Microsoft Word - 6- Study Guide.doc

Earth Space Science Mr. Winter (C-226)
Name Class 2 / 3 / 4 / 6 / 7 Date
What are minerals made of ?
Most minerals are made up of a
Elements such as
Minerals Guided Notes of .
– and others that you might recognize from the periodic table of elements combine together to form minerals.
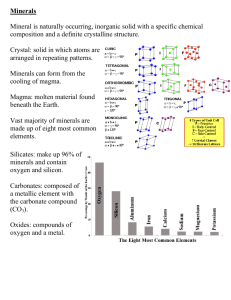
Minerals
What is a mineral? There are nearly 4000 minerals known on Earth !!!
A mineral must include these 5 aspects: 1. Naturally occurring 2. Inorganic 3. Solid 4. Crystal 5. Definite Chemical Composition
If even just one of these requirements is not satisfied, then the substance is a mineral.
1. Naturally Occurring o Something o Example: o Minerals are a girl’s best friend! o Diamond is a mineral WHY??? o Cubic Zirconium is not
2. Inorganic o Something that was o An
. was
Is ice inorganic? Yes no
Is paper inorganic? Yes no
Is rock solidified from magma inorganic? Yes no
Is my dead cat inorganic? Yes no
Are synthetically created substance minerals? Yes no by .
3. Solids o Something that has a o Gas and liquids are not minerals. o Is air a mineral? Yes no o Is mercury a mineral? Yes no
.
4. Crystalline Substance o A o The patterns are is a whose over and over again. are .
5. Definite chemical composition o Every mineral has its own o A chemical composition is like a o A mineral has combined in
.
.
Na + Cl = Salt
Si + O
2
= Quartz
Just like baking, you must have the ingredients in just the right amounts.
Si + O
2 is not the same as Si + O
3
1 egg
1 cup of flour … will make something totally different than...
2 cups sugar
5 eggs
1 cup flour
8 cups sugar
How do minerals form? o Minerals form through processes called o Remember though, while all minerals are crystals, not all crystals are minerals. Sugar is a crystal. Why is it not a mineral? o Minerals (crystals) can form in two ways: 1.
. Crystallization is a “crystal-forming process.” As you know, minerals are crystals!
2.
Cooling of Magma
- Magma is
- Magma that cools
- Magma that cools liquefied into a
- Just like water cooling to form ice,
- The elements and
- The size of the minerals crystals depends on can so the to
. Things like Fe, Mg, Ca are all floating around in the liquid magma. mineral crystals have lots of time to grow so they are in the liquid
- Where would magma cool slowest? Where would it cool fastest? Where would we find large crystals in minerals?
. to fall out of the liquid magma.
.
.
.
Solution Evaporation
- Minerals dissolve in
- Eventually, the water will
- When minerals fall out of a solution they are said to
- Ex: and create a solution. and the
. of solution and be left behind.
Earth Space Science Mr. Winter (C-226)
Name Class 2 / 3 / 4 / 6 / 7 Date
Identification o What if you have two minerals that look exactly alike? How will you be able to tell one from the other? o There are a number of different or characteristics that can give you clues to recognize different minerals. o Those properties include: Color, luster, streak, hardness, cleavage, fracture, specific gravity, and a number of useful others.
Color o Although color is an obvious feature of a mineral, it is often o Slight can
. the mineral changing its color. Example: Quartz can be white, pink, purple.
Luster o Luster is the way a mineral
Metallic Luster: Shines like shiny metal or
Non-Metallic Luster:
. It is often described as either
. Mineral Examples Include: like metal. Mineral Examples Include:
Non-Metallic luster is also often described using the following terms: or
Streak o If you were to scratch a mineral against a hard surface, like a it would leave behind a streak of colored powder. o Streak is the of a mineral in form. Scientists use a o While a mineral’s color may change, the color of its streak usually does not. Streak is often a much more helpful way to use color to identify a mineral. o
Where do you use streak in your everyday day life? Which mineral do you use to leave the streak? to do the streak test.
Hardness o The measure of o Hardness of a mineral has nothing to do with o
Hardness is measured by using o The scale is from 1-10. is the mineral and is known as its hardness. easily or not.
, which is a scale that ranks ten common minerals hardness. is the mineral.
How does the hardness scale work?
- Let’s say you have a mineral that is white and you know its either fluorite or quartz.
- You scratch it with your fingernail and then and iron nail.
- You are not able to scratch it with your fingernail, but the iron nail does scratch it.
- You use the table and find the value for the fingernail and the iron nail.
Because your fingernail did not scratch it, but the iron nail did, the mineral has a hardness value somewhere between the hardness of your fingernail and the iron nail.
Fingernail = 2-2.5
Iron nail = 4.5
Using the chart, you see that quartz has a value of 7. That’s too high!
But, fluorite has a value of 4, which is between that of your fingernail the iron nail. The mystery is solved. Using the hardness scale, you were able to find the identify of the mineral.
Moh’s Scale of Hardness of Minerals
1
2
3
Talc
Gypsum
Calcite
Common Items Hardness
Fingernail =
Copper coin =
2-2.5
3.5
4
5
6
Fluorite
Apatite
Orthoclase
7
8
Quartz
Topaz
9 Corundum
10 Diamond
Iron Nail =
Glass =
Streak plate =
4.5
5-5.5
6.5-7
Cleavage and Fracture o The way a mineral is another way that is helpful in identifying it. o Sometimes when you break a mineral, it will break along surfaces. o This results in a nice o This is called
.
. Think of the way a sharp meat cleaver cuts meat. Nice, clean cuts. o Sometimes, minerals do not break in nice clean, flat cuts. o Minerals that break along o The way a mineral breaks depends on surfaces are said to .
.
Minerals with cleavage:
Minerals that fracture: (All minerals fracture to some extent.)
Specific Gravity o o o
Minerals can be identified by
The specific gravity of a mineral is the
Gold has a specific gravity of of its
. Pyrite has a specific gravity of of equal samples. compared to the weight of an
. o That means the gold is times heavier than water and pyrite is heavier than water. o If gold and pyrite look the same, you can tell them apart by finding their specific gravity. o If you were to , or lift two different minerals, the one with the specific gravity would feel .
.
OTHER USEFUL PROPERTIES
- Magnetism: Some minerals are attracted to
- Acid Test: Weak HCl acid on carbonate minerals (those with CO
2
- Smell: Some minerals have a peculiar smell. Ex:
- Taste: Some minerals have a peculiar taste. Ex:
) will produce a
Feel: Some minerals have a peculiar feel. Ex:
- Double Refraction: Light enters the mineral as one beam of light, but then it separates into to
- Fluorescence: Some minerals glow brightly under a . Minerals glow because they have
.
. CO
2 is given off as beams. You then see . Ex: in them called activators.
.