Poetry Terms & Drama Terms Poetry Terms Alliteration Allusion

Poetry Terms & Drama Terms
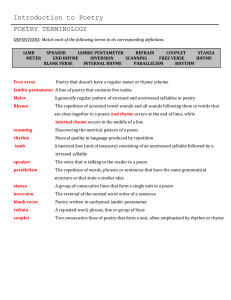
Poetry Terms
Alliteration : repetition of consonant sounds in words that are close to one another.
Allusion : a reference to a statement, person, place, event, or thing that is known from literature, history, religion, mythology, politics, sports, or pop culture.
Assonance : repetition of vowel sounds.
Couplet : two lines, usually in the same meter and joined by rhyme, that form a unit.
Free verse : poetry that has no regular meter or rhyme scheme.
Hyperbole : exaggeration.
Iamb : a unit in poetry consisting of one unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable.
Iambic pentameter : a poetic line containing five iambs, or ten syllables.
Imagery : language that evokes the senses, especially visual description.
Line : element of a verse or stanza; a phrase or sentence.
Metaphor : a comparison not using “like” or “as,” usually of two unlike things.
Meter : the rhythm of the poem; regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in poetry.
Motif : a theme or idea repeated in design or pattern in a work of literature.
Onomatopoeia : the use of a word whose sound imitates or suggests its meaning; ex. buzz, knock, splash, bark, crash.
Oxymoron : a figure of speech in which apparently contradictory terms appear together.
Personification : giving human characteristics to a non-human thing.
Pun : a joke exploiting the difference possible meanings of a word
Refrain : a repeated line or number of lines in a poem, typically at the end of each verse.
Rhyme scheme : the pattern of rhymed lines; ex. AABBCC.
Setting : the time and place of the poem; it establishes atmosphere, contributes to the emotional effect.
Simile : a comparison using “like” or “as.”
Sonnet : a poem of fourteen lines, with a formal rhyme scheme, and typically ten syllables per line.
Speaker : the voice that is talking to us in the poem.
Symbol : a thing that stands for itself and something else.
Theme : the subject or message conveyed in a work of literature.
Tone : feeling.
Verse or stanza : a group of lines forming a unit in a poem.
Drama terms
Act : a main division in a play.
Aside : words spoken by a character in a play, usually in an undertone, not intended to be heard by other characters on stage.
Blank verse : verses written in iambic pentameter with no rhyme scheme.
Comedy : a literary work that is amusing and/or ends happily.
Dialogue : conversations held by characters.
Drama : a story acted out by actors who take parts of specific characters.
Dramatic irony : a device whereby the audience is given information regarding a situation that the characters involved do not have.
Epilogue : a short speech at the end of the play which provides further comment or information.
Foil : a character who sets off another character by contrast.
Prologue : a short speech at the beginning of a play which introduces the action.
Scene : a division in a play which marks a change in the time or place of the play’s action.
Soliloquy : a speech in which a character, alone on stage, expresses his or her thoughts aloud.
Tragedy : a serious play in which the central characters meet an unhappy or disastrous end.