Minerals
advertisement

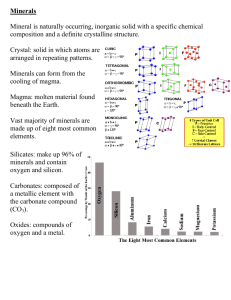
What is a Mineral? Naturally-formed solid substance with a crystal structure Pyromorphite What do all minerals have in common? All: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Are formed by natural processes. Are NOT alive and NEVER were alive Have a definite volume and shape Are elements or compounds with a unique chemical makeup Are made up of particles that are arranged in a pattern that is repeated over and over (called a CRYSTAL) What do all minerals have in common? They must occur naturally within the earth. Cement, bricks, steel, and glass are not minerals because they are man made. What do all minerals have in common? Minerals must be inorganic. This means that they cannot arise from materials that were once part of a living thing. Coal is not a mineral because it comes from the remains of plants and animals What do all minerals have in common? Minerals have a definite volume and shape. The particles that make up the sample do not move apart. What do all minerals have in common? Minerals have definite chemical compositions. A mineral always contains certain elements in definite proportions. Most minerals are compounds. Compounds are two or more elements combined. Some minerals are just elements Copper, Gold, and Silver. What do all minerals have in common? Minerals have crystal structures. These are particles in minerals that line up in a pattern that repeats over and over again. Sometimes a crystal structure is obvious and sometimes its only visible under a microscope. Watch “Crystals” by Brainpop… 1.What element are diamonds made from? 2. What do all crystals have in common? Groups of Minerals Minerals are grouped by the elements they are made of. Beryl (Emerald) Calcite Amethyst Mineral Group Characteristics Contain Silicates oxygen & silica The most abundant group of minerals MICA Examples Quartz, mica Quartz Mineral Group Characteristics Make Non-Silicates Silver up only 5% of the Earth’s crust Include some of the most important minerals Examples iron, copper, gold, silver, diamonds, rubies Copper Diamond Gold Ruby Iron Mineral Group Carbonates Characteristics Carbon Examples & Calcite (CaCO3) oxygen and a positive ion, such as calcium Calcite with Duftite inclusions Mineral Group Oxides Characteristics Metallic ion and oxygen Examples Hematite (Fe2)O3 Mineral Group Sulfides Characteristics Sulfur and a metallic ion Examples Galena (PbS) Mineral Group Sulfates Barite on Calcite BaSo4 / CaCO3 Characteristics Metallic Sulfur & oxygen ion, Barite BaSo4 Examples Barite (BaSO4) Mineral Group Native Elements Characteristics Single elements Examples Gold (Au), Diamond (C), Silver (Ag) How do minerals form? 1) Cooling of magma (hot, liquid rock and minerals inside the earth (from the mantle)) Fast Cooling = No Crystals (mineraloids) Medium Cooling = small crystals Slow Cooling = large crystals How do minerals form? 2) Elements dissolved in liquids (usually water) Physical Properties of Minerals Mineral appearance Hardness Luster Specific gravity Streak Cleavage and fracture Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Color Can be misleading Can vary with the type of impurities Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Hardness How easily a mineral scratches materials Mohs Hardness Scale Scale from 1 (softest) to 10 (hardest) Test by seeing if the mineral can scratch different objects (like human fingernail, copper, penny, glass, steel file) Properties of Minerals Mohs Hardness Scale Mineral Rating Testing Method Talc 1 Softest known mineral. It flakes easily when scratched by a fingernail. Gypsum Calcite 2 A fingernail can easily scratch it. 3 A fingernail cannot scratch it, but a copper penny can. Fluorite Apatite Feldspar 4 A steel knife can easily scratch it. 5 A steel knife can scratch it. 6 Cannot be scratched by a steel knife, but it can scratch window glass. Quartz Topaz Corundum Diamond 7 Can scratch steel and hard glass easily. 8 Can scratch quartz. 9 Can scratch topaz. 10 Hardest known mineral. Diamond can scratch all other substances. Find out more… “Electronic” Hardness Test http://www.childrensmuseum.org/geomy steries/cube/b2.html Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Luster Surface reflection metallic = shiny like metal non-metallic = dull, non-shiny surface Pyrite has a metallic luster Calcite has a non-metallic luster Specific Gravity or Density The specific gravity of a mineral is the ratio of its mass compared with the mass of an equal volume of water. Gold has specific gravity of 19 It means gold is 19 times heavier than water. 19 times heavier Density Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Streak The color of the powdered form of the mineral The color of the streak can be different than the mineral Minerals must be softer than the streak plate Streak…can help identify quartz http://www.childrensmuseum.org/geomysteries/cube/b3.html Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Cleavage & Fracture The way the mineral breaks Cleavage—minerals break along smooth, flat surfaces and every fragment has the same general shape Fracture—minerals that break at random with rough or jagged edges Cleavage Cleavage is the way that mineral breaks. Minerals that break along smooth, flat surfaces have cleavage. Mica has cleavage and Fracture!... Mineral that breaks uneven, rough, or jagged surfaces have fracture. Quartz has fracture quartz Identify the minerals below for cleavage and fracture CLEAVAGE FRACTURE in Physical Properties of Minerals (can be used to identify the mineral) Other Properties Specific gravity (*excellent clue to mineral’s identity) http://www.childrensmuseum.org/geomysteries/cube/b4.html Attraction to magnets Bending of light Reaction with hydrochloric acid Smell & taste An illustration appearance:luster,color and streak An illustration cleavage and fracture Watch Classifying Minerals Clip Watch Brainpop—“Mineral Identification” 1. If a mineral can scratch your fingernail, the mineral is _______________ than your fingernail. 2. What is luster?