File
advertisement

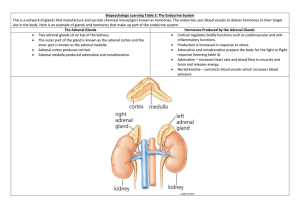
To know about communication within the body Outline the need for communication systems within multi-cellular organisms State that cells need to communicate with each other by cell signalling State examples of cell signalling Define key terms Describe secondary messenger systems Describe the functions of the adrenal glands What conditions do you need to consider for efficient enzyme action? Internal Changes External Changes Co-ordinate activities of different organs Endocrine gland Exocrine gland Hormone Target Tissue Endocrine Secretes hormones directly into the blood Exocrine gland gland Secretes molecules into a duct which carries them to where they are used Hormone Molecules released by endocrine glands directly into blood. Act as messengers carrying signal from endocrine gland to target tissue Target Tissue Possess specific receptor on their plasma membrane. Shape of receptor is complementary to the shape of the hormone molecule. Cell Nervous System Signalling Neurones & Synapses Rapid Hormonal System Hormones carried in blood Only recognised by target cells Longer term responses Draw round a member of your group Cut out the different glands and place them where you think they are in the body Label them Task: One person will describe what they see The other person will draw Task: each draw labelled diagram of cAMP Adrenal Responds to stress e.g. pain or shock Widespread effect as most cells have receptors for adrenaline Adrenal Medulla Cortex Makes steroid hormones Task: use p23 to add 2 specific examples of the roles of AM & AC Plenary Adrenaline binds to receptor on target cell Adrenaline first messenger Adrenaline can’t enter the cell Changes shape of Adenyl cyclase inside cell Activates adenyl cyclase Changes ATP into cAMP cAMP second messenger cAMP activates enzyme in the cell See print out of page 10