Disk and File Systems.ppt
advertisement

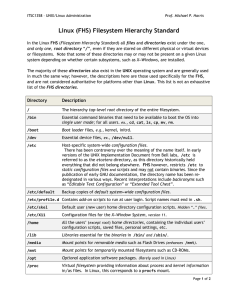
Chapter 8. Disks and Filesystems Ordinary Files What is a file? – a container for ordered data – persistent (stays around) and accessible by name Unix files – regular Unix files are pretty simple essentially a sequence of bytes – Unix files are identified by a name in a directory this name is actually used to resolve the hard disk name/number, the cylinder number, the track number, the sector, the block number – you see none of this it allows the file to be accessed Files, Directories, Devices Unix files come in other flavors as well, such as – Directories a file containing pointers to other files equivalent of a “folder” on a Mac or Windows – Links a pointer to another file used like the file it points to similar to “shortcuts” in Windows, but better – Devices access a device (like a soundcard, or mouse, or ...) like it is a file Figure 3-3 A Directory Hierarchy System Directories Some standard directories and files in a typical Unix system – – – – – – – – / /bin /sbin /lib /dev /etc /usr /tmp the root BINaries (executables) used to start system System BINaries for Superuser LIBraries used for startup DEVices (peripherals) hardware interfaces unique settings for system, config, passwds Biggest filesystem, sys tools, X, apps temp storage, good to separate partition Typical System Directory Contents – – – – – – – – – – – – – /usr USeR stuff /usr/bin BINaries again /usr/include include files for compilers /usr/lib LIBraries of functions etc. /usr/local local stuff for apps installed later /usr/local/bin local BINaries /usr/local/lib local LIBraries for apps /usr/X11R6 X window stuff /usr/sbin sysadmin stuff /usr/tmp place for more TeMPorary files /var VARiable stuff—mail, print jobs, logfiles /var/mail the mail spool /var/log security info VERY IMPORTANT The /proc filesystem /proc is a virtual directory. in RAM rather than in HDD. /proc contains info about your system’s state. amount of free memory processes running external devices plugged in remaing battery power if you are working in a laptop You can, though, navigate around it with cd command and list its contents with ls command or view some of its file contents with cat command The /proc file system Numbers are directories representing each of the running process on the system and contain all info related to it. terra$ ls /proc/480/ auxv cwd exe maps mounts stat status wchan cmdline environ fd mem root statm task For example: cmdline contains the command the process started with mem contains the amount of memory this process holds . /proc contains information about the hardware of the system cat /proc/meminfo contains information about memory state more /proc/ioports gives all the information about the availability of I/O ports on the system and the hardware device assigned to each. Figure 3-8 Inodes Each file on the disk has an inode which keeps information about the file, it’s address, etc