Poetry
advertisement

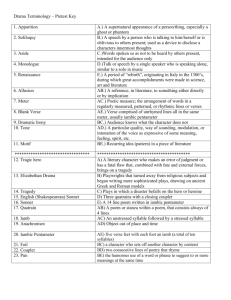
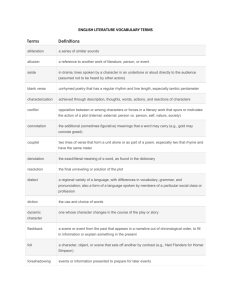
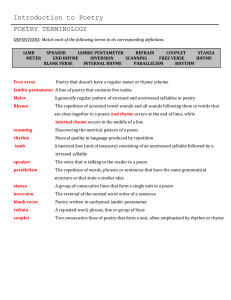
What though, for showing truth to flattered state, Kind Hunt was shut in prison, yet has he, In his immortal spirit, been as free As the sky-searching lark, and as elate. Minion of grandeur! think you he did wait? Think you he nought but prison-walls did see, Till, so unwilling, thou unturnedst the key? Ah, no! far happier, nobler was his fate! In Spenser's halls he strayed, and bowers fair, Culling enchanted flowers; and he flew With daring Milton through the fields of air: To regions of his own his genius true Took happy flights. Who shall his fame impair When thou art dead, and all thy wretched crew? • A fourteen-line lyric poem, usually written in rhymed iambic pentameter. • Two types—English (or Shakespearean) and Italian (or Petrarchan) • English consists of three quatrains and a couplet • Italian consists of an octave and a sestet. • A three-line verse form. • The 1st and 3rd line of the haiku each have 5 syllables. • The 2nd line has seven syllables. • A haiku seeks to convey a single vivid emotion by means of images of nature. • Poetry written in unrhymed iambic pentameter • Popular verse form—widely used by Shakespeare. •Poetry not written in a regular rhythmical pattern, or meter •it is the opposite of blank verse. • Formal division of lines in a poem, considered • • • • • • as a unit Couplet—2 lines Quatrain—4 lines Cinquain—5 lines Sestet—6 lines Heptastich—7 lines Octave—8 lines • Anything that stands for or represents something else. • An object that serves as a symbol has its own meaning but it also represents something abstract. A figure of speech in which like or as is used to make a comparison between two basically unlike ideas. • Figure of speech in which one thing is spoken of as though it were something else. • Does not use like or as to make the comparison. • My nephews are animals-metaphor Same as a regular metaphor but in this case a subject is spoken of or written of as though it were something else. Several comparisons are made Writing or speech not meant to be interpreted literally. Frequently used figures of speech are metaphors, similes, and personification Uses words in their ordinary senses. It is the opposite of figurative language. •Excessive exaggeration •I’m so hungry I could eat a horse. Type of figurative language in which a nonhuman subject is given human characteristics. The screaming phone woke me up. Use of words that imitate sounds Whirr Sizzle Hiss Woof Meow varrrrrrooooooommmmmm The repetition of initial consonant sounds. “Black reapers with the sound of steel on stone/Are sharpening scythes…” “Sarah, Cynthia, Sylvia Stout wouldn’t take the garbage out…” • The repetition of sounds at the end of words • End rhyme occurs when the rhyming words come at the end of lines • Internal rhyme occurs when the rhyming words fall within a line. •The pattern of beats, or stresses, in spoken or written language. • A regular pattern of rhyming words in a poem. • The rhyme scheme of a poem is indicated by using different letters of the alphabet for each new rhyme.