power point
advertisement
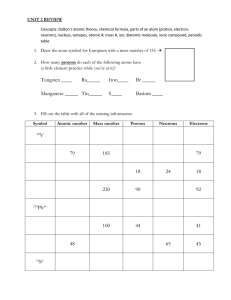
Atomic Structure Unit 4: Ch 18.1-2, 7.1, 9.1-2, 4 Geo Ch ?? Reading the Periodic Table Practice - Label this own on your own! What are different ways of identifying atoms? • Atomic Number: Equal to the number of protons (+) • Examples: •H=1 •C=6 •O=8 What are different ways of identifying atoms? • Mass Number: • Unit of measurement = amu (atomic mass unit) • 1 proton = 1 amu • 1 neutron = 1 amu • 1 electron = 0 amu (too light to count) • Reminder: Round to the closest whole number What are different ways of identifying atoms? MASS NUMBER = PROTONS + NEUTRONS or NEUTRONS = MASS NUMBER – ATOMIC NUMBER Example: How many neutrons are in U-236? Neutrons = 236 – 92 = 144 neutrons Determining Charge Electron = negative + -3 +3 =0 Proton = positive Practice – Determine charge on your own! Ions • The previous example had a charge • An atom that has a charge is called an ion • A positive ion = cation • A negative ion = anion Ion Symbols Atomic number (protons) = 3 Charge = +3 + -2 = +1 Element symbol = Li Ion symbol = Li+ Practice – Write ion symbol on your own! Making Ions • Changing number of neutrons = changing mass number • Changing number of protons = changing atomic number = different element • Changing number of electrons = making atom charge = ION! Isotopes • Atoms of the same element do not always have the same number of neutrons • These are called isotopes • The atomic number (number of protons) DOES NOT change • The mass number (protons plus neutrons) DOES change Mass number Atomic number Isotope Symbols Isotope Symbols 1. What is the element symbol? 2. What is the name of the element (find on periodic table)? 3. What is the atomic number? 4. What is the mass number? 5. How many protons does this element have? 6. How many neutrons does this element have? Practice- Answer these questions on your own! 1. What is the element symbol? 2. What is the name of the element (find on periodic table)? 3. What is the atomic number? 4. What is the mass number? 5. How many protons does this element have? 6. How many neutrons does this element have? Warm-Up Fill in the missing information: Element Boron Atomic Symbol B Number of Protons Number Number Mass of of Number Neutrons Electrons Isotope Symbol 5 Oxygen Element Atomic Number 18 Atomic Symbol Number of Protons Number of Electrons Atomic Number Ion Symbol N-3 Electric Charge, pg. 194-201 • • • • • • • • • • Can be positive (protons) Can be negative (electrons) When they are even, the atom is neutral. Some atoms hold their electrons more tightly than others. To become positively charged, atoms must ____ electrons. To become negatively charged, atoms must ____ electrons. Law of Conservation of Charge Charge, force, distance relationship? Conductors vs Insulators Charge by contact vs Charge by induction Check for Understanding 1. How do you make an object positively charged? 2. How do you make an object negatively charged? 3. What are two ways to charge an object? (Hint: charging by ___ or ___.) 4. What happens to two positive charges brought near each other (attract/repel)? 5. What happens when a positive and negative are brought near each other (attract/repel)? 6. If two charges are brought closer together, what happens to the force? 7. If one charge is increased, what happens to the force? 8. State the law of conservation of charge. Warm-Up 1. What do these picture make you think of? Write down as many things as you can! Nuclear Fission • Fission and Fusion Video • Fission means “to divide” • The process of splitting a nucleus into two nuclei with smaller masses • This occurs when a neutron hits the nucleus of an atom • Only large nuclei can underdo fission reactions • The total mass of the products is slightly less than the mass of the original nuclear and the neutrons that break free • The missing mass is converted into large amounts of energy Nuclear Fission Lighter element Neutrons Neutron + Energy Uranium - 235 Lighter element Nuclear Fission • The free neutrons released from the original nucleus hit other atoms and cause a chain reaction energy energy energy energy energy energy Nuclear Fusion • The process of combining two low mass nuclei into one larger mass nucleus • On the Sun, this process occurs using hydrogen nuclei • Overall, 4 hydrogen atoms fuse to form one helium • Just like in fission, a small amount of mass is converted into a large amount of energy Nuclear Fusion positron energy neutrino positron energy neutrino Energy to Mass Conversions • Think back to the law of conservation of energy • We need to include mass in this law when talking about fission and fusions reactions • This relationship is shown by Einstein’s theory of relativity • This states that energy and mass are equivalent and can be converted using the equation E=mc2 Warm-Up 1. What type of nuclear reaction shown below? 2. Write an equation for the reaction. You only need to include the symbol and mass number. 3. What type of nuclear reaction is shown below? Radiation • When a nucleus becomes unstable, it decays releasing particles and energy called nuclear radiation • Radiation comes from radioactive isotopes, or radioisotopes • The release of radiation is called decay • Some radiation is more powerful than others • There are three types of nuclear radiation – • alpha (α) – made of 2 p= and 2 n0 • beta (β) – n0 decays into p= and e- (beta particle) • gamma (γ) – no mass or charge, just energy Radiation, continued • Alpha particles • Large • Cannot pierce deep into matter – easily stopped by thin layer of material • Beta Particles • beta particle (small, light, fast) • Can only be stopped by thick materials, like stacked sheets of metal, blocks of wood or heaving clothing • Gamma Radiation • Travels in waves as electromagnetic radiation (or light) • Can pass through most types of materials – need a material thicker than blocks of concrete Types of Radioactive Decay Radiation, continued Particle Type Symbol Mass Charge Alpha Beta 4 2He or α 4 +2 Gamma β 0.0005 -1 γ 0 0 Radiation, continued • Half-life • The amount of time it takes for half of the nuclei of a radioactive isotope to decay • The original substance is called the parent • The new substance is called the daughter Warm-Up 1. What is the electron that is produced when a neutron decays called? (choose from: alpha particle/beta particle/gamma radiation) 2. What is a helium nucleus with two protons and two neutrons called? (choose from: alpha particle/beta particle/gamma radiation) 3. How many half-lives have passed when 1/16 of the parent material remains? 4. What happens to the atomic number and mass number when a beta particle is emitted? 5. What happens to the atomic number and mass number when an alpha particle is emitted? Warm-Up 1. 2. 3. 4. What is fusion? What is fission? What is radiation/radioactivity? Where does the energy produced in fission and fusion reactions come from?