hormones that affect blood sugar - Glebe
advertisement

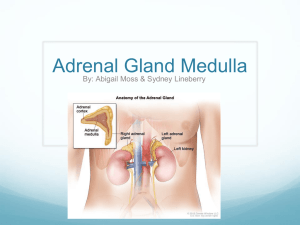
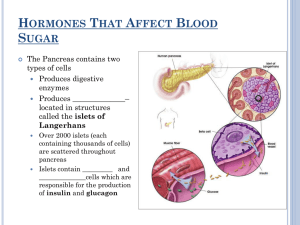
HORMONES THAT AFFECT BLOOD SUGAR The Pancreas Contains two types of cells o digestive enzyme producers o Hormones producers Two types of hormone producing cells: alpha cells and beta cells Both are found in structures called the islets of Langerhans Beta cells Produce insulin Released when blood sugar levels rise (e.g. after a meal) Causes muscle and liver cells (and other cells to a lesser degree) to become permeable to glucose Cellular absorption of glucose returns blood sugar levels to normal Individuals with diabetes mellitus do not produce sufficient insulin due to degeneration of the beta cells Without insulin injections the body becomes starved for glucose and begins to metabolize fats and proteins Excessive fat and protein metabolism can lead to a decrease of blood pH (ketoacidosis) Alpha cells Produce glucagon Released when blood sugar levels are low (e.g. after fasting) Causes an increase in blood sugar level by promoting the conversion of glycogen to glucose The Adrenal Glands Located above each kidney Each adrenal gland is made up of two glands, one surrounds the other Outer gland is the adrenal cortex and inner gland is the adrenal medulla Adrenal cortex Regulated by hormones from the pituitary gland Regulates the long-term stress responses Produces three types of hormones: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgen Glucocorticoids: Group of hormones that help control blood glucose levels Cortisol: An important glucocorticoid that acts as an antagonist to insulin and helps the body restore homeostasis after stress o Causes gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose – the reverse of glycolysis) and the breakdown of lipids and proteins o Increases blood glucose levels and causes the formation of glycogen by the liver o Lowers the activity of the immune system Mineralocorticoids: Hormones used to regulate the salt-water balance Aldosterone: A mineralocorticoid that increases sodium retention and water reabsorption by the kidneys o Helps to maintain body fluid levels and raise blood pressure Adrenal medulla Regulated by the nervous system Regulates the short-term stress responses Produces two hormones: epinephrine (i.e. adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Adrenal medulla is stimulated during times of stress Effects of the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood: o Blood sugar rises o Glycogen is converted into glucose o Heart rate, breathing rate, and cell metabolism increase o Blood vessels dilate (allowing more oxygen to reach the tissues) o Pupils dilate Response to Stress Long-term stress Brain identifies stressful situation Hypothalamus sends a releasing hormone to the anterior lobe of the pituitary Pituitary secretes adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) into blood ACTH is carried to target cells in the adrenal cortex Adrenal cortex secretes mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids (including cortisol) which are carried to target cells in the liver, muscles, and kidneys High cortisol levels signal the cells in the hypothalamus and pituitary to decrease production of stress hormones o Negative feedback causes the eventual fall of cortisol levels Short-term stress Hypothalamus sends a nerve signal to adrenal medulla Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine