blood sugar level - RMC Science Home
advertisement
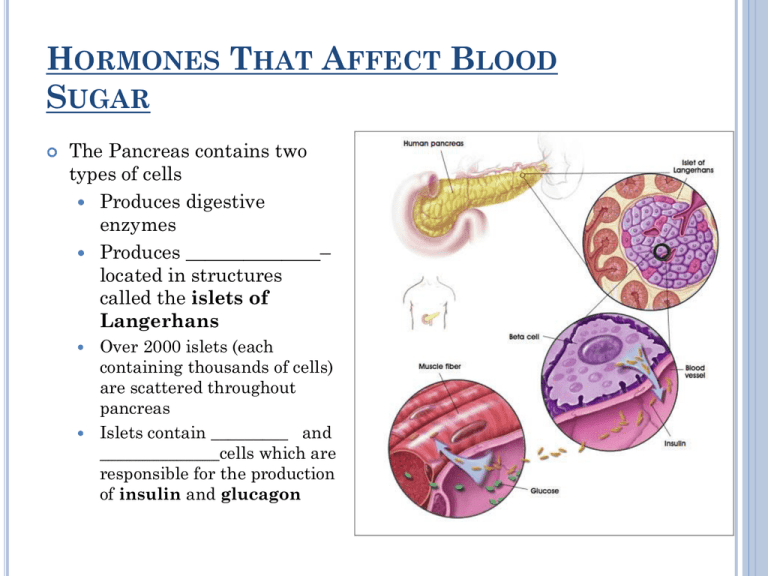
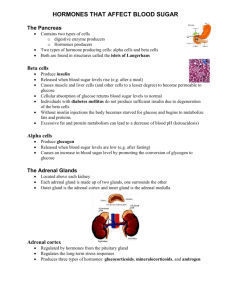
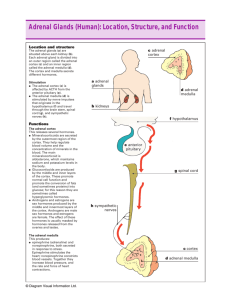
HORMONES THAT AFFECT BLOOD SUGAR The Pancreas contains two types of cells Produces digestive enzymes Produces ______________– located in structures called the islets of Langerhans Over 2000 islets (each containing thousands of cells) are scattered throughout pancreas Islets contain _________ and ______________cells which are responsible for the production of insulin and glucagon Endocrine System Control Feedback REGULATION OF BLOOD SUGAR islets of Langerhans insulin beta islet cells body cells take up sugar from blood liver stores glycogen high blood sugar level (90mg/100ml) low triggers hunger liver releases glucose islets of Langerhans glucagon alpha islet cells reduces appetite STORING AND RELEASING GLUCOSE! Insulin released when blood sugar levels ________ insulin causes cells of muscles, liver, and other organs to become _________________to glucose. Liver converts glucose to _____________________________ Insulin causes ____________________in blood sugar level Glucagon causes _________________in blood sugar level (released when blood sugar levels are _____, promotes conversion of glycogen to ____________. GREAT CANADIANS! Dr. Charles ________ and Dr. Frederick _____________________ 1923 Nobel Prize for the discovery of ________________(Best was excluded!!) Did not profit from the discovery...unheard of today! ADRENAL GLANDS Located above each _______________________ Inner gland – adrenal _____________________ medulla surrounded by outer casing (adrenal cortex), regulated by the _____________________________________ hormones regulate the adrenal cortex Adrenal medulla produces ___________hormones (produced when cells within adrenal medulla are stimulated by sympathetic nerves in times of __________________. _____________________________ _____________________________ FIGHT OR FLIGHT!! These two hormones initiate fight-or-flight biological responses blood sugar level _______________________ glycogen converted to _____________________ ensures greater energy reserve available increase _______________and __________________ rates as well as cell metabolism blood vessels _____________________= allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach tissues irises ___________________________ ADRENAL CORTEX Stimulated by _______________________________ Produces ___________different types of hormones ___________________________ ____________________________ one of the most important - ____________________, increases level of _______________________in blood and helps in recovery of stress by being converted to _________________ in liver, supplying more ______________________needed for repair or recovery by cells or participating in protein synthesis Salt and water balance – ALDOSTERONE! ____________________________ Small amounts! LONG TERM STRESS RESPONSE hypothalamus sends hormone to ___________________lobe of pituitary stimulates pituitary to secrete corticotrophin (adrenocorticotropic hormone; ___________) blood carries ACTH to target cells in ___________ cells of adrenal cortex secrete mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids (one of which is ____________) these are carried to target cells in _____________ and _______________________ as cortisol levels rise, hypothalamus and pituitary production of _______________hormones ______________________ eventually cortisol levels begin to ____________ SHORT TERM STRESS RESPONSE regulated by adrenal ________________________ epinephrine & norepinephrine _________________________________is one of most important mineralocorticoids increases ______________________retention and ____________________reabsorption by kidneys