Minerals:
advertisement
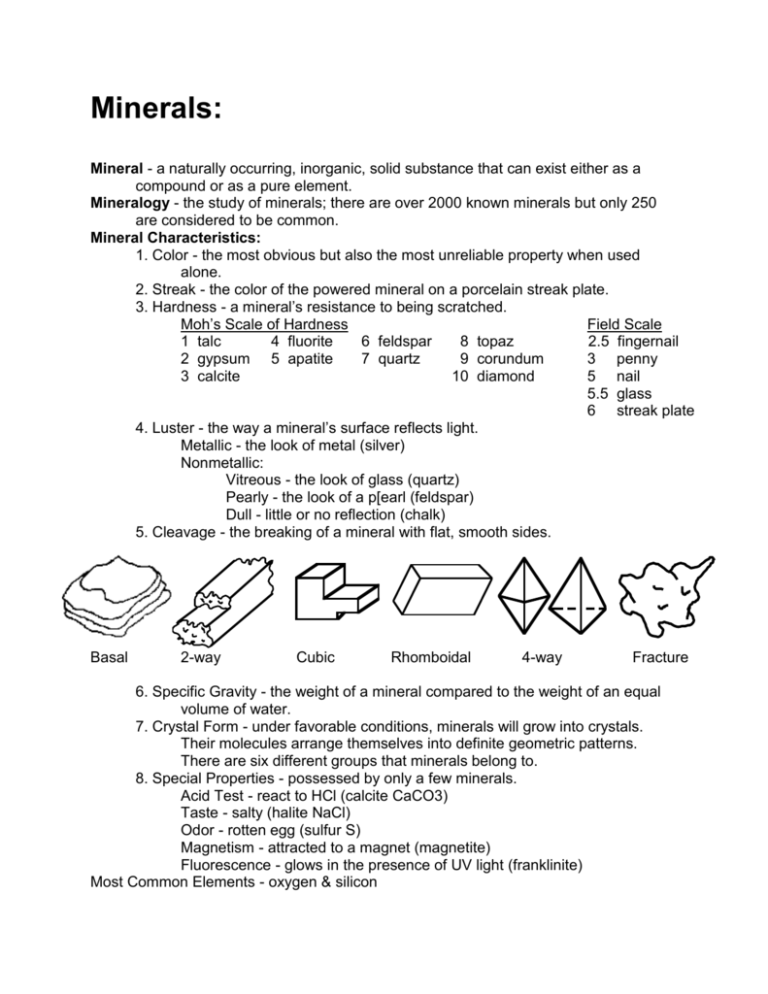
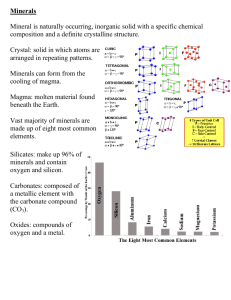
Minerals: Mineral - a naturally occurring, inorganic, solid substance that can exist either as a compound or as a pure element. Mineralogy - the study of minerals; there are over 2000 known minerals but only 250 are considered to be common. Mineral Characteristics: 1. Color - the most obvious but also the most unreliable property when used alone. 2. Streak - the color of the powered mineral on a porcelain streak plate. 3. Hardness - a mineral’s resistance to being scratched. Moh’s Scale of Hardness Field Scale 1 talc 4 fluorite 6 feldspar 8 topaz 2.5 fingernail 2 gypsum 5 apatite 7 quartz 9 corundum 3 penny 3 calcite 10 diamond 5 nail 5.5 glass 6 streak plate 4. Luster - the way a mineral’s surface reflects light. Metallic - the look of metal (silver) Nonmetallic: Vitreous - the look of glass (quartz) Pearly - the look of a p[earl (feldspar) Dull - little or no reflection (chalk) 5. Cleavage - the breaking of a mineral with flat, smooth sides. Basal 2-way Cubic Rhomboidal 4-way Fracture 6. Specific Gravity - the weight of a mineral compared to the weight of an equal volume of water. 7. Crystal Form - under favorable conditions, minerals will grow into crystals. Their molecules arrange themselves into definite geometric patterns. There are six different groups that minerals belong to. 8. Special Properties - possessed by only a few minerals. Acid Test - react to HCl (calcite CaCO3) Taste - salty (halite NaCl) Odor - rotten egg (sulfur S) Magnetism - attracted to a magnet (magnetite) Fluorescence - glows in the presence of UV light (franklinite) Most Common Elements - oxygen & silicon Most Common Mineral Group - silicates Most Common Minerals - feldspar & quartz (weather into clay and sand) Element / Minerals - gold, silver, sulfur, copper, platinum, carbon (diamond & graphite) Gem Requirements : 1. pretty 2. rare 3. hard