Proteins - Kaikoura High School
advertisement

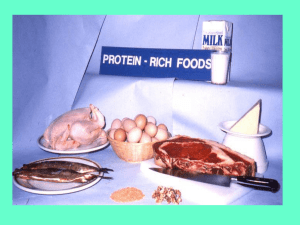
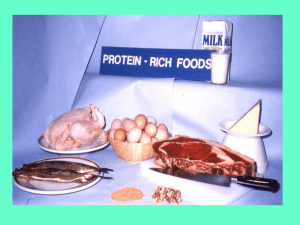
Proteins • Are the enzymes that catalyse all biochemical reactions in the body. • Are the structure of the body • Carry oxygen • Fight disease • Make up cell membranes • Are chemical messengers Structure of proteins • Are polymers • (note: often confusion over peptides, proteins and polypeptides = all are amino acid chains, difference is length.) • Units are amino acids (made up from 64 nucleotide combinations) • 20 different amino acids therefore some amino acids are specified by more than one codon. This is called degeneracy. This buffers against mutations as a single base change may not result in an affect • Are joined together by condensation • Some hydrophilic and some hydrophobic allowing proteins fold into specific shapes. • Fibrous proteins and globular proteins (long and stringy or round and ball like). • AUG is always the start signal • Stop signals always come at the end – UAA,UGA,UAG • Read amino acid tables for mRNA code: read left hand side, top and then right side. • • • • • So remember: DNA: ATG CTG AGG GGT TAT TAA TAC GAC TCC CCA ATA ATT mRNA: AUG CUG AGG GGU UAU UAA Don’t forget – U not T in RNA, read amino acid code from mRNA. Protein structure and Function • There are four levels of protein structure. • The final shape of the protein determines its function. • For enzymes, the shape is crucial for correct function. • Primary structure = order of amino acids • Secondary structure = how tight the coil or chain is • Tertiary structure = how the chains loop back on themselves again and again. • Quaternary structure = how separate protein molecules join to each other.