IT-Enabled Business Transformation
advertisement

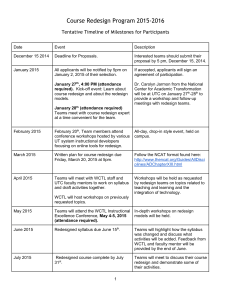
IT-Enabled Business Transformation From Automation to Business Scope Redefinition Agenda • • • • Introduction 5 Levels of Transformations Conclusion Q&A Introduction • Team members 商研一 • • • • 張菽珊 謝文淵 簡見安 林俊吉 Business Logic Evolution 1970s and 1980s: exploiting experience curve for achieving low relative cost through vertical integration (efficiency enhancement). 1990s: low cost, high quality, and fast/flexible response to customers’ need (capabilities enhancement). High Five levels of IT-enabled business transformation Degree of business transformation Business Scope Redefinition Business Network Redesign Business Process Redesign Revolutionary Levels Internal Integration Localized Exploitation Low Low Range of potential benefit Evolutionary Levels High Level 1 Localized Exploitation • Leveraging of IT functionality to design focused, high-value areas of business operations • Example: – Customer Order Entry System – Toll-free Customer Service System Level 1 Localized Exploitation • Strength – Easy to identify and exploit potential IT capability – Minimal organizational resistance to change • Weakness – Potential duplication of efforts with in the same organization – Lack of organizational learning Level 1 Localized Exploitation • Management Challenges – Identification of high-value areas – Benchmark against best practice – Redesign performance assessment Level 2 Internal Integration • Leveraging of IT capability to create a seamless process ----both technical interconnectivity & business process interdependence • Example -Lexus and Infiniti Level 2 Internal Integration • Strengths -Supports the total quality movement -Streamlines the organization process to deliver improved customer service • Weaknesses -limited impact if competitors using newer logic of organizing Level 2 Internal Integration • Management Challenge -business process interdependence and technical interconnectivity -Performance reassessed criteria -Benchmark results against best-in-class Enablers and Inhibitors Enablers and Inhibitors of Evolutionary Level of Transformation *Technological Enablers *Technological Inhibitors 1. Favorable cost-performance trends 1. Obsolescence of technologies 2. Enhanced connectivity capabilities 2. Lack of established standards *Organizational Enablers *Organizational Inhibitors 1. Managerial awareness 1. Managerial resistance 2. Leadership 2. Financial constraints Level 3 Business Process Redesign • Redesign key process for competing in the future • Use IT capability for future organization capability Level 3 Business Process Redesign • Strengths -First mover advantage -Not be hindered by historical process • Weakness -Redesigning process might be obsolete or outsourced to partners Level 3 Business Process Redesign • Management Challenge – Articulate business rationale for redesign – Recognize organization issues and challenges Level 4 Business Network Redesign • Leverage related participants in the business network to provide products and services • Exploiting IT functionality for learning from extended network Level 4 Business Network Redesign • Strengths – Elimination of activities where the focal organization may not have required level of competence – Streamlining business scope to remain flexible and responsive to fast-changing and diverse customer needs – Exploit sources of competence in the larger business network Level 4 Business Network Redesign • Weaknesses – May not provide the requisite source of differential advantage if the participants in the business network not well-coordinated – Lack of a streamlined internal IT infrastructure could hinder the ability to learn from extended business network Level 5 Business Scope Redefinition • Redefining corporate scope enabled and facilitated by IT functionality • Example: McGraw-Hill Level 5 Business Scope Redefinition • Strengths – Opportunity to Create a more flexible and effective business entity – Substitution as an effective alternative to vertical integration • Weaknesses – Not developing a consistent competence for the future – Possibility of “Hollowing” the corporation Level 5 Business Scope Redefinition • Management challenge – Creative mix of internal activities, external relationship and business arrangement – Assessing business success by measuring return on value added or return per employee High Conclusion— Alternative Approaches to BPR Degree of business transformation Business Scope Redefinition Business Network Redesign Seek Efficiency Business Process Redesign Enhance Capabilities Internal Integration Localized Exploitation Low Low Range of potential benefit High Any Question ? Thank You !!!