Poetry forms
advertisement

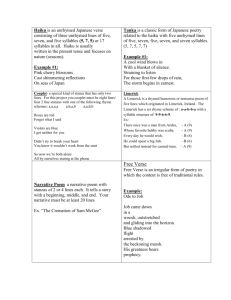
Poetry forms Ballads • Ballads are poems that tell a story. They are considered to be a form of narrative poetry. They are often used in songs and have a very musical quality to them. • The basic form for ballads is iambic heptameter (seven sets of unstressed, stressed syllables per line), in sets of four, with the second and fourth lines rhyming. Sonnets • A lyric poem of fourteen lines, following one or another of several set rhyme-schemes. • Topic is usually love, but not required to be. • the typical rhyme-scheme for the English sonnet is • abab cdcd efef gg. Villanelle • A short poem of fixed form, written in tercets, usually five in number, followed by a final quatrain, all being based on two rhymes Sestina • The lines are grouped into six sestets and a concluding tercet. Thus a Sestina has 39 lines. • The six words that end each of the lines of the first stanza are repeated in a different order at the end of lines in each of the subsequent five stanzas. • The repeated words are unrhymed Acrostic • Acrostic Poetry that certain letters, usually the first in each line form a word or message when read in a sequence. Cinquain • Poetry with five lines. Line 1 has one word (the title). Line 2 has two words that describe the title. Line 3 has three words that tell the action. Line 4 has four words that express the feeling, and line 5 has one word which recalls the title. Elegy • A sad and thoughtful poem about the death of an individual. Haiku • A Japanese poem composed of three unrhymed lines of five, seven, and five syllables, usually containing a season word. Limerick • A short sometimes vulgar, humorous poem consisting of five anapestic lines. Lines 1, 2, and 5 have seven to ten syllables, rhyme and have the same verbal rhythm. The 3rd and 4th lines have five to seven syllables, rhyme and have the same rhythm. Pastoral • A poem that depicts rural life in a peaceful, romanticized way. Rondeau • A lyrical poem of French origin having 10 or 13 lines with two rhymes and with the opening phrase repeated twice as the refrain.