CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
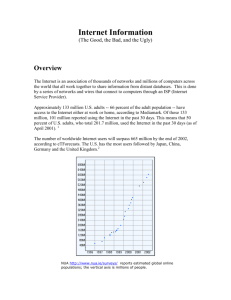
Retirement Planning & Employee Benefits
Session 7
NUA Fundamentals and
Keogh Contributions
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Session Details
Module(s) 3
Chapter(s) 5, 9
LOs
3-5
3-9
Describe the basic characteristics of stock
bonus plans. *This session will cover the
essentials of Net Unrealized Appreciation.
Describe the basic characteristics of a Keogh
plan, and calculate the owner’s contribution
amount.
7-2
Net Unrealized Appreciation (NUA)
• NUA treatment is available for any employer
•
•
stock distributed from a qualified plan
Stock bonus, ESOPs, 401(k) profit sharing, are
all qualified plans, so the NUA rules would apply
An advantage of NUA is that
it is taxed as a long-term
capital gain, not as
ordinary income
7-3
NUA Example
Josephine, age 53, takes a distribution on March 1, 2015, of 3,000
shares of company stock. Her cost basis is $65,000 (the amount of
employer contributions) and the stock is worth $255,000 when
distributed. She sells all 3,000 shares on July 15, 2015, for
$270,000.
Ramifications are:
o $65,000 taxed as ordinary income,
and subject to 10% penalty tax
o $190,000 NUA taxed as a long-term
capital gain
o $15,000 additional gain taxed as
a short-term capital gain (if held
for more than one year from
distribution date, then any
additional gain would be long-term)
7-4
NUA Example
401(k) account balance
$300,000
Company stock ($10,000 basis) taken as a taxable
distribution in kind1
$100,000
Other assets rolled over to Traditional IRA
$200,000
Taxed as ordinary income when received
$10,000
Taxed as long-term capital gains when stock is sold
$90,000
Taxed as ordinary income when withdrawn from
IRA2
1
2
$200,000
Does not consider the possibility of early distribution penalties.
Assumes no increase in value.
7-5
NUA Tax Implications
Income Tax Bracket1
Value
25%
35%
Tax on company cost basis
$10,000
$2,500
$3,500
Tax on NUA Gain2 (15%)
$90,000
$13,500
$13,500
$200,000
$50,000
$70,000
$66,000
$87,000
$75,000
$105,000
$9,000
$18,000
Tax on IRA Rollover when withdrawn3
Total Income Tax
Tax when withdrawn if entire amount rolled
over to an IRA
$300,000
NUA income tax savings
1
2
3
State and local income taxes are not considered
Assumes securities are sold at the distribution price
Assumes no increase in value
7-6
Keogh Plans—Basic Provisions
• Available only to unincorporated businesses—
•
•
sole proprietor or partnership
Takes the form of a qualified plan (defined
contribution or defined benefit)
Certain provisions for owner/employee are
unique to Keoghs:
o Owner/employee’s contribution is calculated on
net earnings
o Lump-sum distribution treatment is not available
to owner/employee for separation from service
before age 59½—available only for death,
disability, or attainment of age 59½
7-7
Calculation of Maximum Deduction for Keogh Plan Contribution
Step 1: Calculate self-employment tax
Schedule C net profit (business profit)
$100,000
Less 7.65% of self-employment income
($7,650)
Self-employment income subject to self-employment taxes
$92,350
Times 15.3% equals self-employment tax
$14,129.55
7-8
Calculation of Maximum Deduction for Keogh Plan Contribution
Step 2: Determine adjusted contribution
percentage for owner
Percentage contribution for employee participants
(employee percentage)
Divide by 1 plus employee percentage
Equals adjusted contribution percentage for owner
.25
1.25
.20
7-9
Calculation of Maximum Deduction for Keogh Plan Contribution
Step 3: Multiply net earnings by adjusted
contribution percentage
Schedule C net profit
$100,000
Less income tax deduction (1/2 self-employment tax)
$7,064.78
Net earnings
Times contribution percentage for owner
Owner’s contribution for his own benefit
$92,935.23
.20
$18,587.05
7-10
Practice Problem
Jane Momeyer is a financial planner who grossed
$200,000 this year. Her expenses including the
plan contribution for her staff were $130,000. Her
profit sharing contribution for her staff was 10% of
compensation. How much can she contribute to
the profit sharing plan for her own account?
7-11
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Retirement Planning & Employee Benefits
Session 7
End of Slides
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.