Retailers
advertisement

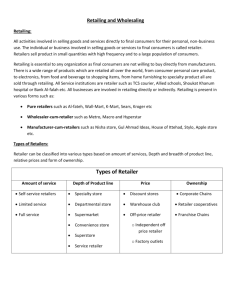
A Global Perspective Philip Kotler Gary Armstrong Swee Hoon Ang Siew Meng Leong Chin Tiong Tan Oliver Yau Hon-Ming 13 Retailing and Wholesaling PowerPoint slides adapted by Oliver Yau Hon-Ming 13-1 Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Explain the roles of retailers and wholesalers in the distribution channel 2. Describe the major types of retailers and give examples of each 3. Identify the major types of wholesalers and give examples of each 4. Explain the marketing decisions facing retailers and wholesalers 13-2 Chapter Outline 1. Retailing 2. Wholesaling 13-3 Retailing • Retailing includes all the activities in selling products or services directly to final consumers for their personal, non-business use. • Retailers are businesses whose sales come primarily from retailing. 13-4 Retailing • Non-store retailing includes selling to final consumers through: • Direct mail • Catalogs • Telephone • Internet • TV shopping • Home and office parties • Door-to-door sales • Vending machines 13-5 Retailing Types of Retailers • Classified in terms of • Amount of service • Product lines • Relative price 13-6 Retailing Types of Retailers • Amount of service • Self-service • Limited service • Full service 13-7 Retailing Amount of Service • Self-service retailers serve customers who are willing to perform their own locatecompare-select process to save money. • Wal-Mart • Supermarkets 13-8 Retailing Amount of Service • Limited service retailers provide more sales assistance because they carry more shopping goods about which customers need more information. • Sears, Sasa, etc. • JC Penney 13-9 Retailing Amount of Service • Full-service retailers assist customers in every phase of the shopping process, resulting in higher costs that are passed on to the customer as higher prices. • Department stores • Specialty stores 13-10 Retailing Types of Retailers: Amount of Service • Specialty stores carry narrow product lines with deep assortments within the product lines. • Department stores carry a wide variety of product lines. • Convenience stores carry a limited line of high-turnover convenience goods. 13-11 Retailing Types of Retailers: Amount of Service • Superstores offer a large assortment of routinely purchased food products, non-food items, and services. • Supercenters have very large combination food and discount stores. 13-12 Retailing Types of Retailers: Amount of Service • Category killers are large stores that carry a very deep assortment of a particular line with knowledgeable staff. • Service retailers’ product lines are actually service. 13-13 Retailing Types of Retailers: Relative Prices • Discount stores • Off-price retailers • Factory outlets • Warehouse clubs 13-14 Retailing Types of Retailers: Relative Prices • Discount stores sell standard merchandise at lower prices by accepting lower margins and selling higher volume. • Off-price retailers buy at less than regular wholesale prices and charge customers less than retail. • Independent off-price retailers are either owned and run by entrepreneurs or are divisions of larger retail corporations. 13-15 Retailing Types of Retailers: Relative Prices • Factory outlets are producer-operated stores. • Warehouse clubs are large, warehouse-like facilities with few frills and offer ultra-low prices. © Joe Bennett 13-16 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Corporate chain stores • Voluntary chain stores • Retailer cooperatives • Franchise organizations • Merchandising conglomerates 13-17 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Corporate chains are two or more outlets that are commonly owned and controlled. • Size allows them to buy in large quantities at lower prices and gain promotional economies. • Sears • Watsons 13-18 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Voluntary chains are wholesale-sponsored groups of independent retailers that engage in group buying and common merchandising. • IGA • Lukfook Jewellery 13-19 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Retailer cooperative is a group of independent retailers that band together to set up a jointly-owned, central wholesale operation, and to conduct joint merchandising and promotion efforts. • Mitre 10 • Associated Grocers 13-20 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Franchise organizations are based • On some unique product or service • On a method of doing business • On the trade name, good will, or patent that the franchisor has developed • McDonald’s, Pizza Hut, etc. 13-21 Retailing Types of Retailers: Organization Approach • Merchandising conglomerates are corporations that combine several retailing forms under central ownership. • Limited Brands 13-22 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions • Target marketing and positioning • Product assortment and services • Price • Promotion • Place 13-23 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions • Target market and positioning involves the definition and profile of the market so the other retail marketing decisions can be made. • Product assortment and service decisions include: • Product assortment • Services mix • Store atmosphere 13-24 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions • Product assortment should differentiate the retailer while matching target shoppers’ expectations. • Offers merchandise that no other competitor carries. • Private or national brands • Merchandising events • Highly targeted product assortment 13-25 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions • Services mix should also serve to differentiate the retailer from the competition. • Customer support • Store atmosphere is the physical layout that makes moving around the store hard or easy. • Experiential retailing • Test driving 13-26 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Price Decisions • Price policy must fit the target market and positioning, product and service assortment, and competition. • High markup on lower volume • Low markup on higher volume 13-27 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Price Decisions • High-low pricing involves charging higher prices on an everyday basis, coupled with frequent sales and other price promotions to increase store traffic, clear out unsold merchandise, create a low price images, or attract customers who will buy other goods at full price. 13-28 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Price Decisions • Everyday low prices (EDLP) involves charging a constant, everyday low price with few sales or discounts. © Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. 13-29 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Promotion Decision • Advertising • Personal selling • Sales promotion • Public relations • Direct marketing 13-30 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Place Decision • Location • Accessibility • Consistent with positioning 13-31 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Place Decision © Florian Pusch • Central business districts are located in cities and include department and specialty stores, banks, and movie theaters. 13-32 Retailing Retailer Marketing Decisions: Place Decision • A shopping center is a group of retail businesses planned, developed, owned, and managed as a unit. • Regional shopping centers • Community shopping centers • Neighborhood shopping centers • Power centers • Lifestyle centers 13-33 Retailing The Future of Retailing • Retailers have to choose target segments carefully, position themselves strongly, and consider the following developments as they plan and execute their competitive strategies: • Non-store retailing • • • • Retail convergence Megaretailers Retail technology Global expansion • Retail stores as communities 13-34 Retailing The Future of Retailing New Retailing Forms and Shortening Life Cycles • The wheel-of-retailing concept states that many types of retailing forms begin as low-margin, lowprice, low-status operations and challenge established retailers. • As they succeed, they upgrade their facilities and offer more services, increasing their costs and forcing them to increase prices, eventually becoming the retailers they replaced. 13-35 Retailing The Future of Retailing New Retailing Forms and Shortening Life Cycles • Growth of non-store retailing includes: • Mail order • Television • Phone • Online 13-36 Retailing The Future of Retailing New Retailing Forms and Shortening Life Cycles • Retail convergence involves • The merging of consumers, producers, prices, and retailers • Creates greater competition for retailers and greater difficulty differentiating offerings 13-37 Retailing The Future of Retailing New Retailing Forms and Shortening Life Cycles • The rise of megaretailers involves the rise of mass merchandisers and specialty superstores, the formation of vertical marketing systems, and a rash of retail mergers and acquisitions. • Superior information systems • Buying power • Large selection 13-38 Retailing The Future of Retailing New Retailing Forms and Shortening Life Cycles • Retail technology includes video-casts, inventory control, electronic ordering, transfer of information, scanning, online transaction processing, improved merchandise handling systems, and the ability to connect with customers. 13-39 Wholesaling Wholesaling • Wholesalers add value by performing channel functions • Selling and promoting • Financing • Buying and assortment building • Risk bearing • Bulk breaking • Warehousing • Market information • Management services and advice • Transportation 13-40 Wholesaling • Selling and promoting involves the wholesaler’s sales force helping the manufacturer reach many smaller customers at lower cost. • Buying and assortment building involves the selection of items and building of assortments needed by their customers, saving the customers work. 13-41 Wholesaling • Bulk breaking involves the wholesaler buying in larger quantity and breaking into smaller lots for its customers. • Warehousing involves the wholesaler holding inventory, reducing its customers’ inventory cost and risk. • Transportation involves the wholesaler providing quick delivery due to its proximity to the buyer. 13-42 Wholesaling • Financing involves the wholesaler providing credit and financing suppliers by ordering earlier and paying on time. • Risk bearing involves the wholesaler absorbing risk by taking title and bearing the cost of theft, damage, spoilage, and obsolescence. 13-43 Wholesaling • Market information involves the wholesaler providing information to suppliers and customers about competitors, new products, and price developments. • Management services and advice involves wholesalers helping retailers train their sales clerks, improve store layouts, and set up accounting and inventory control systems. 13-44 Wholesaling Types of Wholesaler • Merchant wholesalers • Agents and brokers • Manufacturers’ sales branches and offices 13-45 Wholesaling Types of Wholesaler • Merchant wholesalers is the largest group of wholesalers and includes • Full-service wholesalers who provide a full set of services • Limited-service wholesalers who provided few services and specialized functions. 13-46 Wholesaling Types of Wholesaler • Brokers and agents do not take title, perform a few functions, and specialize by product line or customer type. • Brokers bring buyers and sellers together and assist in negotiations. • Agents represent buyers or sellers. 13-47 Wholesaling Types of Wholesaler • Manufacturers’ sales branches and offices is a form of wholesaling by sellers or buyers themselves rather than through independent wholesalers. 13-48 Wholesaling Wholesaler Marketing Decisions • Target market and positioning decisions • Marketing mix decisions 13-49 Wholesaling Wholesaler Marketing Decisions • Target market and positioning decisions • Size of customer • Type of customer • Need for service 13-50 Wholesaling Wholesaler Marketing Decisions • Marketing mix decisions • Product • Price • Promotion • Place 13-51 Wholesaling Trends in Wholesaling • Challenges • Resistance to price increases • Lack of suppliers • Changing customer needs • Adding value by increasing efficiency and effectiveness 13-52