the endocrine system - Madison County Schools
advertisement

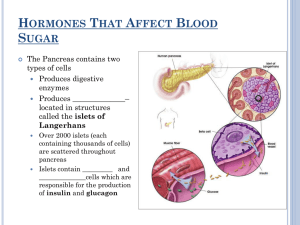
Where they are. What they do. What hormones they produce. The hypothalamus gland has a very important job — to connect the nervous system with the endocrine system. He’s a real smooth operator and releases the hormone oxytocin, which plays a role in what you feel when you’re in love. He works from deep inside your brain to make hormones that make other glands make hormones. He even controls the so-called “master gland,” the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus also has a hand in regulating body temperature, hunger, thirst, fatigue, and anger. He’s kind of a big deal. Even though the pituitary is just a tiny little peasized nubbin hanging out at the base of your brain, he is known as the master gland because he controls all of the other endocrine glands (however, he is controlled, in turn, by the hypothalamus). His main functions include stimulating growth, regulating blood pressure, sex hormones, metabolism and water regulation. He’s one busy fella. Whether you’re a couch potato or a marathon runner, the thyroid tells the body how fast to go. It makes thyroxin. From the front of the neck, this gland serves as the body’s gas pedal, deciding how much energy to burn. It’s metabolism central, baby. Ultrasound Image Chronic Fatigue Weight Gain Puffy Face Droopy Eyelids Depression Slow Reflexes Muscle Aches, Cramps, or Weakness Decreased Sex Drive Excessive Menstrual Bleeding Premenstrual Tension Absence of Periods Loss of Appetite Constipation Memory Loss Difficulty Concentrating Dry, Itchy Skin Diarrhea Goiter Palpitations Nervousness Restlessness Flushing Heat Intolerance Hand Tremor Sweating Fast Heart Rate Increased Heart Rhythms Protruding Eyes Moist Skin Menstrual Irregularity Unintentional Weight Loss Fatigue High Blood Pressure Hair Loss General Weakness Increased Appetite Difficulty Sleeping Involuntary Movements Clammy Skin Infrequent Periods Breast Enlargement in Men No Menstrual Period Motor Tic Flushed Complexion Loss of Part of Visual Field Coronal view Sagital view Hyperthyroid Jungle Michael Beckerman 2003 Acrylic on canvas An important part of the body’s immune system, the thymus gives infectionfighting cells — called T-cells after the thymus — a nice place to live while they grow up and get ready to fight. Don’t be immune to his charms. The parathyroid glands secrete a hormone that tells the body how to divvy up calcium between the bones and the blood. They hang out on the back of the thyroid gland in the neck area, but rumors about a relationship between the two are just that — they’re just friends. The adrenal glands sit atop your kidneys and work with the hypothalamus and pituitary glands to regulate metabolism and immunity. Most famously, the adrenal glands squish out the hormone adrenaline, which controls the body’s “fight or flight” response by speeding up your heart rate and otherwise pumping you up. Relax — don’t do it. Fight or Flight When this state of emergency is maintained for extended periods of time, weakening the immune system, causing interrupted sleep, exhaustion, kidney abnormalities, lower blood sugar and even hypothyroidism. Common Causes Of Adrenal Stress: Physical trauma Chemical toxins Poor diet / Digestion issues Excess exercise Lack of sleep Infections Emotional trauma Anxiety, depression Prescription drugs (Many) Pregnancy Stress what can i do? Treatment for adrenal fatigue includes lifestyle modifications, diet, rest and supplementation. Simple changes including: breaks to rest, regular meals, light exercise and stretching, early bedtimes and sleeping more, and laughter (increases the parasympathetic supply to the adrenals) can help support the healing process of the adrenal glands. The pancreas is a cute little organ nestled between the bottom of the stomach and the top of the small intestine. This little guy produces digestive enzymes, but he is best known for producing the hormone insulin. We need insulin to help us process glucose from the blood stream. Say pancreas in Japanese: suizou! CAUSES: Too little food, too much insulin or diabetes medicine, or extra exercise. ONSET: Sudden, may progress to insulin shock. SUGAR: Below 70 mg/dL. Normal range: 70-115 mg/dL WHAT CAN YOU DO? Drink a cup of orange juice or milk or eat several hard candies Test Blood sugar Within 30 minutes after symptoms go away, eat a snack CAUSES: Too much food, too little insulin, illness or stress. ONSET: Gradual, may progress to diabetic coma. BLOOD SUGAR: Above 200 mg/dL. Normal range: 70-115 mg/dL WHAT CAN YOU DO? Test blood sugar If over 250mg/dL for several tests, CALL YOUR DOCTOR! Protected by the scrotum, these family jewels produce sex hormones and sperm. Testosterone makes the man, helping sperm find and fertilize those lady eggs. Sperm is the swimming cell responsible for fertilizing the egg. Absolutely nuts! Testicular cancer is the most common solid tumor diagnosed in men between the ages of 15 and 35. However, it is a relatively rare type of cancer, which accounts for only about 1 percent of all cancers in men. The American Cancer Society estimates that approximately 8,000 new cases of testicular cancer will be diagnosed in the United States this year. Advances in treatment mean that most men with testicular cancer, especially those diagnosed when the cancer is at an early stage, can now expect to survive the disease. In fact, the cure rate for all stages and types of testicular cancer combined is higher than 90 percent. The ovaries produce eggs and release sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, which control all kinds of female reproductive mayhem from period regulation to babymaking. Attached to the uterus, the two ovaries take turns releasing eggs down the fallopian tubes for possible fertilization. It’s the gland of the ladies. Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in women. It is idiopathic, meaning that the exact cause is usually unknown. The disease is more common in industrialized nations, with the exception of Japan. In the United States, females have a 1.4% to 2.5% (1 out of 40-60 women) lifetime chance of developing ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer usually produces no specific signs or symptoms in the early stages. However, if symptoms such as bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, or urinary symptoms (urgency or frequency) continue for several days, you should consult with a healthcare professional. Ovarian cancer is usually diagnosed with a pelvic examination and transvaginal ultrasound (an imaging procedure that uses a special imaging wand inserted into the vagina to identify tumors).