Chapters 16-18 vocab
advertisement

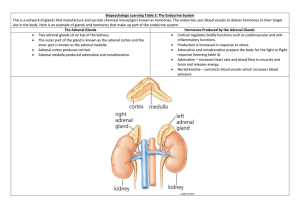
Vocabulary Chapter 16-18 DH 111 Islets of Langerhans: regions of the pancreas that contains its hormone producing cells Fetal macrosomia: Big baby syndrome, primary risk factor is poorly controlled gestational diabetes. Increased in maternal plasma glucose levels as well as insulin stimulated fetal growth. Hyperbilirubinemia: when a newborn’s liver is not able to properly process the bilirubin causing jaundice. Bilirubin: produce in liver, produced when the liver breaks down red blood cells. A brownish yellow substance in the bile that is excreted from the body in feces. Microangiopathic: high blood glucose levels cause the lining of the blood vessels to take in more glucose than normal. Walls of the vessels become thick but weak, they may bleed or leak proteins and slow the flow of blood through the body Gangrene: when a mass of body tissue dies (necrosis). Primary cause is reduced blood supple to the affected tissue resulting in cell death Lichen planus: disease that presents itself in the form of papules, lesions or rashes. In the mouth it looks like white lacy streaks on the gingival, tongue, palate or lips Candidiasis: thrush, fungal infection caused by yeasts Adrenal glands: endocrine glands that sit at the top of the kidneys. Responsible for releasing hormones in response to stress through the synthesis of cortisol and epinephrine and norepinephrine and produce androgens. Adrenal glands affect kidney function through the secretion of aldosterone Endocrine glands: part of the endocrine system (system of glands, each secreting different types of hormones directly into the bloodstreen) that secrete hormones directly into blood rather than through a duct. Medulla: part of the adrenal gland located at the center of the gland surrounded by the adrenal cortex. Innermost part of the adrenal gland with cells that secrete epinephrine and norephinephrine. Adrenal medulla increases energy, heart rate and metabolism. Adrenal cortex: surrounds adrenal gland, mediates the stress response through production of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, including aldosterone and cortisol. Cortisol: steroid hormone- glucocorticoid- releases when body is stressed and there is a low level of blood glucocorticoids Aldosterone: steroid hormone- produced by adrenal cortex, causes conservation of sodium secretion of potassium, increased water retention, increased blood pressure. Addison’s disease: endocrine disorder where the adrenal glands do not produce enough steroid hormone. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): also known as a corticotrophin. Produced in response to stress. Effects- increased production and release of corticosteroids. Atrophy: partial or complex wasting away of a part of the body. Can be caused by poor nourishment, poor circulation, and loss of hormonal support. Aguanulocytosis: severe and dangerous lowered white blood cell count, patient is at a high risk for infection Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver Hypoparathyroidism: decreased function of parathyroid glands, leads to low calcium causing tetany Hypothermia: core body temperature drops below a level for normal metabolism for normal body functions Exophthalmoses: bulging of the eye out of the orbit Macroglossia: unusual enlargement of the tongue Ptosis: drooping of upper or lower eyelids Periorbital edema: puffy eyes or swelling around the eyes