The Endocrine system
advertisement

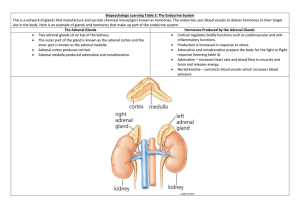
Ch 18 Lesson 1 A system in your body that is made up of glands that secrete hormones to help regulate many of the body functions Especially important during the teen yearshelps regulate growth and development Endocrine glands- ductless, or tubeless organs or group of cells that secrete hormones directly into the blood stream Hormones- chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of your body’s functions Pituitary Gland- one of the most important glands because it regulates and controls all the other endocrine glands “master gland” Hypothalamus- links endocrine system with nervous system, tells Pituitary gland what to do Thyroid- regulates metabolism, body heat, and bone growth Gonads- ovaries and testes, male and female reproductive glands Pancreas- regulates level of blood glucose Adrenal- control body’s emergency response, regulates salt and water balance Divided into three sections; anterior, intermediate, and posterior Anterior (front)- stimulates normal body growth and development, stimulates the thyroid to produce hormones, stimulates production of hormones in the adrenal glands, controls growth, development, and function of the gonads Intermediate (middle)- controls darkening of the skin Posterior (rear)- regulates the balance of water in the body Helps the body recover from stress and respond to emergencies Adrenal Cortex- secretes hormone that inhibits amount of sodium excreted in urine and serves to maintain blood volume and pressure, aids in metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates Adrenal Medulla- secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine which increase heart beat and respiration, raises blood pressure, and suppresses digestive process during periods of high emotion Produces hormones that regulate metabolism Located in the front of the throat, shaped like a butterfly Produces Thyroxine, which regulates the way cells release energy from nutrients Diabetes mellitus- disorder in which the pancreas produces too little or no insulin, resulting in high blood glucose levels Graves Disease- hyperthyroidism overactive thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroxine Cushing’s Disease- overproduction of adrenal hormones; symptoms round face, humped upper back, thin and easily bruised skin Goiter- enlarged thyroid gland, caused mainly by lack of iodine in diet Growth Disorder- abnormal amounts of growth hormone, with early diagnosis and proper treatment a child can reach normal height