Week 2 - bYTEBoss
advertisement

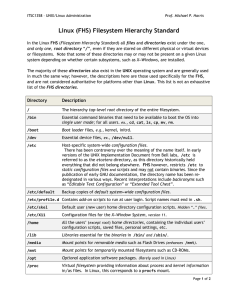
POS/420 Introduction to Unix Philip Robbins – March 19, 2013 (Week 2) University of Phoenix Mililani Campus Agenda: Week 2 • Quiz #1 Due (Review & Grade) • Week 2 - File Structure - Basic Terminal Commands - Permissions • In Class Lab (Assignment) #1 Due Today • Take Quiz #2 Review Week 1 List of Commands man ls pwd passwd sudo su shutdown – manual pages – list directory contents – print working directory – change password – execute command as superuser – login as superuser – shutdown Linux File System Structure Linux File System Structure root (/) File Structure: Binaries • What’s the difference between: - /bin - /sbin - /usr/bin - /usr/sbin File Structure: Binaries • What’s the difference between: /bin & /usr/bin When UNIX was first written, /bin and /usr/bin physically resided on two different disks: /bin being on a smaller faster (more expensive) disk, and /usr/bin on a bigger slower disk. /bin • Essential User Command Binaries - Contain commands used by both system administrators and users. - There must be no subdirectories in /bin. /boot • Static files of the boot loader - Contains everything for the boot process (at boot time). - Does not include boot configuration files not needed at boot time. - Stores data that is used before the kernel begins executing. - OS Kernel is stored in either / or /boot. /dev • Device Files - Location of special or devices files. /etc • Host-specific system configuration - Contains configuration files. - Must be Static and cannot be an executable binary. - Required in /etc: opt, X11, sgml, xml /etc /srv • - Data for services provided by this system. Contains site-specific data which is served by this system. Naming methodology not specified. e.g. /srv/ftp, /srv/pos420/www Data that is of interest to a specific user should go into that users home directory. /tmp • Temporary Files - Must be made available for programs that require the use of temporary files. - Recommend that /tmp files be deleted upon system reboot. /usr • - User Hierarchy Second major section of the file system. Used for shareable, read-only data. Required directories: bin - essential command binaries sbin - essential system binaries include - header files used by C programs lib - object files, binaries, libraries local - put apps you build yourself here share - shared (Static) /usr • What’s the difference between: /usr & /usr/local /usr/share/man • Directory for System Manual Pages man1: User programs Manual pages that describe publicly accessible commands are contained in this chapter. Most program documentation that a user will need to use is located here. man2: System calls. This section describes all of the system calls (requests for the kernel to perform operations). man3: Library functions and subroutines. Section 3 describes program library routines that are not direct calls to kernel services. This and section 2 are only really of interest to programmers. man4: Special files. Section 4 describes the special files, related driver functions, and networking support available in the system. Typically, this includes the device files found in /dev and the kernel interface to networking protocol support. /usr/share/man • Directory for System Manual Pages man5: File formats. The formats for many data files are documented in the section 5. This includes various include files, program output files, and system files. man6: Games. This chapter documents games, demos, and generally trivial programs. Different people have various notions about how essential this is. man7: Miscellaneous. Manual pages that are difficult to classify are designated as being section 7. The troff and other text processing macro packages are found here. man8: System administration. Programs used by system administrators for system operation and maintenance are documented here. Some of these programs are also occasionally useful for normal users. /usr/share/man • Manual Section Summary man apropos apropos apropos man6: Games. This chapter documents games, demos, and generally trivial programs. Different people have various notions about how essential this is. /var • Variable Hierarchy - Contains variable data files. - Spool files & directories, logging data, temporary files (for system reboots). - Not Shareable. - e.g. /var/log, /var/mail, /var/cache, /var/crash (dump files) - Can be placed in /usr/var. (If separate partition for /var is not possible). /var • • - Use the “more” command to view files. man more for more information view syslog view kern.log Also use the “head” and “tail” command to view files. man head & tail for more information know how to head & tail –n lines of a file /proc • Kernel and process information virtual file system - Used for handling process and system information - Kernel and memory information man ps top FHS Compliant System • Rationale: - Not all files can be shared - Static and Variable files should be segregated - Static files can be stored on read-only media - Different backup schedules man fdisk sudo fdisk -l • Use fdisk to list all partitions (as root) fdisk Typical Partitions Virtual Terminals (TTY) • Six tty (1 – 6) - Hold Ctrl + Alt, press F1 (for tty1) - F2 (for tty2) … F6 (for tty6) - Hold Ctrl + Alt, press F7 (to return to GUI) - Press and hold Ctrl + Alt to switch between VM and GUI who who User ($) vs. Root (#) Shells • What is an OS shell? • Types - ksh, tcsh, csh, sh, bash • What shell are you running? - echo $SHELL Shells • csh man usermod man ssh ssh Directory Notation • / • /. • /.. • /~ - Represents a directory Represents current directory Represents the parent directory Represents a user’s home directory File Permissions File Permissions • Octal (numerical) Representation man chmod man chown man chgrp File Permissions Command Summary Run Levels • runlevel - Previous runlevel, current runlevel • init - Change between run levels (process id 1) • telinit - Change system run level (user process) runlevel vi (text editor) Review essential user commands (/bin) Break • Let’s take a break… RETURN @ 800PM Assignment #1 • • • • • • 30 Questions Use PrintScreen (PrtSc) Work in groups (optional) Submit individual assignments! Post to OLS. -- use pdf format. Due before you leave class tonight. Quiz: Week 2 • 10-15 minutes