2. A rectangular solid measures 1.0 m by 5.6 cm by 2.1dm. Express its volume in cubic meters, liters, cubic inches and cubic feet. 3. The density of pure silver is 10.5 g/cm3 at 20ºC. If 5.25 g of pure silver pellets is added to a graduated cylinder containing 11.2 mL of water, to what volume level will the water in the cylinder rise? 4. Classify the following as physical or chemical changes. a. Moth balls gradually vaporize in a closet. b. Hydrofluoric acid attacks glass, and is used to etch calibration marks on glass laboratory utensils. c. A French chef making a sauce with brandy is able to burn off the alcohol from the brandy, leaving just the brandy flavoring. d. Chemistry majors sometimes get holes in their cotton jeans they wear to lab because of acid spills. 5. Complete the following table: Symbol Protons 33 128 2Te 16 81 195 Pt Neutrons 42 Electrons 16 123 16 6. Which of the following sets of elements are all in the same group in the periodic table? a. Fe, Ru, Os c. Sn, As, S b. Rh, Pd, Ag d. Se, Te, Po 7. Name each of the following compounds. a. Rb2O f. S4N4 b. Hg2O g. NaOCl c. NH4NO2 h. SnO2 d. ICl i. SO2 e. H2SO4 j. Co2S3 8. Write the formulas for each of the following compounds. a. sulfur difluoride f. sodium dihydrogen phosphate b. lithium nitride g. chromium (III) carbonate c. mercury (I) chloride h. nitrous acid d. diphosphorus pentoxide i. copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate e. potassium cyanide j. cadmium selenide Answers: 1. a. 102.623 cm b. 75 µm2/mL c. 6.67 x 1012 cg/hL 2. 1.2 x 10-2 m3; 12 L; 730 in3; 0.42 ft3 3. The volume will rise to 11.7 mL 4. a. physical b. chemical c. physical d. chemical 5. Net charge 3+ 1+ Unit 1 Notes Symbol Protons Neutrons Electrons Net charge 75 3+ As 33 42 30 3+ 128 Te252 76 54 232 S 16 16 16 0 204 + Tl 81 123 80 1+ 195 Pt 78 117 78 0 6. a and d 7. a. rubidium oxide b. mercury (I) oxide c. ammonium nitrite d. iodine monochloride e. sulfuric acid f. tetrasulfur tetranitride g. sodium hypochlorite h. tin (IV) oxide i. sulfur dioxide j. cobalt (III) sulfide 8. a. SF2 b. Li3N c. Hg2Cl2 d. P2O5 e. KCN f. NaH2PO4 g. Cr2(CO3)3 h. HNO2 i. CuSO4∙5H20 j. CdSe AP CHEMISTRY UNIT 1 REVIEW PART 2 (Chapter 3) 1. Balance the following equations: a. CO(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) b. N2O5(g) + H2O(l) HNO3(aq) c. C5H10O2(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) d. Mg3N2(s) + H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + (NH4)2SO4(aq) e. aluminum metal undergoes a combustion reaction with oxygen. f. copper (II) hydroxide decomposes into copper (II) oxide and water when heated. 2. Calculate the percentage by mass of oxygen in codeine, C18H21NO3. 3. Calculate the following quantities: a. mass, in grams, of 0.105 moles sucrose (C12H22O11) b. moles of zinc nitrate in 143.50 g of this substance c. number of molecules in 1.0 x 10-6 mol CH3CH2OH. d. number of N atoms in 0.410 mol NH3. 4. The molecular formula of aspartame, the artificial sweetener marketed as NutraSweet® is C14H18N2O5. a. What is the molar mass of aspartame? b. How many moles of aspartame are present in 1.00 mg of aspartame? c. How many molecules are present in 1.00 mg of aspartame? d. How many hydrogen atoms are present in 1.00 mg of aspartame? 5. Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of ibuprofen, which contains 75.69% C, 8.80% H, and 15.51% O by mass. Ibuprofen has a molar mass of 206 g/mol. 6. Combustion analysis of toluene, a common organic solvent, gives 5.86 mg of CO2 and 1.37 mg of H2O. If the compound contains only carbon and hydrogen, what is its empirical formula? 7. When 5.061 g of Epsom salt (MgSO4∙xH2O) is heated to 250°C, all the water of hydration is lost, leaving 2.472 g of MgSO4. What is the value of x? 8. Hydrofluoric acid cannot be stored in glass bottles because compounds called silicates in the glass are attacked by the HF(aq). Sodium silicate, for example, reacts as follows: Na2SiO3(s) + 8 HF(aq) H2SiF6(aq) + 2 NaF(aq) + 3 H2O(l) How many grams of Na2SiO3 can react with 0.800 g of HF? 2 Unit 1 Notes 9. Solutions of sodium carbonate and silver nitrate react to form solid silver carbonate and a solution of sodium nitrate. A solution containing 3.50 g of sodium carbonate is mixed with one containing 5.00 g of silver nitrate. How many grams of sodium carbonate, silver nitrate, silver carbonate, and sodium nitrate are present after the reaction is complete? 10. When benzene reacts with bromine, bromobenzene is obtained: C6H6 + Br2 C6H5Br + HBr a. What is the theoretical yield of bromobenzene in this reaction when 30.0 g of benzene reacts with 65.0 g of bromine? b. If the actual yield of bromobenzene was 42.3 g, what was the percentage yield? Answers: a. 2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g) b. N2O5(g) + H2O(l) 2 HNO3(aq) c. 2 C5H10O2(l) + 13 O2(g) 10 CO2(g) + 10 H2O(g) d. Mg3N2(s) + 4 H2SO4(aq) 3 MgSO4(aq) + (NH4)2SO4(aq) e. 4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 Al2O3(s) f. Cu(OH)2(s) CuO(s) + H2O(g) 2. 16.1% 3. a. 35.9 g b. 0.7576 mol c. 6.0 x 1017 molecules d. 2.47 x 1023 N atoms -6 18 4. a. 294.30 g/mol b. 3.40 x 10 mol c. 2.05 x 10 d. 3.68 x 1019 H atoms 5. empirical and molecular formulas are both C13H18O2. 6. C7H8 7. MgSO4∙7H2O 8. 0.610 g 9. 1.94 g Na2CO3; 0 g AgNO3; 4.06 g Ag2CO3; 2.50 g NaNO3 10. a. 60.3 g b. 70.10% 1. Additional UNIT 1 Practice PROBLEMS 1. A solid white substance A is heated strongly in the absence of air. It decomposes to form a new white substance B and a gas C. The gas has exactly the same properties as the product obtained when carbon is burned in an excess of oxygen. Based on these observations, can we determine whether solids A and B and the gas C are elements or compounds? Justify your conclusions for each substance. 2. An experiment requires 45.0 g of ethylene glycol, a liquid whose density is 1.114 g/mL. Rather than weigh the sample on a balance, the chemist chooses to dispense the liquid using a graduated cylinder. What volume of liquid should the chemist use? 3 Unit 1 Notes 3. A cubic piece of metal measures 5.00 cm on each edge. If the metal is nickel, whose density ios 8.90 g/cm 3, what is the mass of the cube? 4. What is the number of significant figures in each of the following measured quantities? (a) 358 kg (b) 0.054 s (c) 6.3050 cm (d) 0.0105 L (e) 7.0500 x 10-3 m3 5. Carry out each of the following operations and express the answers with the appropriate number of significant figures. (a) 12.0550 + 9.05 = (b) 257.2 – 19.789 = (c) (6.21 x 103)(0.1050) = (d) 0.0577 / 0.753 = 6. Perform the following conversions (note: you might have to research some conversion factors): (a) The speed of light in a vacuum is 2.998 x 108 m/s. Calculate its speed in km/hr. (b) An individual suffering from high cholesterol level in her blood has 252 mg of cholesterol per 100 mL of blood. If the total blood volume of the individual is 5.2 L, how many grams of total blood cholesterol does the individual’s body contain? (c) The recommended adult dose of Elixophyllin®, a drug used to treat asthma, is 6 mg per kg of body mass. Calculate the dose in a 150-lb person. 4 Unit 1 Notes (d) A pound of coffee beans yields 50 cups of coffee (4 cups = 1 quart). How many milliliters of coffee can be obtained from 1 gram of coffee beans? 7. A 15.0-cm long cylindrical glass tube, sealed at one end, is filled with ethanol. The mass of ethanol needed to fill the tube is found to be 11.86 g. The density of ethanol is 0.789 g/mL. Calculate the inner diameter of the tube in centimeters. 8. A 32.65-g sample of a solid is placed in a flask. Toluene, in which the solid is insoluble, is added to the flask so that the total volume of solid and liquid together is 50.00-mL. The solid and toluene together weigh 58.58 g. The density of toluene at the temperature of the experiment is 0.864 g/mL. What is the density of the solid? 9. Fill in the following table: Symbol 52 Atomic Number Mass Number Protons Neutrons Electrons 25 30 25 21 18 Cr 3+ 19 133 80 55 54 Br 1- Zinc-65 10. Three isotopes of silicon occur in nature. 92.23% occur as Silicon-28 (which has an atomic mass of 27.97693 amu); 4.68% occur as silicon-29 (which has and atomic mass of 28.97649 amu); and 3.09% occur as silicon-30 (which has and atomic mass of 29.97377 amu). Calculate the atomic weight of silicon. 5 Unit 1 Notes 11. Predict the chemical formulas of the compounds formed by the following pairs of ions: (a) Cu2+ and Br(b) Fe3+ and O2(c) Hg22+ and CO32(d) Ca2+ and AsO43(e) NH4+ and SO42- 12. A 0.150 g sample of solid lead(II) nitrate is added to 125 mL of 0.100 M sodium iodide solution. Assume no change in volume of the solution. The chemical reaction that takes place is represented by the following equation. Pb(NO3)2(s) + 2 NaI(aq) 2(s) + 2 NaNO3(aq) (a) List an appropriate observation that provides evidence of a chemical reaction between the two compounds. (b) Calculate the number of moles of each reactant. (c) Identify the limiting reactant. Show calculations to support your identification. (d) Calculate the molar concentration of NO3–(aq) in the mixture after the reaction is complete. (e) Circle the diagram below that best represents the results after the mixture reacts as completely as possible. Explain the reasoning used in making your choice. 6