Introduction to Anatomy
advertisement

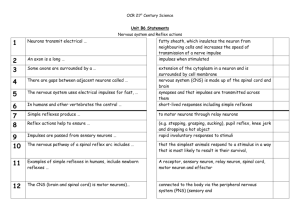
Spinal Cord A. Spinal cord anatomy 1. Protection and coverings a. Vertebral column b. Meninges 2. External anatomy of the spinal cord 3. Internal anatomy of the spinal cord B. Spinal cord physiology 1. Reflexes 2. Reflex arc and homeostasis a. Physiology of the stretch reflex b. Physiology of the flexor (withdrawal) reflex and crossed extensor reflexes C. Spinal nerves 1. Composition and coverings 2. Distribution of spinal nerves 3. Dermatomes The Spinal Cord 1. 2. 3. 4. is continuous with brain mediates spinal reflexes is site for integration provides the pathways Protection and Coverings 1. vertebral canal 2. meninges 3. cerebrospinal fluid Meninges and Spaces 1. epidural space 2. dura mater 3. subdural space 4. arachnoid membrane 5. subarachnoid space 6. pia mater -- denticulate ligaments External Anatomy 1. cylindrical 2. flattened A-P 3. foramen magnum to L2 4. differential growth 5. cervical enlargement 6. lumbar enlargement 7. conus medullaris 8. filum terminale 9. cauda equina 10. functional segments GROSS ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD Internal Anatomy 1. 2. 3. 4. gray matter white matter gray commissure central canal Gray Matter 1. nuclei 2. horns a. dorsal -- sensory b. ventral -- motor c. lateral -- autonomic Spinal Nerve Roots 1. dorsal root (axons of sensory neurons) -- dorsal root ganglion (cell bodies of sensory neurons) 2. ventral root (axons of motor neurons) Dorsal roots Dorsal root ganglion Ventral roots White Matter 1. columns a. anterior b. posterior c. lateral 2. tracts a. ascending b. descending Posterior columns Lateral columns Lateral columns Anterior columns Tracts of the Spinal Cord Terminology Review The Spinal Cord Has Two Essential Functions 1. convey impulses between the periphery and the brain 2. provide integrating centers for spinal reflexes Reflexes are… 1. inborn 2. unlearned 3. unconscious Somatic Reflexes Versus Visceral Reflexes Somatic reflexes involve the somatic nervous system. Visceral reflexes involve the autonomic nervous system. Reflex Arc 1 3 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. receptor sensory neuron integration center motor neuron effector sensory receptor center of integration with association neuron 3 center of integration with association neuron 2 sensory (afferent) neuron sensory receptor 2 sensory (afferent) neuron motor (efferent) neuron 4 motor (efferent) neuron effector 4 5 effector 5 THE REFLEX ARC AS A FEEDBACK SYSTEM CONTROLLED CONDITION A stimulus or stress disrupts membrane homeostasis by altering some controlled condition RETURN TO HOMEOSTASIS The action of the effector returns the body process to within its normal homeostatic range RECEPTOR The receptors in a reflex are sensory neurons associated with a receptor device (transducer) and which relay nerve impulses to a central control center CONTROL CENTER The control center is an integrating center of neurons in the CNS. It relays the information to motor neurons EFFECTORS The motor neurons initiate some response by an effector (muscle or gland) to counteract the stimulus that originally disrupted homeostasis Reflex arc Stretch Reflex 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. monosynaptic muscle spindle muscle tone ipsilateral reciprocal innervation The Flexor and Crossed Extensor Reflex Intersegmental Polysynaptic Ipsilateral Pain receptor Role of association neurons Reciprocal innervation Intersegmental Polysynaptic Contralateral Pain receptor Role of association neurons Reciprocal innervation excitatory neurons inhibitory neurons