File
advertisement
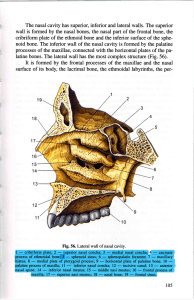
Axial Skeleton Bones of the Skull 1) FRONTAL FOREHEAD 2) PARIETAL Means “wall bone” Meet at midline of skull 3) TEMPORAL Bone AT TEMPLES Connects with the mandible (lower jaw bone) 4) OCCIPITAL BACK OF SKULL where the *FORAMEN MAGNUM (large hole) is which the spinal cord goes through 5) Sphenoid Forms floor of cranial cavity (butterfly shaped) Forms back and side of orbit (eye socket) 6) Ethmoid Forms top of nasal cavity and is between the two orbits 7) NASAL Form bridge of nose 8) MAXILLA Two bones that are fused to form upper jaw; carry teeth 9) PALATINE Lie posterior to the palatine process of the maxillae; Form posterior part of hard palate (when palatine processes don’t fuse medially = cleft palate) 10) MANDIBLE Lower jaw; largest and strongest bone of face Joins temporal bones to form the only freely movable skull joints 11) ZYGOMATIC Cheekbones Major part of the lateral walls of the orbits 12) LACRIMAL Form medial walls of each orbit Each bone has groove that is a passageway for tears (lacrima = tear) 13) VOMER Single bone in the median line of the nasal cavity Forms most of nasal septum 14) INFERIOR NASAL CONCHAE Thin curved bones that project from lateral walls of nasal cavity (superior and medial conchae are considered part of ethmoid bone) Frontal/Coronal Suture Between the frontal bone and the parietal bones Lambdoid Suture Between the parietal and occipital bones Sagittal Suture Between the 2 parietal bones Squamous Suture Between the parietal bone and the temporal bone